Properties of Waves - Part B
Properties of Waves
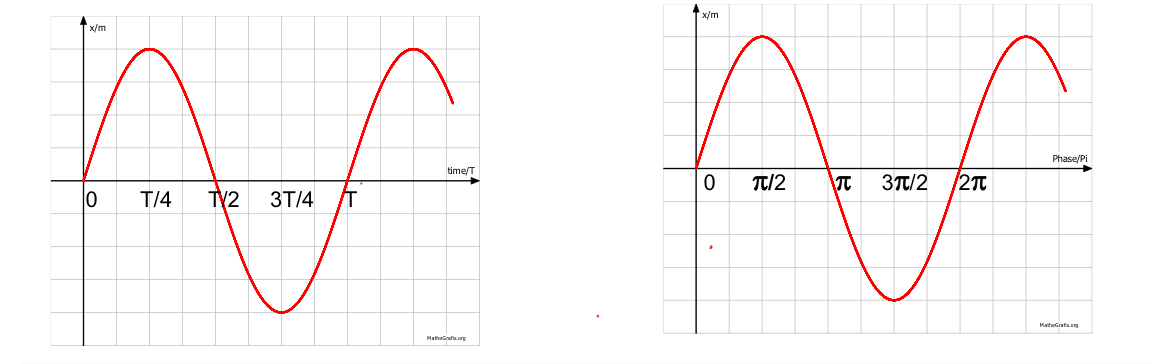
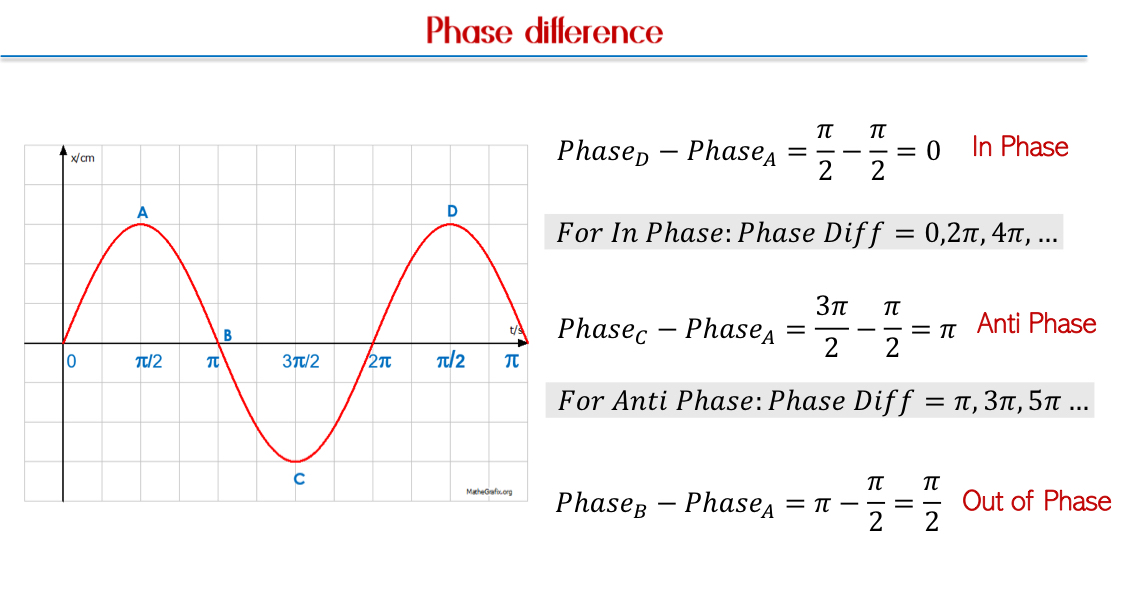
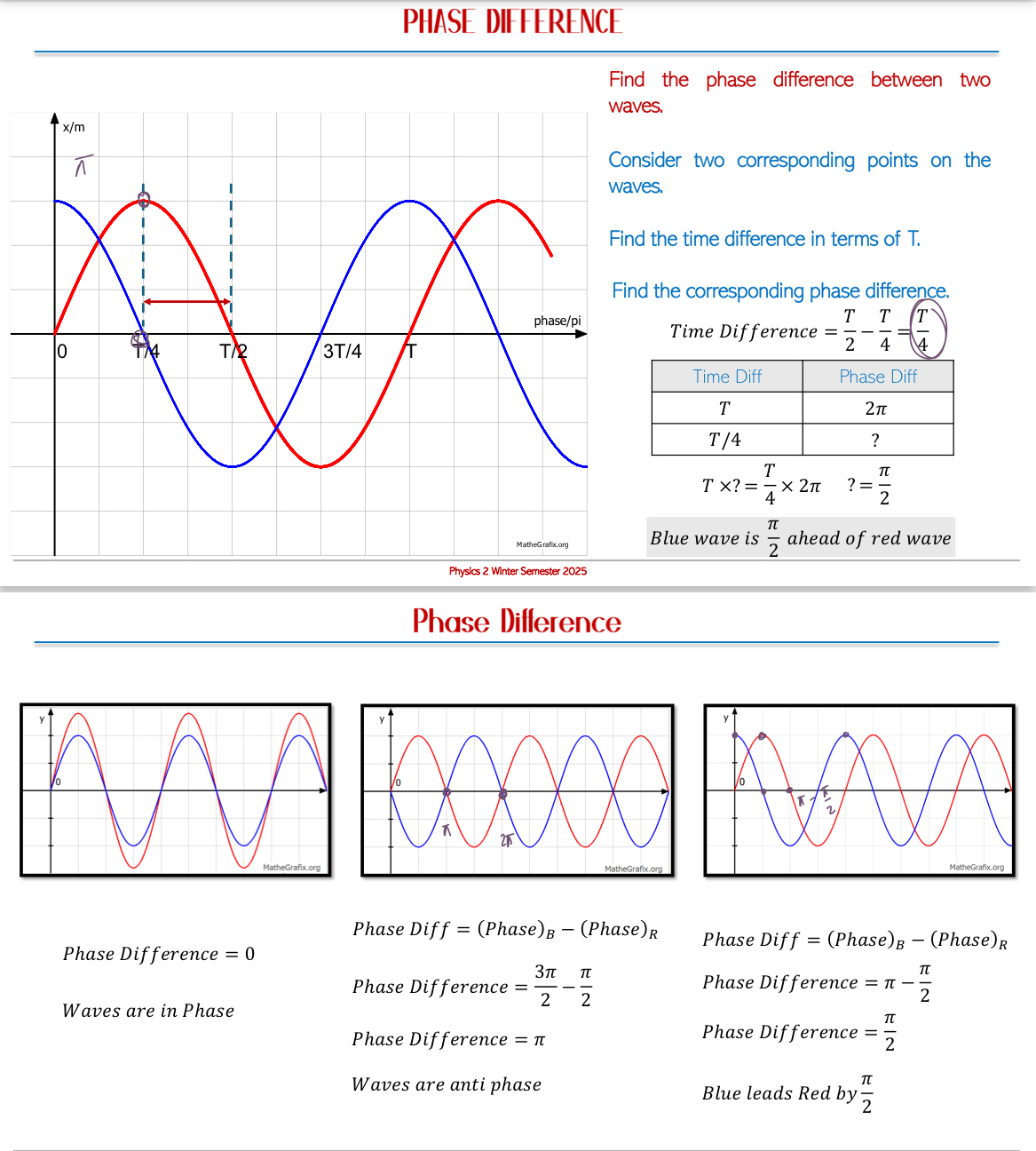
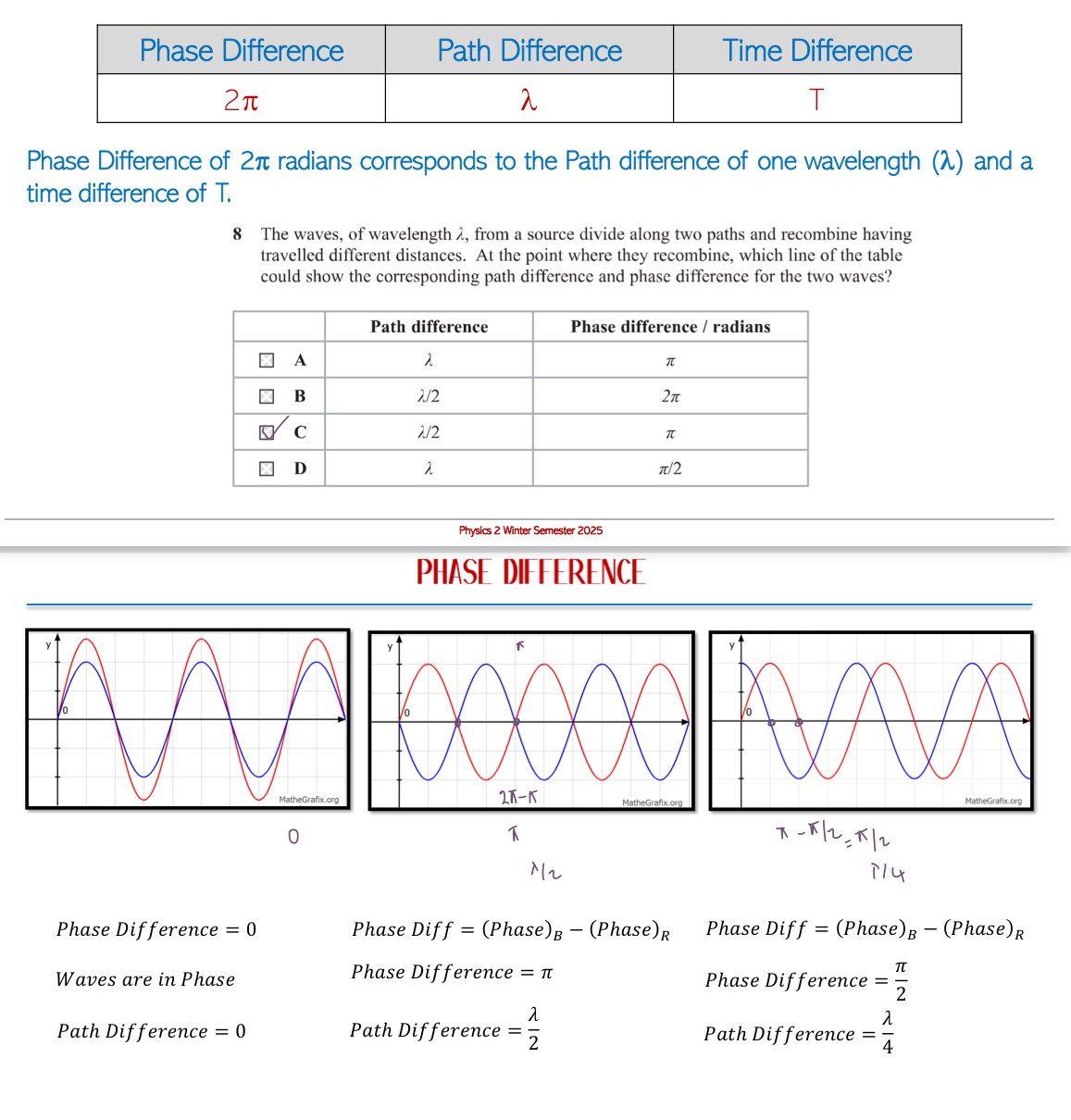
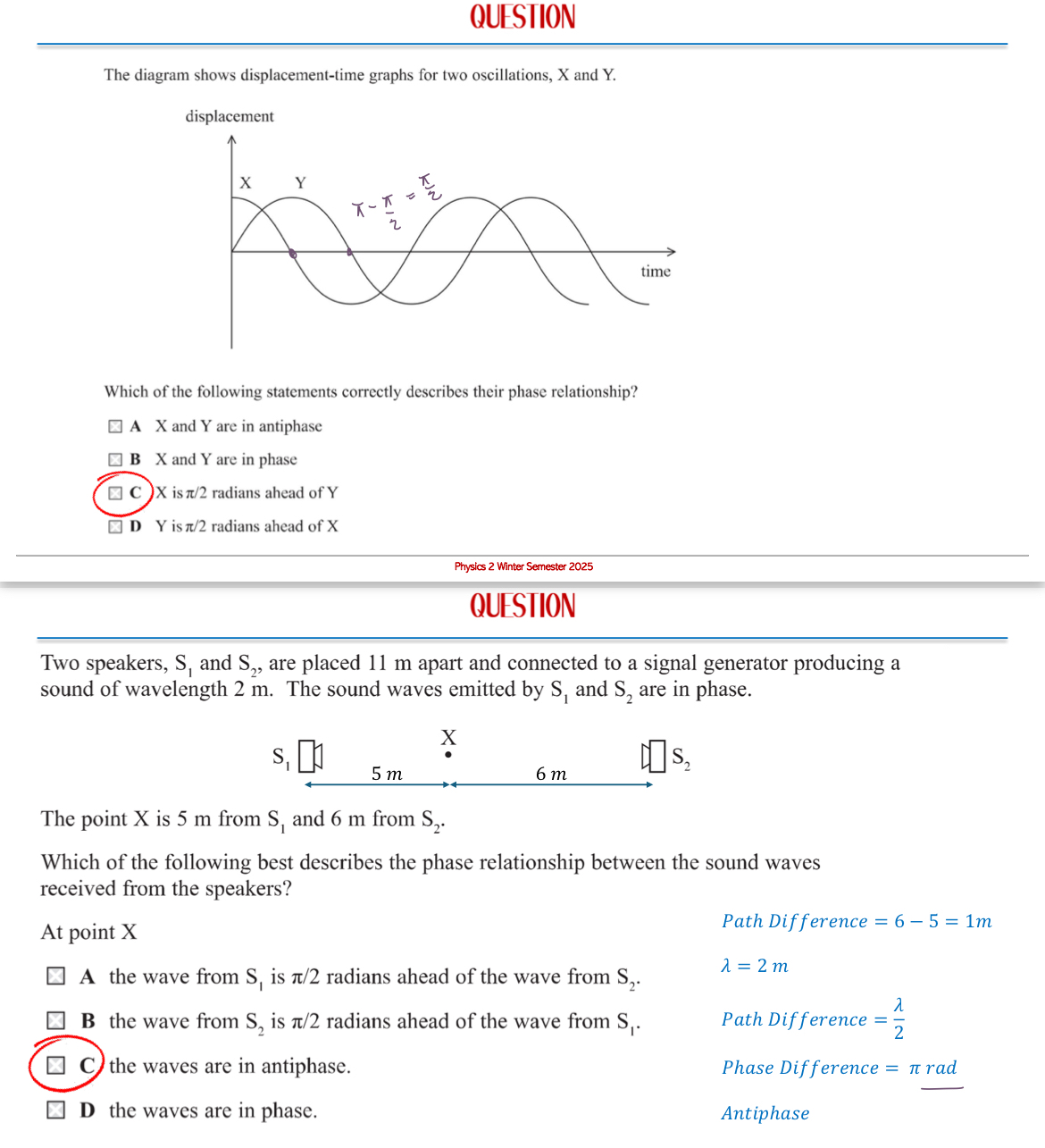
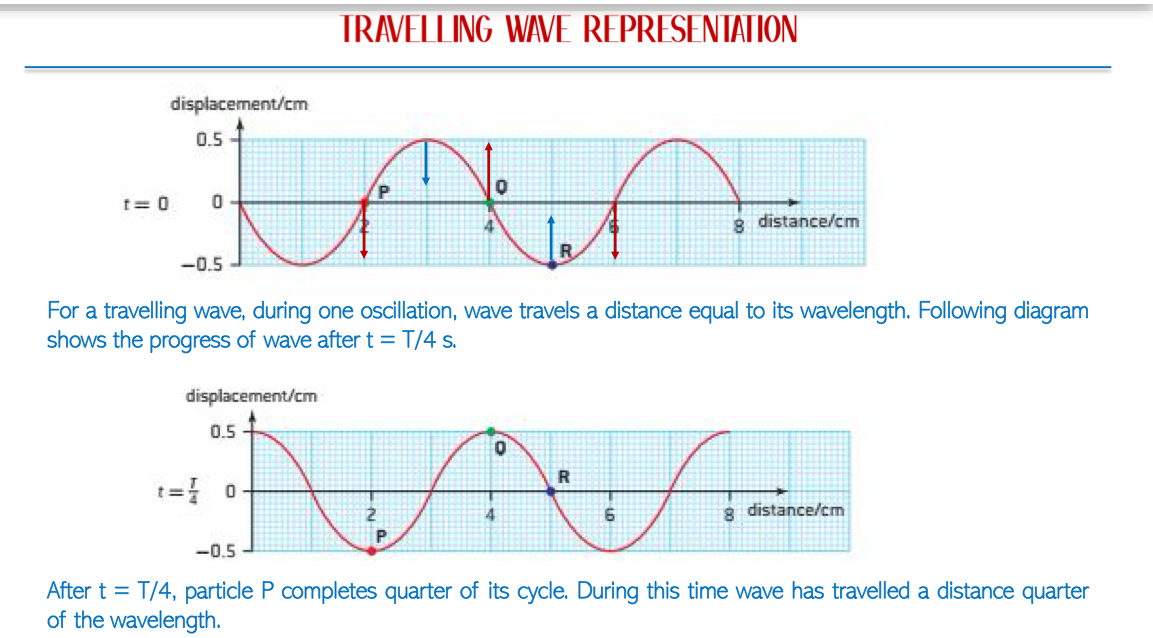
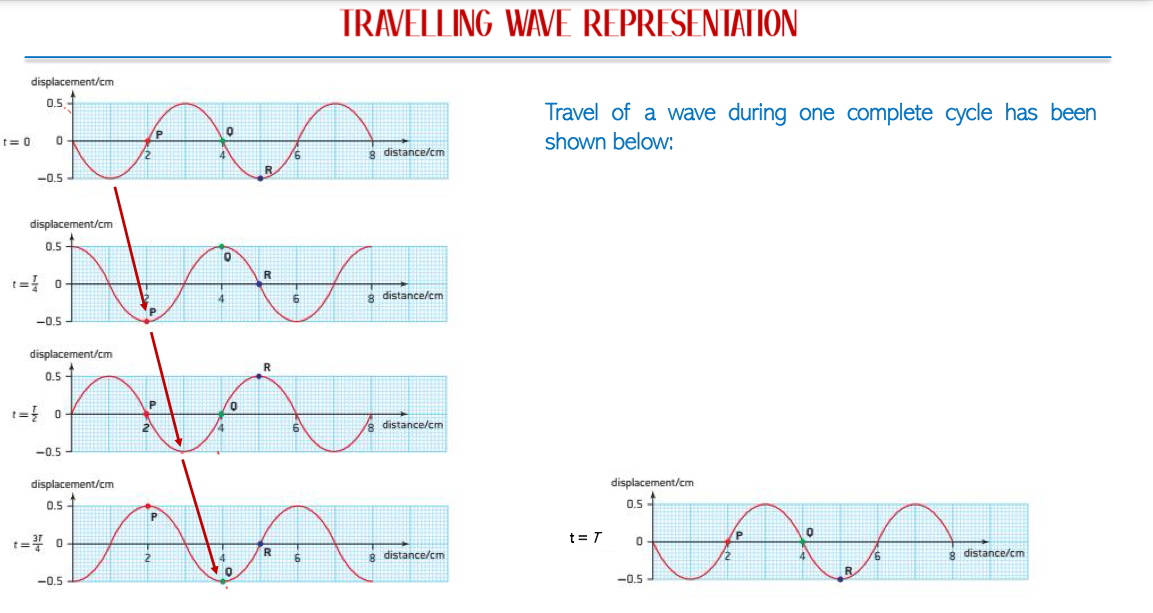
Phase of a Wave: Refers to the position of a point in a wave cycle at any instant of time from mean position. It is crucial to understand phase differences between multiple waves rather than their absolute phase values.

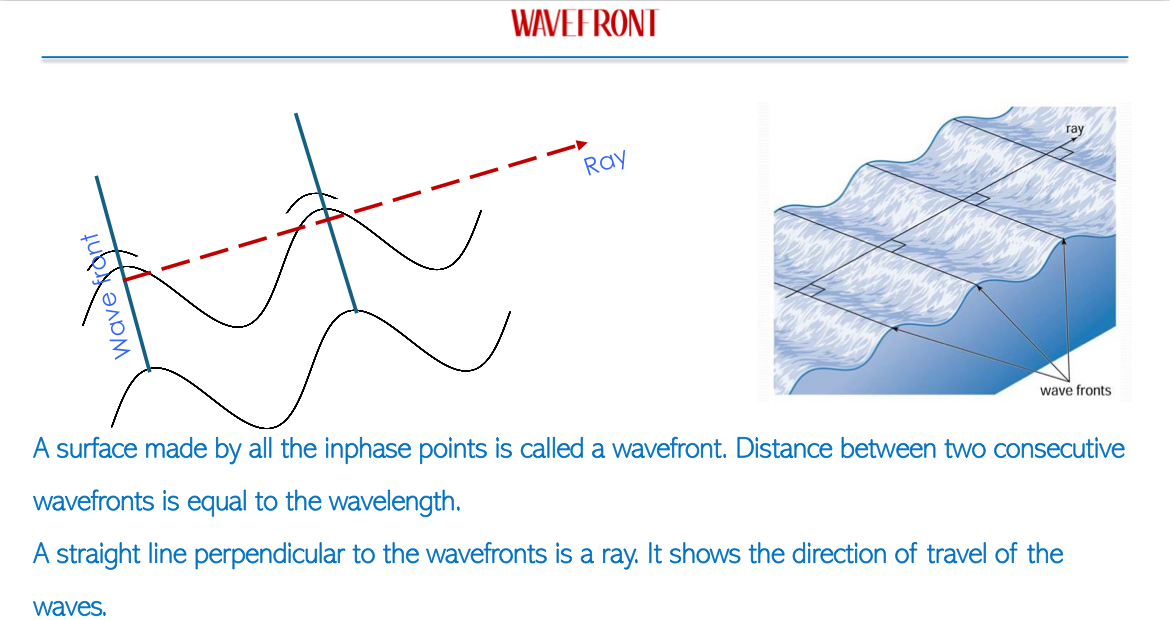
Reflection of Waves: All types of waves (light, sound, water) experience reflection when they encounter a boundary. Reflection is defined as the change in direction of wave propagation when meeting a boundary where properties are:
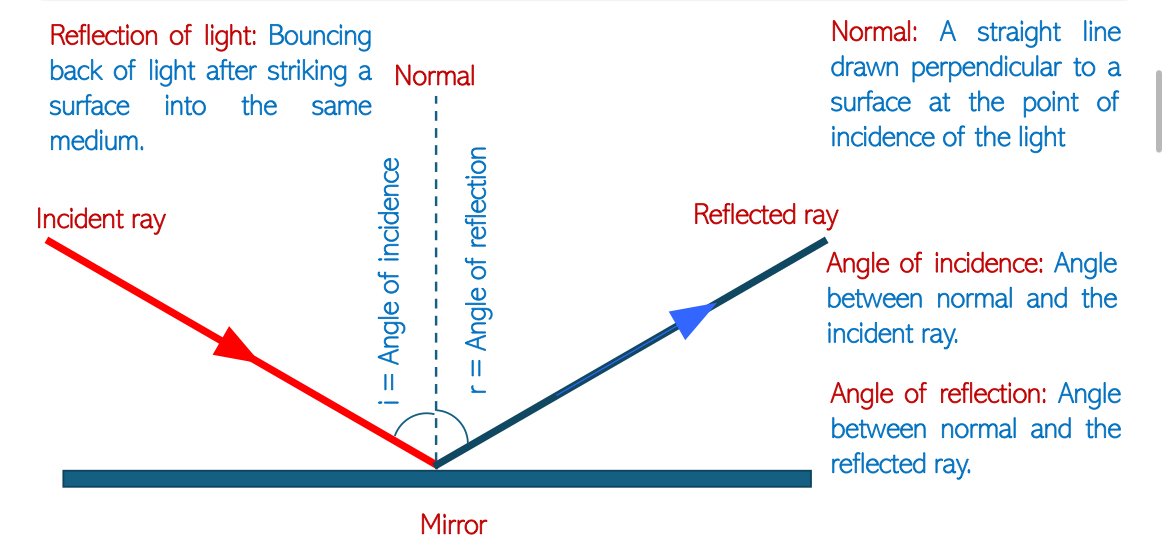
Law of Reflection states:
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection.
Properties of Reflection:
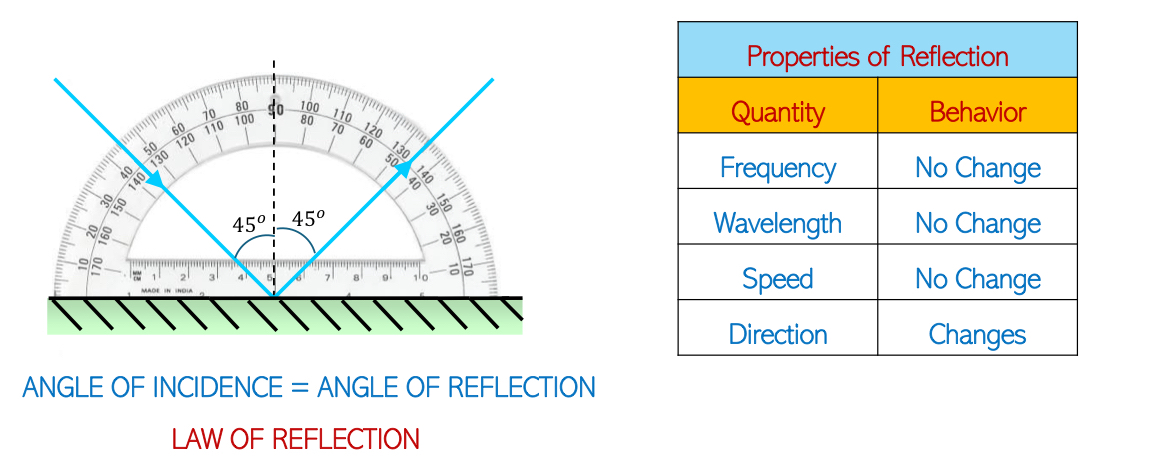
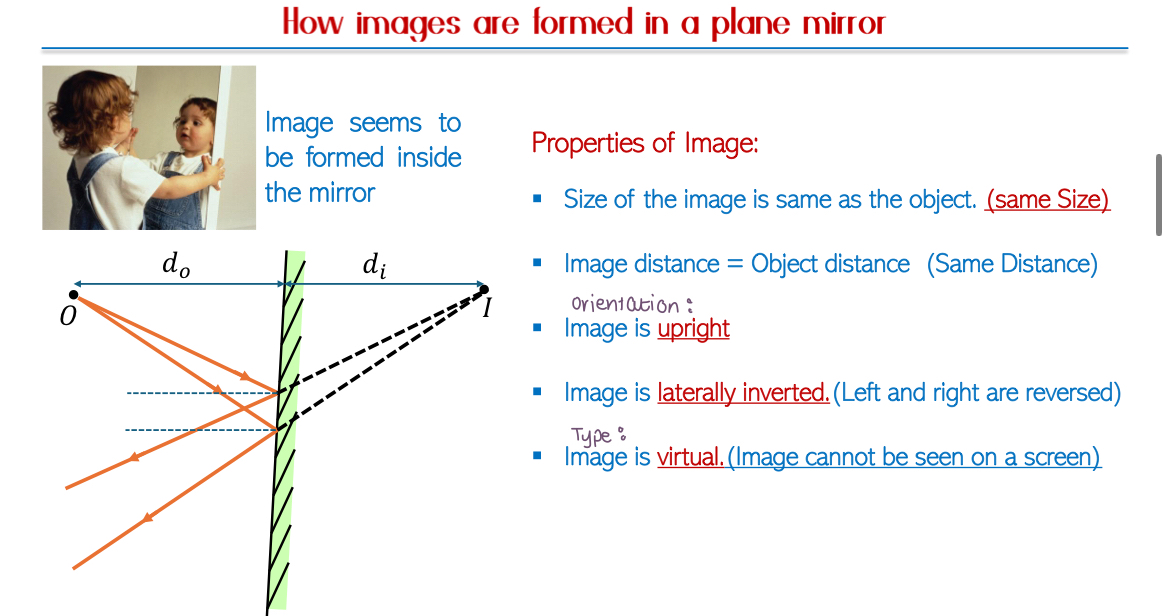
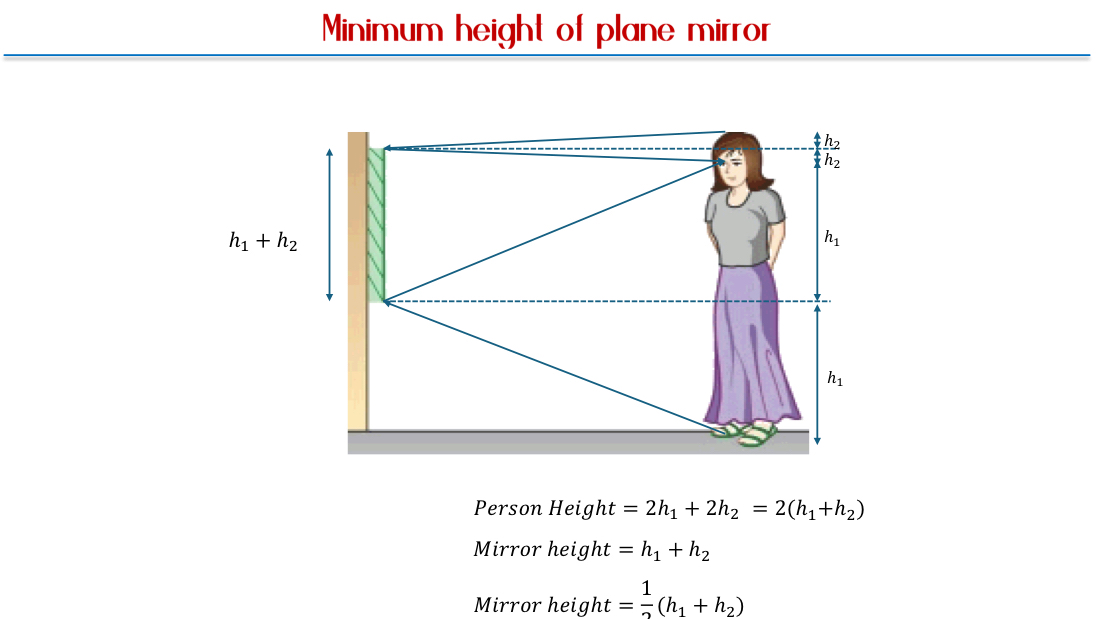
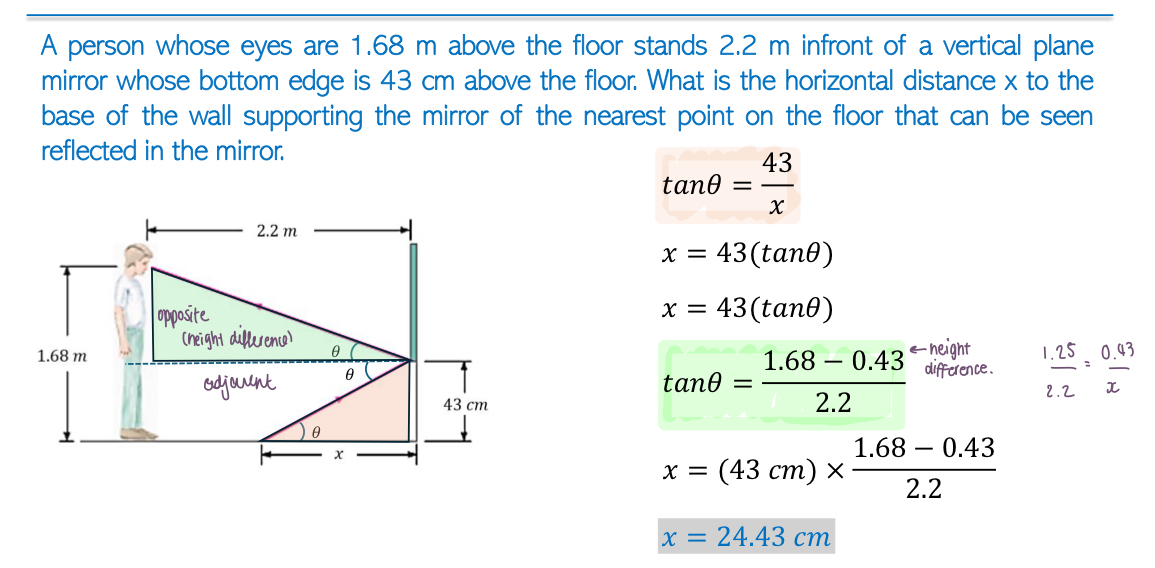
Image Formation via Reflection:
Images formed by a plane mirror have specific properties:
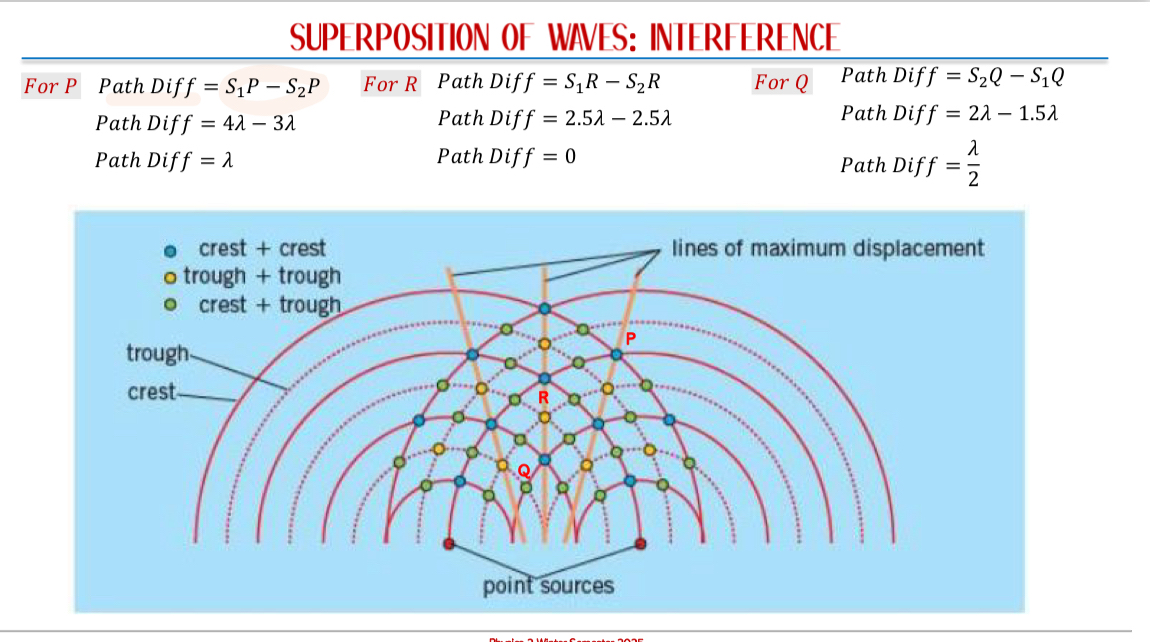
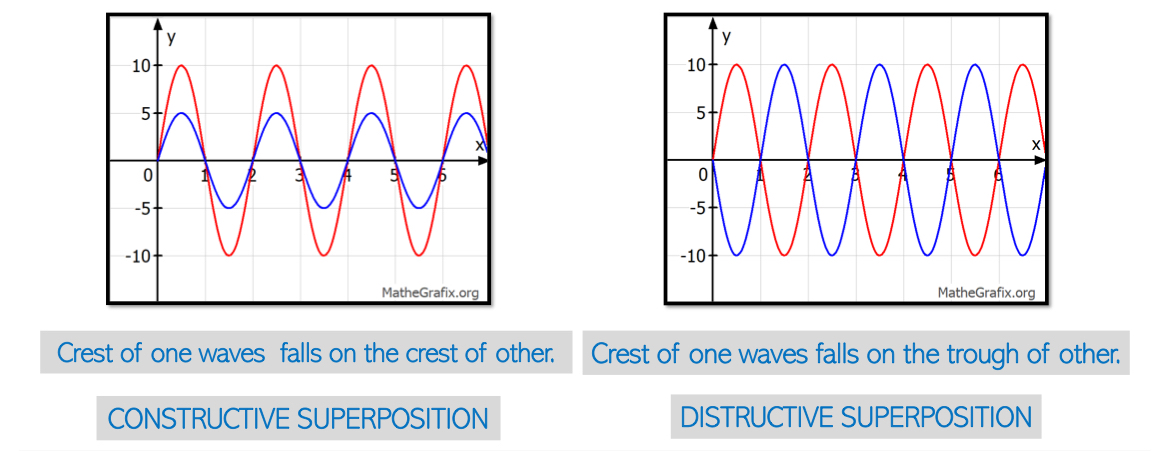
Superposition of Waves: When two or more waves of the same type cross paths in the same medium:
Constructive Interference: Occurs when waves are in phase. Resultant amplitude = sum of individual amplitudes.
Destructive Interference: Occurs when one wave’s crest meets another’s trough. Resultant amplitude = difference of individual amplitudes.
Shows where regions of high and zero amplitude occur.
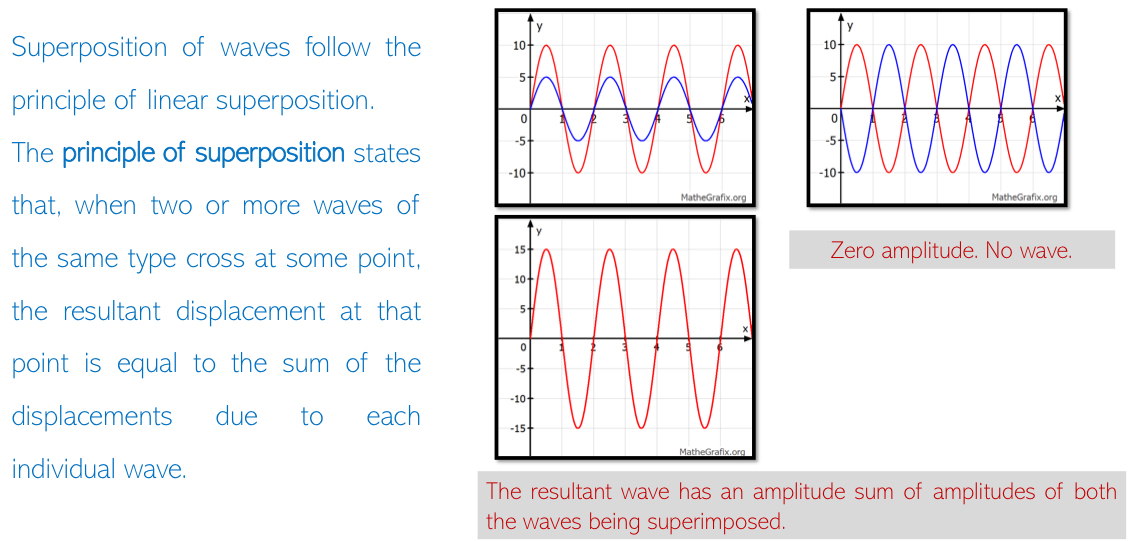
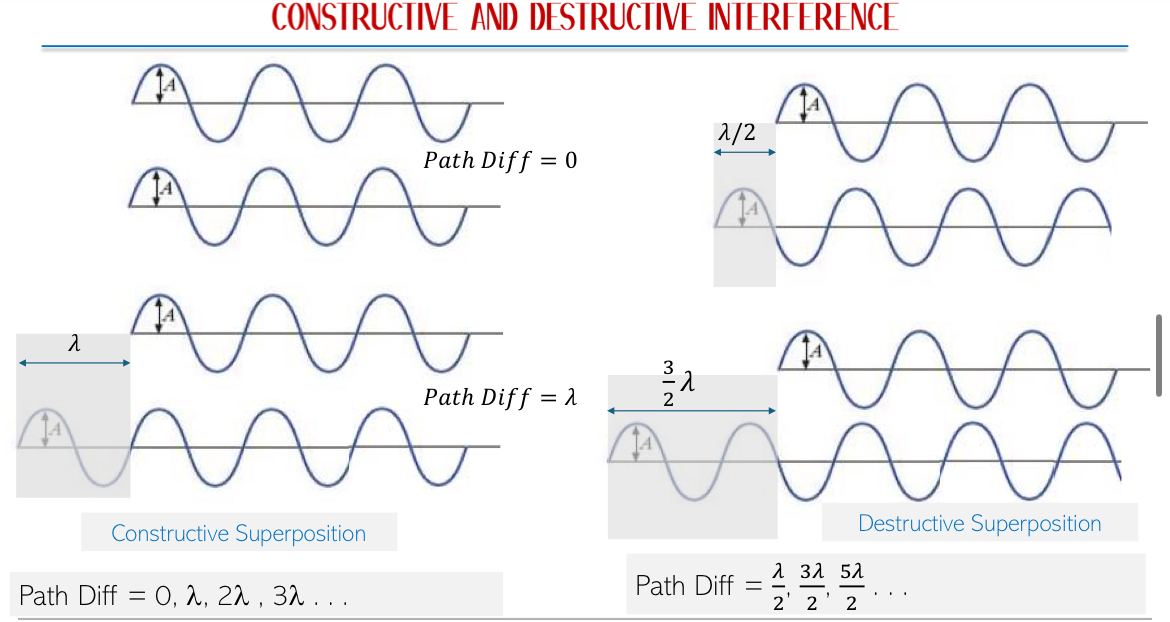
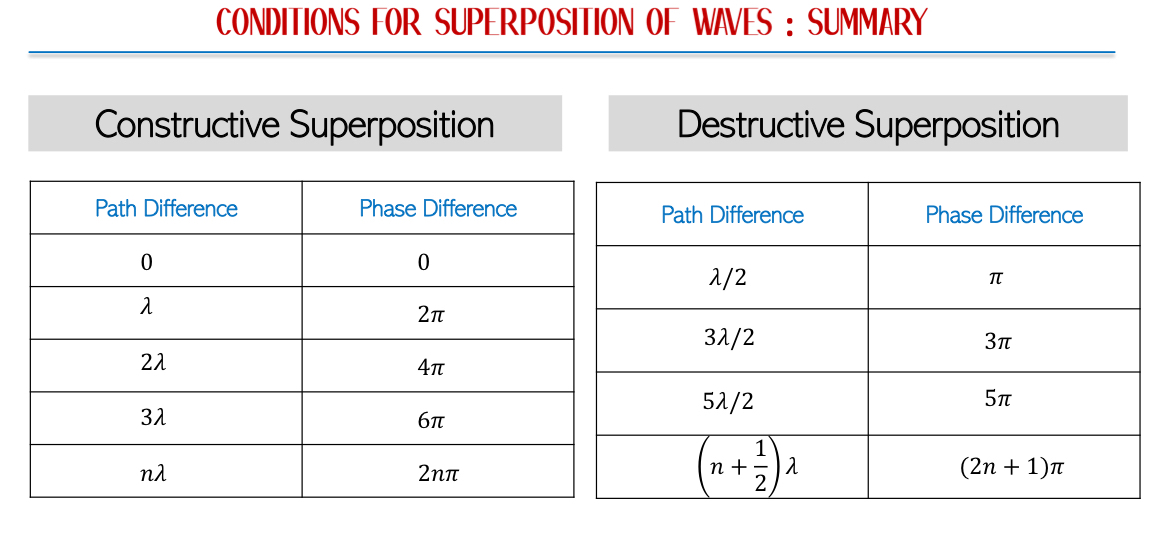
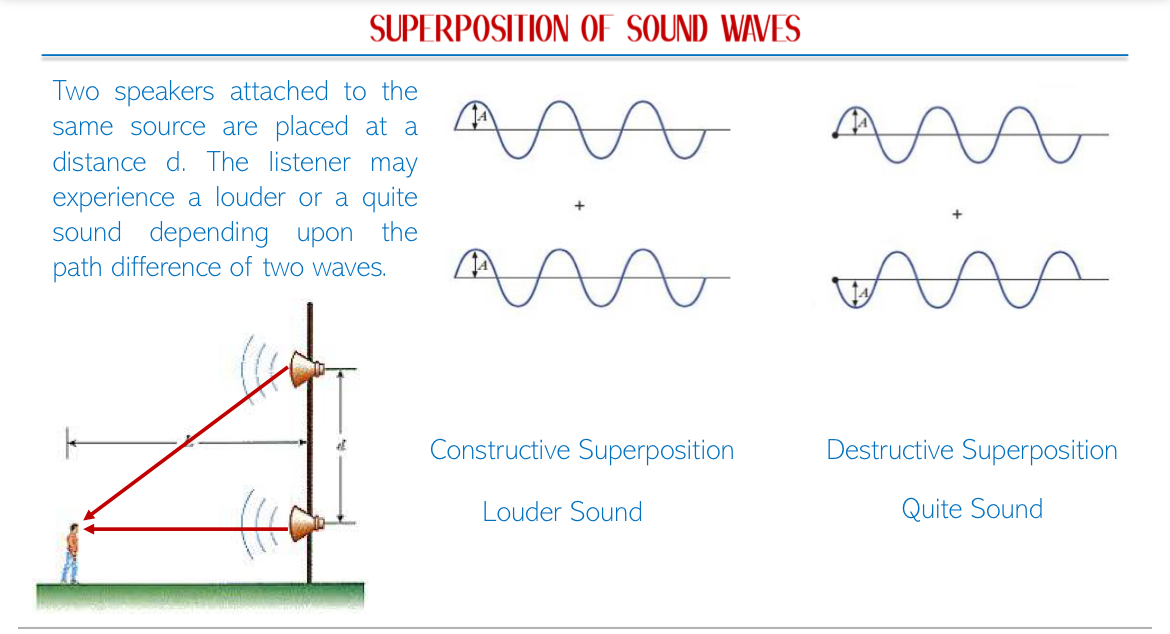

Interference: Superposition of two waves of same frequency & amplitude travelling in the same direction when produced by two coherent sources.

Conditions for Interference:
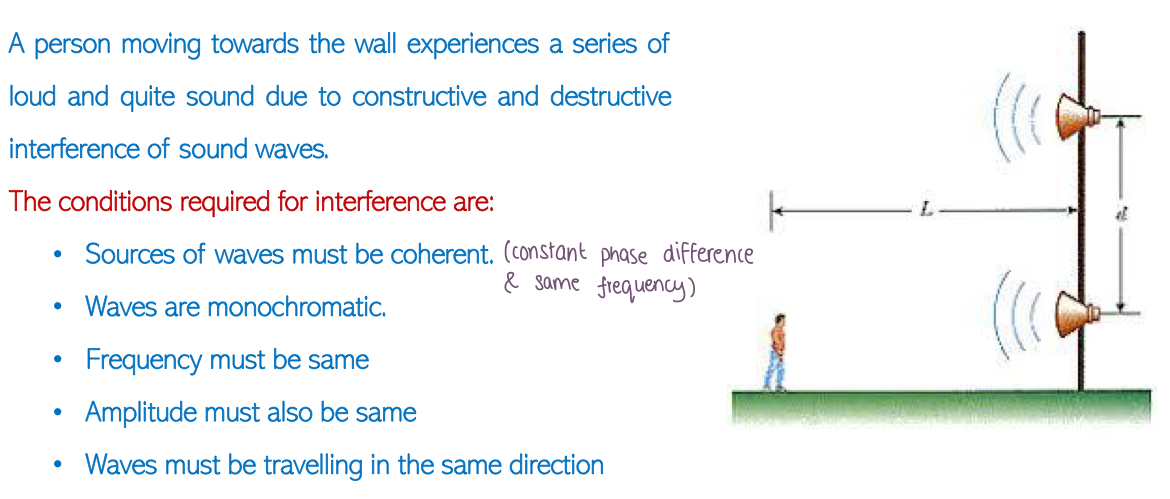
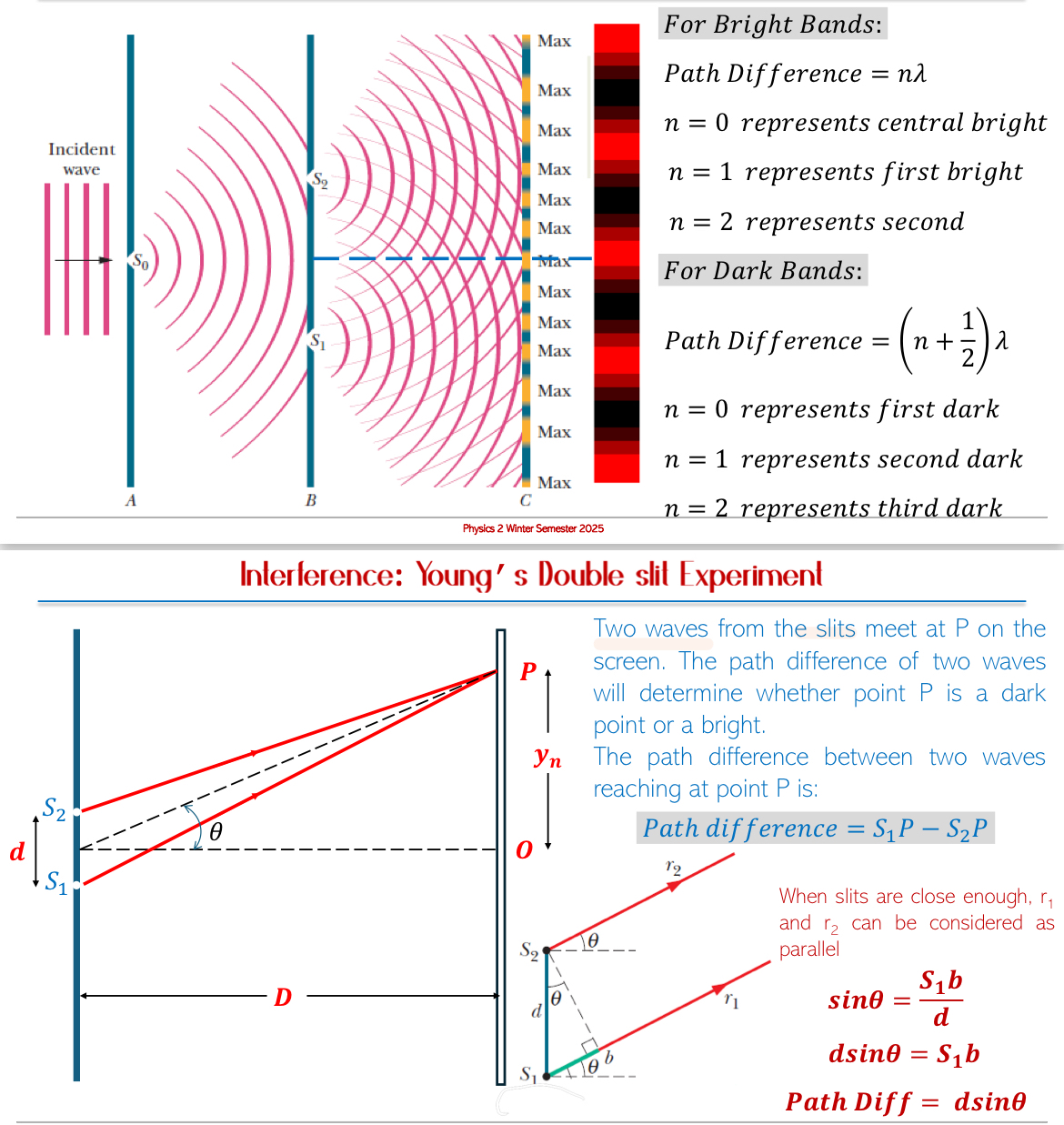
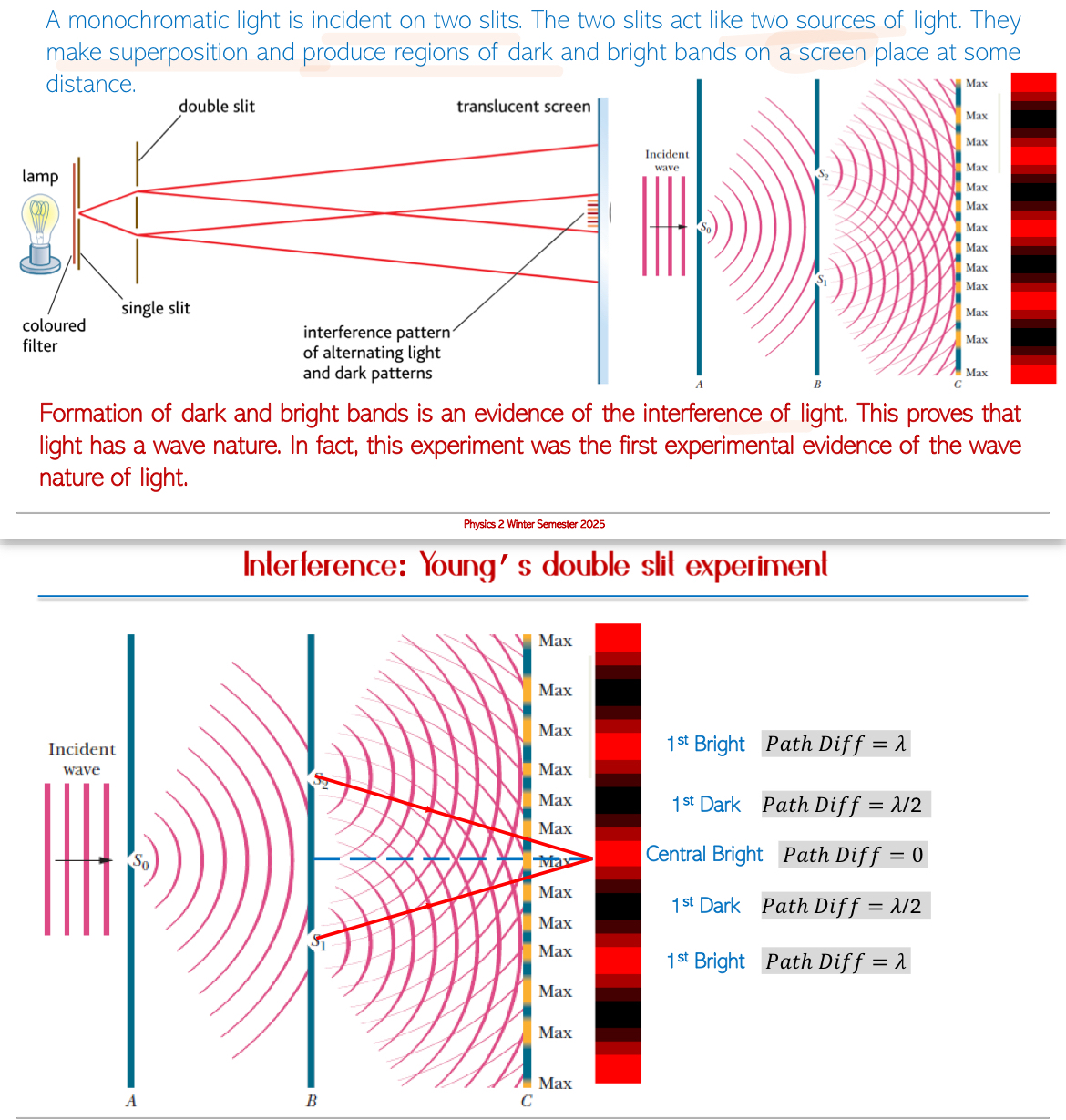
Interference with Light: When monochromatic light passes through two slits:
Bright regions (constructive interference) and dark regions (destructive interference) are produced.
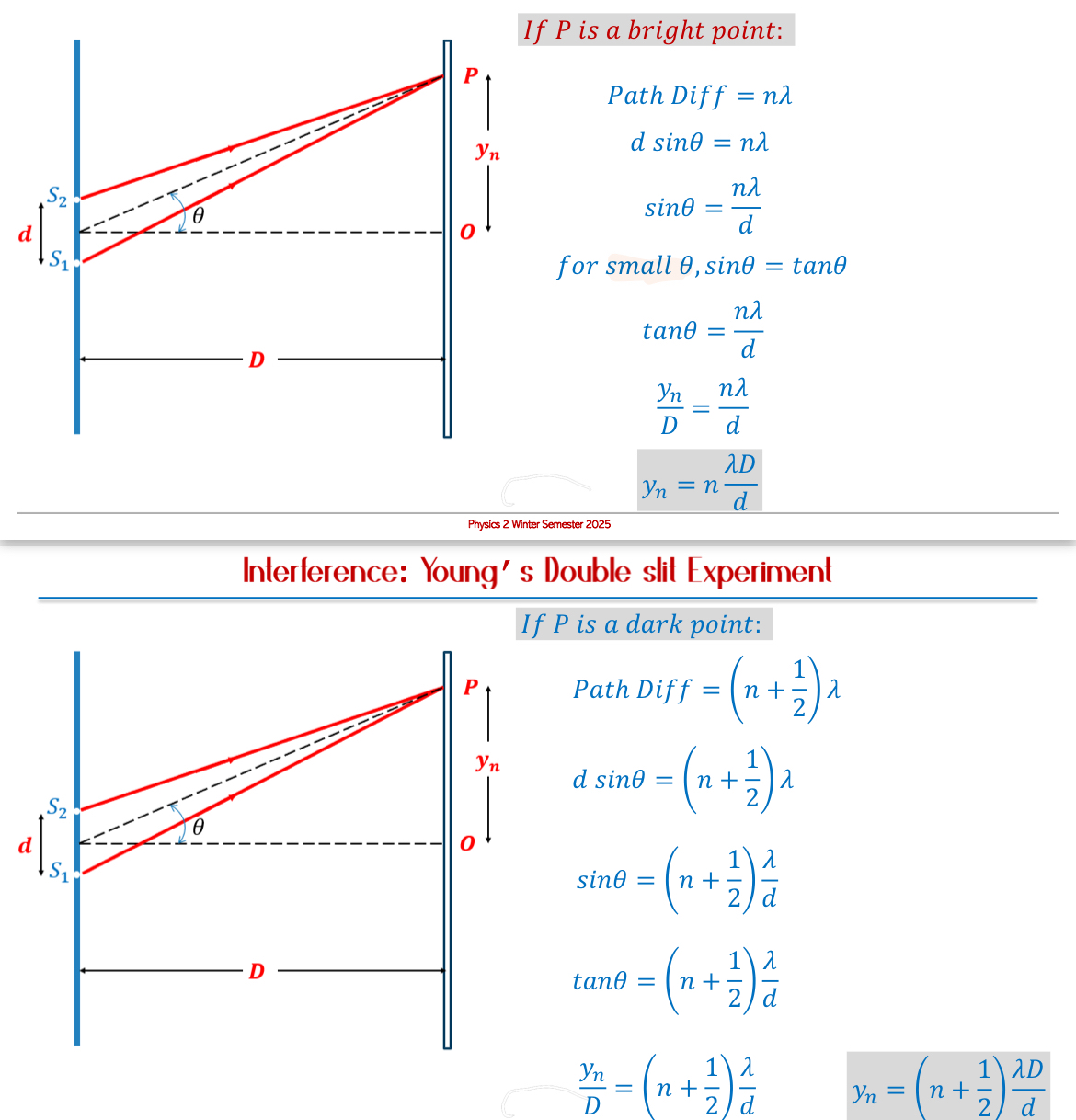
Bright bands correspond to path differences of 𝑛𝜆 where n = 0, 1, 2,…
Dark bands correspond to path differences of (𝑛 + 1/2)𝜆
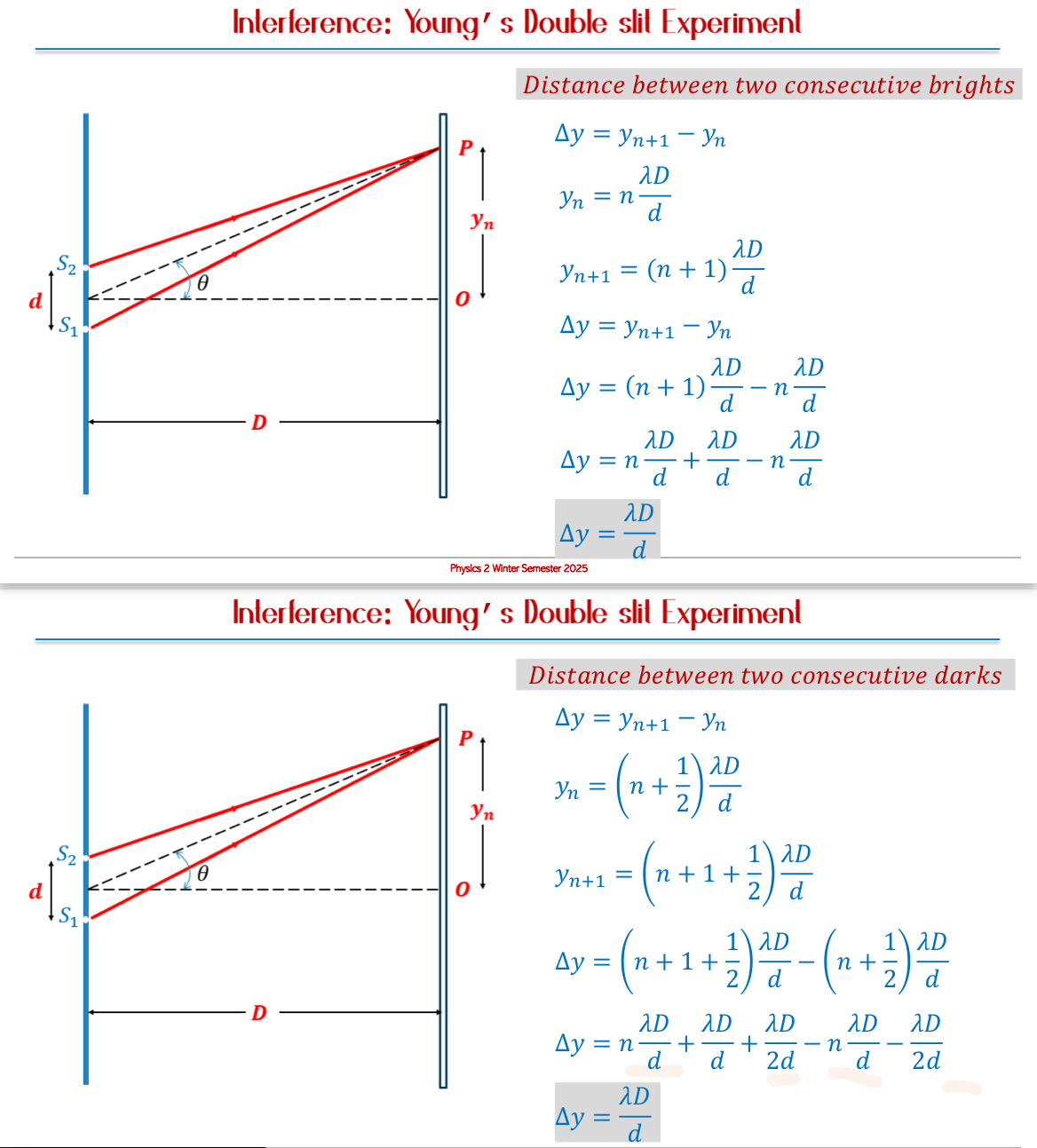
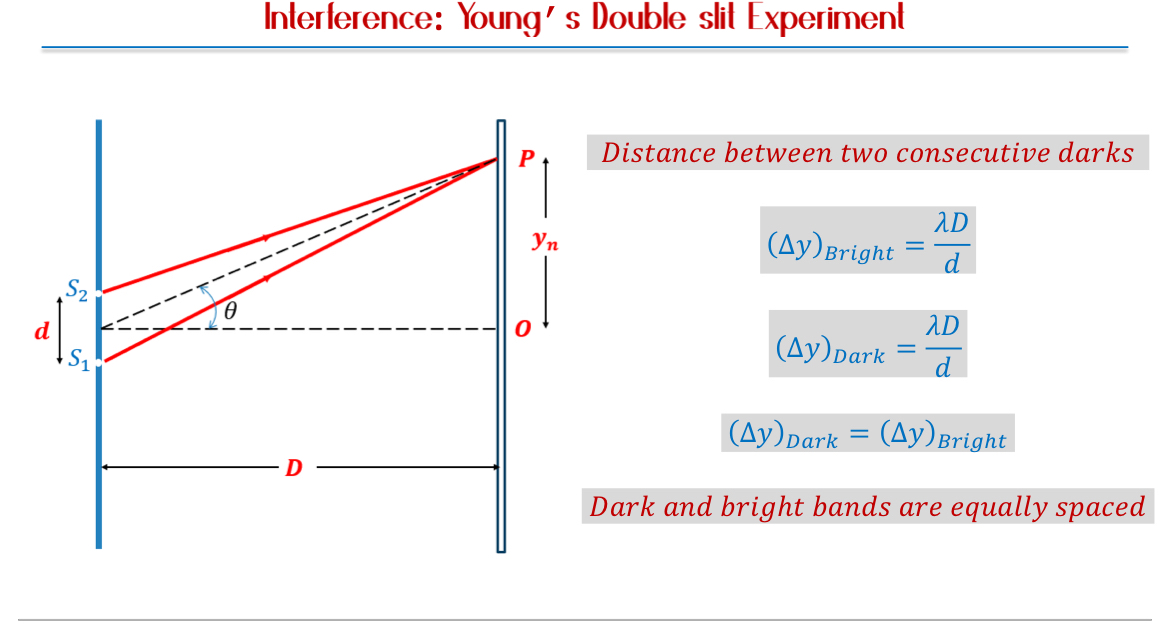
Calculating Path Differences: When two waves travel different distances.
Use sine functions in small angle approximations for calculations based on the distance and angle involved.
For constructive: 𝑑 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 = 𝑛𝜆
For destructive: 𝑑 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 = (𝑛 + 1/2)𝜆