Functions of different Biomolecules (#2)
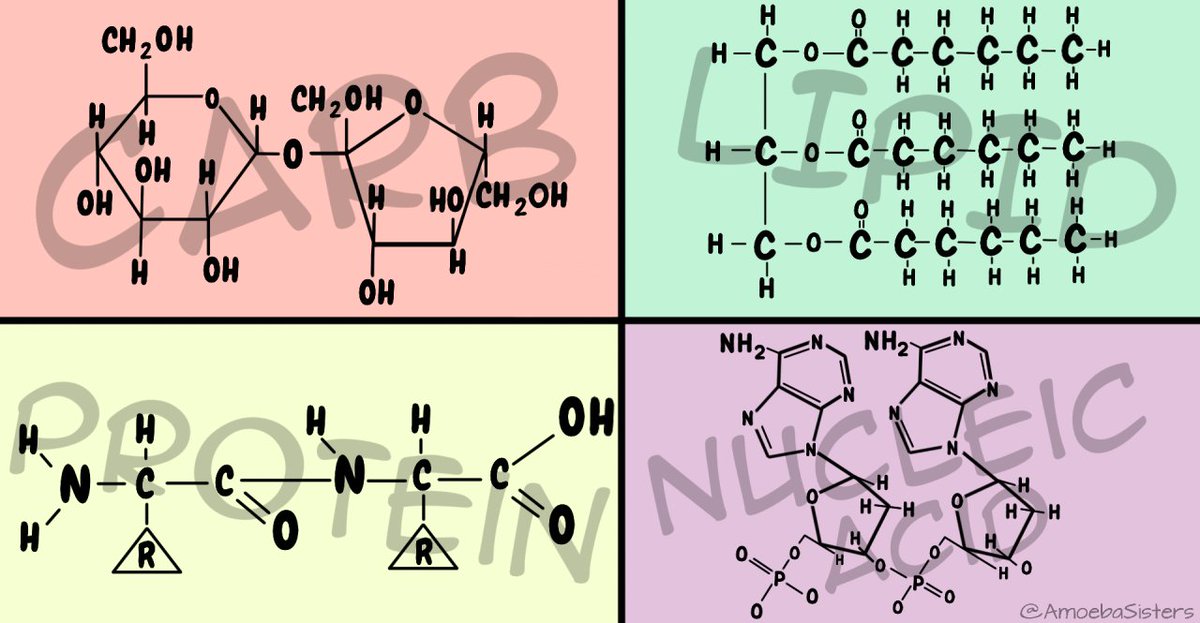
Biomolecules/ Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acid, and Proteins.
Monomer: Building blocks
Carbohydrates:
Food sources; FOR ENERGY.
E.g. Sugar, bread, pasta, fruit & veggies.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen. (Ratio of 1:2:1)
Carbohydrates are a FAST SOURCE OF ENERGY FOR CELLS. THE ENERGY CAN BE STORED IN A POLYSACCHARIDE FORM. (e.g. starch for plants, glycogen for animals.)
Monomer of Carbohydrates: Monosaccharide (e.g. sugar, glucose)
MONOSACCHARIDE + MONOSACCHARIDE= DISACCHARIDE
Polysaccharide: BIG CARBOHYDRATE (Poly=many).
Function: Major energy source (starch, glucose).
Lipids:
Long-term energy storage; reserves & moves energy, builds & acts as hormones (chemical messengers for different processes), absorbs vitamins
e.g. fats & oils, butter, olive oil
Lipids are diverse.
(e.g. Triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids.)
Phospholipids build the cell-membrane structure
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (Ratio of 1:2)
Lipids are hydrophobic or contain significant hydrophobic components.
Lipids make up cell-membrane structures
Important for different insulations.
Monomer for lipids: Glycerol & Fatty Acids
Proteins:
Proteins build muscle tissues, and cells, and repair; structural biomolecules.
E.g. beans, meat, nuts, eggs
Can be embedded in cell membranes as protein channels.
Receptors
Enzymes, Antibodies, some hormones, and many DNA codes for /are made of protein
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
Monomer of Proteins: Amino Acids (20 essential amino acids)
Nucleic Acids:
Carrier of genetic information & instructions for protein synthesis
Includes DNA & RNA
Needed for the coding of your traits
EVERY ORGANISM CONTAINS NUCLEIC ACID
Carbohydrate group, phosphate group, nitrogen base
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
Monomer of Nucleic Acids: Nucleotide
Hydrolysis: The chemical breakdown of compounds due to a reaction with water; breaks polymers into monomers.
Dehydration Synthesis: Joins monomers into polymers.
Role of Enzymes
Enzymes:
MOST enzymes are proteins; they’re biological catalysts.
Catalysts: Enzymes that can be reused in the reaction
Speeds rate of chemical reactions.
TIP: Enzymes end in “-ase”
Sugars end in “-ose”
E.g. Lactase enzymes, lactose sugar, oil saccharide
Lactase is a disaccharide- two sugar molecules bond together
Lactose can be quickly broken down and digested
Lactase can break lactose
Fights infections
Regulates body processes
Looks like Pacman
(Protein)
Active site: Where items combine
Substrate: Surface on which an organism lives; includes abiotic and biotic material.
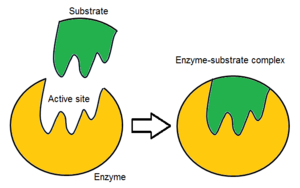
Induced Fit Theory: The binding of a substrate/ another molecule to an enzyme causes a change in the shape of the active site to inhibit its activity.
Cofactors & Coenzymes: Helps enzyme do its job of building up or breaking down substrates into products.