Study guide 8
Relationship Between Algae and Land Plants
Both algae and land plants share a common ancestor
Both groups are photoautotrophic, multicellular eukaryotes, with cellulose in their cell walls and chlorophyll A and B in their chloroplasts.
Closest Relatives to Land Plants
Charophytes and charaplants are identified as the closest relatives to land plants.
charophyte: first plant to colonize 500 mya
Benefits and Challenges of Life on Land
Benefits
More Co2 in atmosphere
unfiltered sunlight
Access to rich mineral soils.
Challenges
water scarcity and gravity
Adaptations to Life on Land
Cuticle
A waxy outer covering that prevent desiccation ( drying out).
Stomata
Specialized pores that allow gas exchange; Co2 in, o2 out, help regulate H2O reserve
Vascular Tissue
Specialized tissue that transport water and nutrients,
(not all plants possess this).
Shared Derived Features of Land Plants
Alternation of Generations
plants alternate between multicellular haploid and multicellular diploid life stages
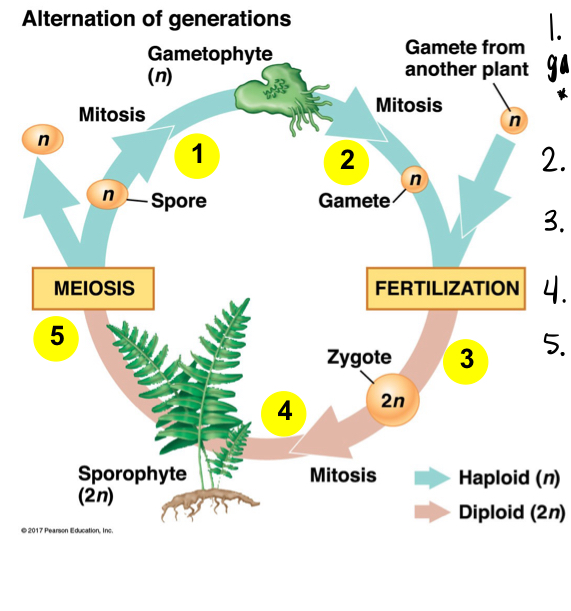
sporophytes (2n) produces spores(n) through meiosis
spores form gametophyte (n) through mitosis which in turn forms gametes (n) through mitosis
gametes fuse to form 2n zygote and sporophyte
B. Mulicellular, dependent embryos:
Zygotes are retained (protected and nourished) within the tissues of the female gametophyte
C. Spore walls made from pollenin
spores (n) covered in proctective sporopollenin polymer
spores generated by sporocytes (2n) inside sporangia
sporongia contains sporocyte (2n). These cells undergo meiosis to produce spores (n)
D. Apical meristems
are the plant version of stem cells
they are regions of rapidly dividing cells
allows growth at the root and shoots ( ROOT MERISTEMS ALLOW PLANT TO OBTAIN H2O AND NUTRIENTS)
Features of Seedless Vascular Plants
Include structures to transport water and nutrients:
Xylem: Transports water and minerals from roots upwards. Composed of tracheids (dead cells).
Phloem: Transports sugars and amino acids (bi-directional).
Life Cycle of Mosses
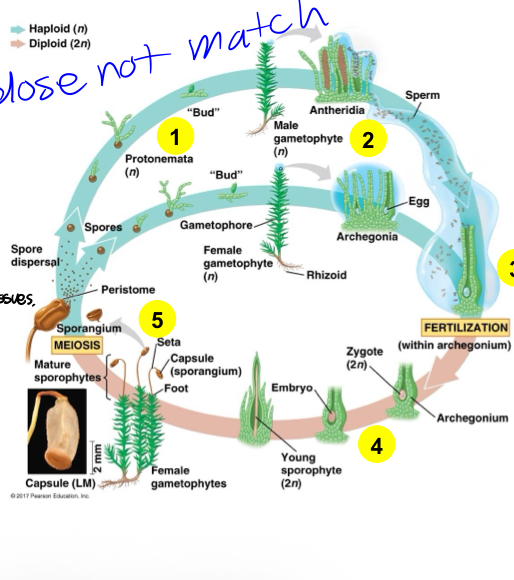
Dominant gametophyte is produced from spores that develop into protonema (filamentous structure).
Male organs (antheridia) produce sperm; female organs (archegonia) produce eggs.
Sperm swim through water to fertilize eggs within the archegonia.
Fertilized zygote evolving into a sporophyte.
Spores are produced by the sporophyte via meiosis in the sporangium.
Ferns Life Cycle
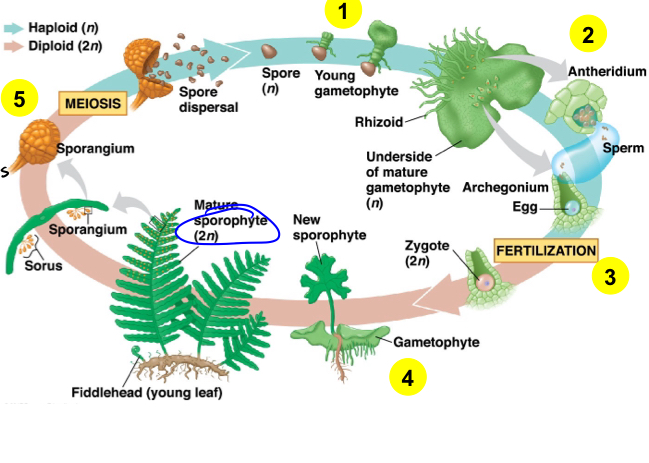
Gametophyte is produced from dividing spores
Antheridia produce sperm; archegonia produce eggs.
Sperm swim through water to fertilize eggs in archegonia.
Zygote develops within gametophyte tissues and transforms into sporophyte (dominant form).
Spores form via meiosis within the sporangium of the sporophyte.
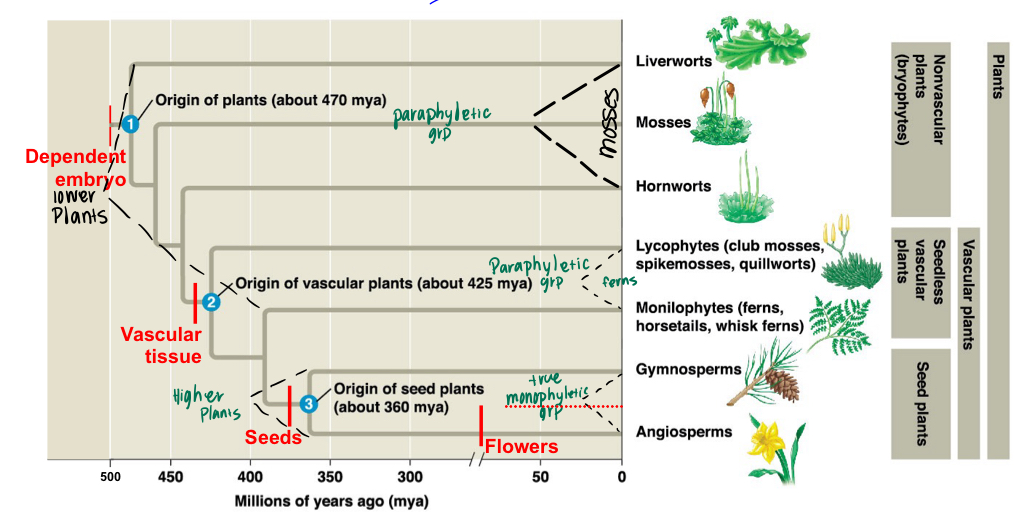
Main Groups/Lineages
Bryophytes: Include Hepatophytes (liverworts), Bryophyta (mosses), and Anthocerophyta (hornworts).
Seedless Vascular Plants: Include Lycophytes (Club mosses) and Monilophytes (ferns).