Korean War 1950-53
The leaders
- Communist north - Kim Il Sung
- Capitalist south - Syngman Rhee
Key terms
==Domino effect== - Idea that if one country fell to communism others would follow
==Containment== - Prevent the spread of communism
==Roll Back== - Turn the communist country capitalist (not just contain it)
==Proxy War== - A war where the Soviet Union aren’t directly involved and US didn’t just use their own troops - not fighting each other directly
The causes
- Domino effect
- Thought the Russians were behind it
- Test run for the UN army
Consequences
- Important development in Cold War - first Proxy war in a third country - strategy used in Vietnam
- W for containment as communism didn’t spread beyond 38th L for General MacArthur and Roll back
- Tense relationship between China and Us as the troops still remained in South Korea
KEY DATES
==25 June 1950== - North invade south backed by China and Soviet Union - illegal
==July 1950== - USA send troops to South Korea (also appealed to UN for troops and permission to fight)
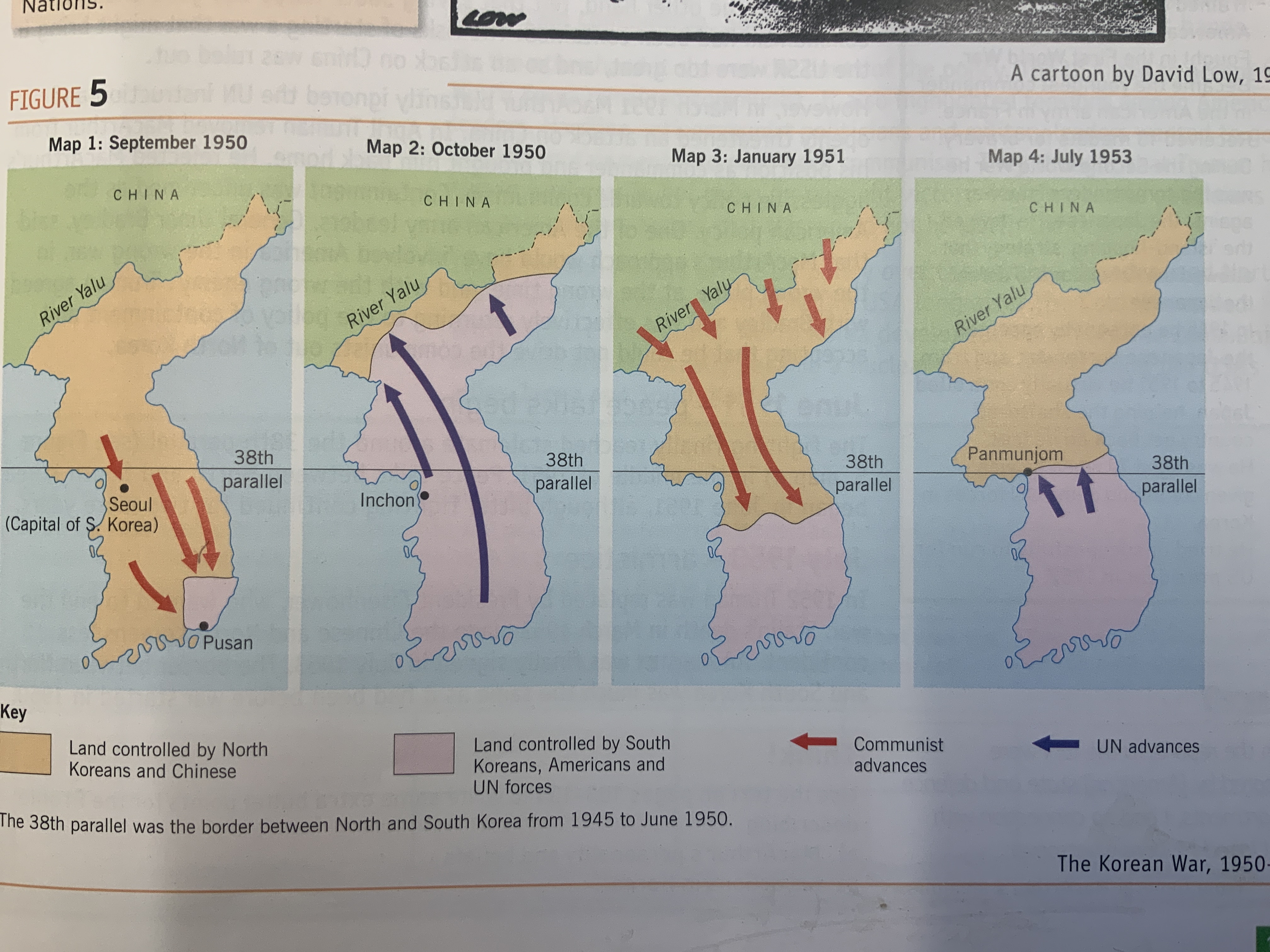
==September 1950== - UN fight back beyond 38th parallel almost at Yalu river by October
==15 October 1950== - China joined invasion and pushed UN forces back beyond 38th MacArthur called for use of atomic weapons denied and sacked in April 1951
==June 1951== - more UN troops were deployed to Korea and the communists were eventually driven back to the 38th parallel. The war became a stalemate.
==November 1952== - Republican, General Dwight D Eisenhower won the US presidential election, promising he would go to Korea to see how the war could be ended.
==July 1953== - an armistice was signed at Panmunjom on the 38th parallel, which left Korea divided as it had been in 1950, and still is today.