Physical Science Unit 10
Newton’s First law is called Law of Inertia - Objects at rest will remain at rest, an object in motion will remain in constant motion unless and unbalanced force acts upon it.
Inertia - The tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay at rest or an object “wants” to keep doing what its doing. INERTIA DEPENDS ONLY ON MASS
Momentum - Is inertia of motion or how hard it is to stop and object p(momentum) = mass x velocity
Conservation of momentum law - State that momentum (energy) is not lost but transferred from one object to another
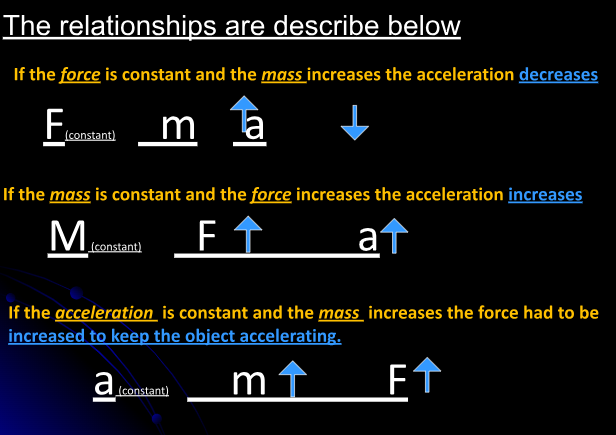
Newton’s Second Law - The relationship of force, mass and acceleration. Force (Newtons) = Mass (Kg) x Acceleration (m/s²) to Solve for mass the equations is M=F/A & to Solve for Acceleration the equation is A=F/M
A example of N-2 - Why do smaller less massive cars get better mileage? (more miles for every gallon) - Smaller cars have less mass so they require less force to accelerate than larger cars.
Newton’s 3rd Law: All forces come in pairs, For every action, there is an equal & opposite reaction.
A example of N-3 - Rockets, Action of rocket is the rocket pushes fuel downward, the Reaction: fuel pushes the rocket upward
Gravity - Is the attractive force between all objects in the universe, Gravity is produced by all objects that have mas, Gravity accelerates objects on Earth at 9.9m/s/s, Gravity is a weak universal force Only noticeable with massive object, Strength of gravity depends on 2 factors Mass (Density) & Distance
Measuring Gravity - Weight: measures the force of gravity (Units - Newtons or pounds) Formula for weight, Weight = mass x gravity(9.8m/s²), Weight can vary according to location not mass. the closer you are to the center of the Earth strong the force. So if you were at the beach or mountain top you would weigh a little less on the beach, close to earth’s core
Newton’s UNIVERSAL LAW OF GRAVITY and his 3 laws of motion allowed him to
Prove that the planets elliptical orbits were resultant because of result from gravity
Calculate the mass of each planet
Calculate the flattening of the Earth at the poles
Determine that gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon create the Earth’s tides
All objects in the universe attract each other with the force of gravity, The force of gravity is related to the masses of the object and their distance, This means the behavior of an object can be predicted
The real reason that objects fall at different speeds is due to Air resistance or fluid friction in the absence of air a , free fall a bowling ball & a feather would reach ground at the same time
Terminal Velocity: is the maximum speed of a falling object is reached when air friction = gravity, Results in balanced forces (N-3), How does it effect acceleration? - Once the force are balanced there are no change to falling object, continue falling constant speed. Less massive object will accelerate faster than more massive objects “light” objects (f=ma) actually fall faster than heavy object.
Example Questions
Imagine a place in the mosmos far from all gravitational & frictional influence. Suppose that you visit that place and throw a rock. The rock will (gradually stop or contine in motion ) because : Lack of air resistance & inertia
What will happen to the astronaut: Newton's 3rd law will go in the opposite direction