Psych notes
ts is just shyt i dont already know, there is more material i skipped cuz i know them already
Pre-Units (For MCQ and FRQ answering)
Concept Application (MCQ)
Modern Perspectives on Psychology, there are 7
1) Behavioral
John Watson, Skinner
External environmental stimuli influences your behaviors (conditioning is big)
“Everything is taught”
Observable behaviors main thing
2) Cognitive
Piaget, Noam Chomsky
Mental processes (memory, problem solving, perception) are main thing that direct behavior and are how ppl interact w/ world
3) Evolutionary
Darwin
Natural selection, behaviors are because of evolution and for reproductive success
4) Psychoanalytic
Freud
Childhood experiences and unconscious influences behavior (Repression, personality)
5) Humanistic
Carl Rodgers, Maslow (Hierarchy of Needs, Self-actualization)
Ppl are inherently good; Individual potential and personal growth to achieve highest potential
6) Sociocultural
Vygostky
Culture and social (norms, values, traditions) influence our behavior and thinking
7) Biological
Brain functions, genetics, hormones influence behavior and thinking
8) Eclectic: Just a combination/mix of the perspectives
Research Methods & Design (MCQ)
B) State the operational definition of a variable (its alr in study, js copy over)
C)

The Scientific Method
Come up with hypothesis, define variables, check for confounding var.
Experimental Research
Hypothesis
Often based on a broader theory; a testable prediction
Has to be falsifiable (able to be proven wrong)
Confounding variables
Any external factor that could change the results of a study (ex: test takers are in different temp rooms, temp is confounding variable)
Quantitative vs Qualitative:
Qualtitative: Non-numerical data (Interviews); Can gather deeper data and more personal information
Quantitative: Numerical data (Surveys); Can help see trends/patterns
Representative Sample
A sample that shows key characteristics of the larger population (Able to assume the findings from this sample applies to entire population)
Helps avoid biased results; Best way to achieve rep. sample is to do random sampling
Single & Double Blind Study:
Participants or/and researchers don’t know which group is control and which is experimental
Nonexperimental Research
Case Study
Looking into a single person/group and provides understanding of single/unique cases (not generalizable)
Correlational Study
Does one correlate to the other? (Relationship between multiple variables to see how and if they change together)
Correlation =/ Causation
Meta-Analysis
Take other studies and make a general conclusion
Poor studies can lead to bad meta analysis
Naturalistic Observation
Observe people in their natural environment
Data Interpretation (MCQ)
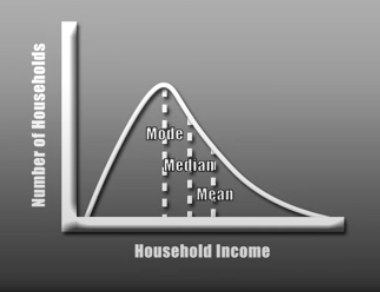
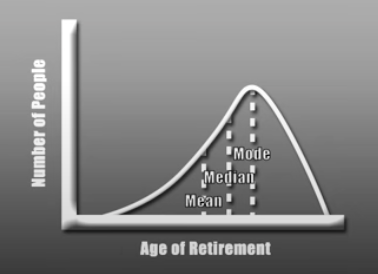
Mean - Average
Median - Middle score
Mode - Most frequently appearing score
Variability
Positively Skewed Curve (More high scoring outliers)
Negatively Skewed Curve (More low scoring outliers)
Bimodal: Two Peaks
Inferential Statistics: Use stats to make inferences about whole population
Positive Correlation: One variable increase, other also increase
Negative Correlation: One variable increase, other decrease
Correlational Coefficient: Value between 0 and 1 that quantifies strength/direction of a relationship is between two variables (ex: -0.83 or +0.23) (1 is strongest either - or +)
Empirical Rule (68-95-99.7 Rule)
Argumentation (AAQ and EBQ)
Task verbs:
Describe: Provide the relevant characteristics of a specified topic.
Explain: Provide information about how or why a relationship, process, pattern, position, situation, or outcome occurs, using evidence and/or reasoning to support or qualify a claim.
“Explain how” analyzing the relationship, process, pattern, position, situation, or outcome;
“Explain why” analysis of motivations or reasons for the relationship, process, pattern, position, situation, or outcome.
Identify/State: Indicate or provide information about a specified topic, without elaboration or explanation. (Just name a concept/note a key point, keep it short)
Propose: Provide a claim for a specific topic using your own words. (Your argument/hypothesis)
Support or Refute: Provide reasoning that explains whether a claim or evidence should be upheld or rejected.
Use Evidence: Provide information from a study (i.e., data, rationales, conclusions, hypotheses) that is specific and relevant to a given topic.
Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
Eugenics:
Basically selectively breeding people cuz some traits are “superior”
Nervous System:
Network of nerves and neurons that carry messages from/to the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
Central Nervous System
Brain: Acts as command center and process incoming data and thinks of responses
Spinal cord: Acts relay station to organize and send messages
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerve endings that branch out from brain and spine to body
Transmits info to CNS and takes orders from CNS
Somatic Nervous System: Manages voluntary movements and gives sensory information to CNS (waving bye)
Autonomic Nervous System: Manages involuntary movements (heartbeat, digestion, breathing)
Sympathetic: Fight/flight reactions
Parasympathetic: Rest/digest after stress
Neurons: Communication dudes in NS
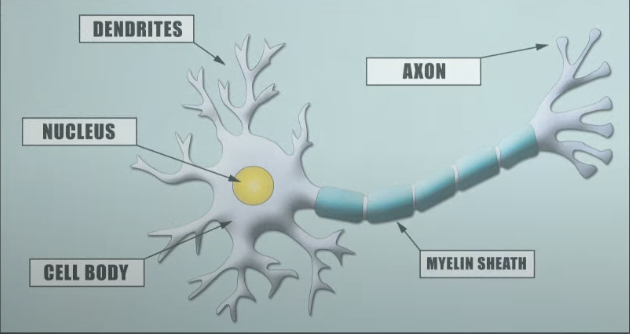
Nucleus: Brain of cell
Cell body: Provides structure and process nutrients
Dendrites: Receives incoming msgs from other neurons
Axon: Gives next neuron info
Myelin Sheath: Made up of glial cells, faster speed of messages
Interneurons: Neurons that communicate internally straight to motor neuron from sensor neuron (doesn’t go to brain) (ex; hot stove (sensor neuron senses, interneuron tells motor neuron to pull tf away)
Afferent Neurons: Transmits info from sensory neurons to CNS
Firing process:
Stim. Threshold → AP → Refractory Per. → Resting Potential → Reuptake
Glial Cells: Support protect maintain neurons
Neurotransmitters: Messages that cross synaptic gap
Excitatory (Increase chance of next AP)
Inhibitory (Decrease chance of next AP)
Types: Dopamine, ACH (Memory, attention, muscles), Endorphins (reduce pain), Glutamate (learning/memory), GABA (slow down/deexcite), Serotonin (Control mood), Norinepinephrine (Alertness)
Endocrine System:
Secretes hormones in bloodstream
Controlled by hypothalamus and pituitary gland
Adrenaline, Leptin (time to stop eat!), Ghrelin (time to eat!), Melatonin (sleep), Oxytocin (love)
Drugs can be: Agonist: Make neurons fire Antagonist: Stop neural firing
Brain Structures
Hypothalamus: Regulates vital functions (hunger thirst temp) & Endocrine
Thalamus: Senses (except smell)
Amygdala: Fear & Anger emotions
Hippocampus: Memory
Cerebellum: Fine muscle movements
Medulla: Survival functions - breathing, blood pressure, heartbeat
4 lobes:
Frontal: Thoughts and emotions (Brocas, Motor)
Parietal: Sensory
Occipital: Sight
Temporal: Hearing (Wernickes)
Broca (speak) Wernicke (Understand speech)
Sleep
4 stages (S1 NREM (light), S2 NREM (light), S3 NREM (delta, deep), REM (increase brain activity, alpha waves, dreams))
Why do we sleep?
Restorative theory: Sleep is for repairing and consolidating memories
Adaptive theory: Sleep is for surviving since night is dangerous yo
Why do we dream?
Activation-synthesis theory: We dream to make sense of weird shyt during REM
Memory consolidation theory: We dream to make memories of fine shyts
Senses
Transduction: turning sensory shyt into electrical signal shyts
Absolute threshold: point when u can detect a stimulus (ex: faint sound)
Difference threshold: point when u can detect a difference in stimulus
Weber’s law: “Yo the JND is proportional to the magnitude of a stimulus” (ex: adding 1 cookie to a small jar is easier to spot than adding 1 cookie to a huge pile)
Sensory adaptation: Ability to tune out shyt (senses) aka “adapt” to it
Sight
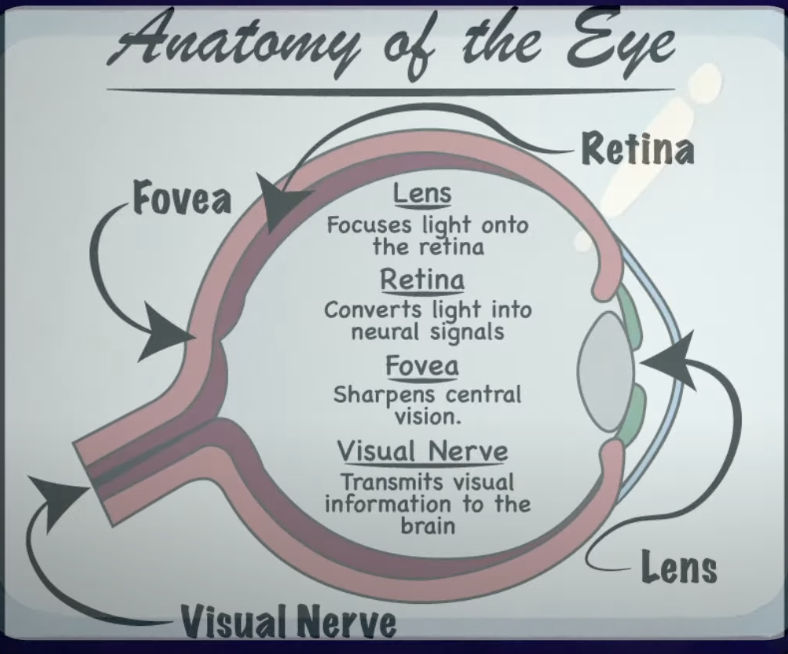
Accommodation (Lens focusing) → Projects to Retina → Concentrated on Fovea → Signals sent to Visual Nerve
Rods: Light and dark
Cones: Color
Hearing:
Place Theory: High and low sounds hit different spots in your ear.
Frequency Theory: The ear sends signals as fast as the sound is.
Volley Principle: Nerve cells take turns sending quick signals to keep up with fast sounds. Like volleyball
Unit 2: Cognition
Bottom up processing: Begins with sensory input, then constructs understanding
Top down processing: Begins with past experiences, then uses expectations to make sense of sensory info
Perceptual set: Tendency to perceive things a certain way based on expectations
\Context effect: See shyt based on environment/context
Change blindness: Failure to notice change in environment (prolly cuz u were doom scrolling reels)
Gestalt Psych: Says that we see shyt as a whole and see patterns
Figure ground: Whats figure and whats ground?
Closure: Brain fills in missing parts of an image to complete it
Proximity: Brain tends to see shyts close together as groups
Similarity: Brain tends to see similar looking shyts as groups
Monocular cues
Relative clarity: Closer shyts look clearer/detailed
Relative size: Smaller object is further away
Texture gradient: More texture means closer
Linear perspective: Parallel lines seem to converge when go further
Interposition: Object overlaps another, overlapped object is further away
Binocular cues
Convergence: More eyes converge, closer the object
Retinal disparity: Two eyes have slight differing image: More difference = closer
Apparent movement: Seems like there’s movement but just fast-blinking lights
Thoughts
Concepts: Mental grouping of similar shyt to organize info
Prototypes: Best example of a category (ex: shiba inu for dogs)
Schema: Mental frameworks that help organize and interpret similar ideas (dog)
Assimilation: New info in existing schema (New breed of dog)
Accomodation: Create/adjust existing schema to fit new info
Problem Solving Strats
Algorithms - Consistent method/steps - guarantees solution but time consuming
Heuristics - Mental shortcuts by using past experiences but prone to error
Rep. Heuristic: Judge event based on a prototype (assumption)
Availability Heuristic: Judge based on events that easily come to mind (like recent events or big events ex: plane crash)
Decision making
Mental set: Approach problems with familiar strats even if they aren’t suitable
Priming: Exposure to one thing influences response to another (hearing doctor will make us easily think of similar shyts such as nurse or hospital)
Working memory: Holding information for a short time (barista)
Types of thinking
Divergent: Explore multiple possible solutions (creative)
Convergent: Narrow solutions into one (logic)
Memory
Explicit: Conscious recall of fax and events
Episodic: Specific events
Semantic: Fax and general info (Birmingham is a shithole)
Implicit: Unconscious memories
Procedural: Knowing a procedure and how to perform a task without conscious effort
Long Term Potentiation: The more you apply a memory, the stronger it’ll be
Memory Model
Sensory Memory: Brief sensory input (a few secs)
Iconic: Visual info
Echoic: Sound info
Long term: Stores info; Unlimited capacity
Short-term: Temporary; Limited (5-9 units)
Encoding: Converting sensory shyt for storage
Working Memory Model (Alan Baddeley)
Central Executive: Manages attention and coordinates cognitive activities.
Phonological Loop: Processes auditory information.
Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad: Handles visual and spatial data.
Encoding
Levels of Processing (Shallowest to Deepest):
Structural Encoding: Focuses on physical features.
Phonemic Encoding: Processes how information sounds.
Semantic Encoding: Understands the meaning and connects it to known concepts.
Hierarchies: Structuring information from general to specific.
Serial Position Effect: Likely to remember items at the beginning and end of a list.
Storage
Maintenance Rehearsal: Repeating information to keep it accessible.
Elaborative Rehearsal: Linking new information to existing knowledge to encode.
Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory (HSAM): Ability to recall many personal events with accuracy.
Retrieval
Encoding Specificity Principle: Retrieval is effective when conditions match encoding.
Context-Dependent Memory: Recall improved in the same environment.
Mood-Congruent Memory
State-Dependent Memory
Testing Effect: Testing improves retention.
Metacognition: knowing your own thinking
Forgetting
Interference Theory: Memories disrupted by other memories.
Proactive Interference: Older memories interfere with new ones.
Retroactive Interference: New memories disrupt old ones.
Source Amnesia: Remembering information but not its source.
Anterograde Amnesia: Inability to form new memories
Retrograde Amnesia: Loss of old memories.
Memory Distortion
Constructive Memories: Building memories based on perceptions, thoughts, and experiences.
Memory Consolidation: Short-term memories become stable long-term memories.
Imagination Inflation: Imagining an event increases belief it happened.
Intelligence and Achievement
Spearman's General Intelligence (G Factor): Single factor determines intelligence
Sternberg's Triarchic Theory: Good at one thing = good at most things
Analytical intelligence: problem-solving and logical reasoning
Creative intelligence: deal with new and unusual situations by using past experiences and current skills
Practical intelligence: logical/practical applications
IQ (Intelligence Quotient)
Let IQ = Mental Age/Chronological Age * 100
Qualities of Intelligence test
Validity: Does the test measure what its supposed to?
Construct validity: ensures the test truly measures the concept of intelligence
Predictive validity: Predicts future performance or outcomes
Flynn Effect: Rising average IQ scores over time.
Achievement and Aptitude Test
Achievement Test: Measures what has been learned.
Aptitude Test: Evaluates potential to learn.
Unit 3: Development & Learning
Developmental Psychology
Longitudinal Research: Observes same group of ppl for a long time (Dropouts over time issue)
Cross-sectional Research: Different age groups of people all at one time
Issue: Cohort Effect - Characteristics could depend on different generations/times
Stages of Physical Development
Prenatal Development: Conception-Birth (Single egg cell divides to make baby)
Teratogens: Harmful substances that can cause issues (drugs, etc.)
Infancy & Childhood:
Fine motor coordination & Gross-motor coordination (walking/crawling)
Infant reflexes:
Rooting: Baby turns head to direction of cheek touch (locating food)
Sucking: Baby sucks when roof of mouth is touched (feed)
Imprinting: Animal forms connection w/ first animal
Puberty:
Menarche: First menstruation
Spermarche: First ejaculation
Piaget’s stages of development
Sensorimotor: 0-2; Sensory and motor skills (Object permanence; Object exists even when not visible)
Preoperational: 2-7; Mental symbols and pretend play; Not logical still
These children dont have the concept of:
Conservation: Shape of glass diff = volume
Reversibility: Understand objects can be changed then brought back (ex: play doh)
Animism: Inanimate objects are conscious
Egocentricism: Only view from own POV
Concrete Operational: 7-11; Kids able to understand logic and previous concepts
Formal Operational: Child-Adulthood; Think abstract
Scaffolding: Vygotsy; Teacher supports kid to grow
Crystallized intelligence: Acquired through experience/knowledge (stays same through aging)
Fluid intelligence: Abstract thinking/quick processing (declines as aging)
Language:
Phoneme: Smallest unit of sound
Morpheme: Smallest meaningful units
Overgeneralization: Grammar rules overgeneralized (runned)
Parenting Styles:
Authoritarian: Very strict and expect obedience
Authoritative: Expect obedience but supports kid
Permissive: Lets kid do whatever
Psychosocial Development (Erik Erikson)
Progression of emotional growth as you age
1) Trust v Mistrust (Baby trust world to get resources?)
2) Autonomy v Shame & Doubt (Autonomy (potty) or doubts abilities?)
3) Initiative v Guilt (Initiate “why?” or scolded for asking)
4) Industry v Inferiority (Formal system (school) feel inferior?)
5) Identity v Role confusion (Who am i?)
6) Intimacy v Isolation (Relationships or isolation?)
7) Generativity vs Stagnation (Unproductive or going as planned)
8) Integrity v Despair (Regret shyt?)
James Marcia’s Identity Statuses
Identity Achievement: Explored options, achieve commitment to one
Identity Diffusion: Don’t know or don’t care
Identity Foreclosure: Commit without exploring options
Identity Moratorium: Still thinking
Learning
Classical Conditioning: Pair stimulus with another
Neutral Stimulus: does nothing alone (rat)
Unconditioned stimulus: Triggers response naturally (Loud noise)
Unconditioned response: Natural response (Albert Cry)
Conditioned stimulus: An NS that triggers a conditioned response after being paired with US (Rat)
Conditioned response: Learned response to CS originally triggered by US (Albert Cry)
Higher order conditioning/Secondary conditioning: New NS is paired with an old CS (flash light with rat, albert cry cuz light)
Habituation: Getting used to a neutral stimulus that does nothing
Operant Conditioning: Pair behaviors w/ + or - consequence
Positive/Negative Punishments and Reinforcements
Primary Reinforcer: Needs (Water, Food)
Secondary Reinforcer: Ex: Money, less important/vital
Shaping: Rewarding step by step (ex: teaching a dawg how to roll)
Instinctive Drift: Individual slowly reverts to innate/instinct behaviors
Reinforcement schedules: Fixed/Variable Ratio (# responses) & Fixed/Variable Interval (time)
Sociocognitive Factors in Learning
Latent Learning: Learning that happens but isn’t immediately shown
Unit 4: Social Psychology & Personality
Social Psychology
Attribution Theory: Process of explaining why ppl do things
Dispositional Attributions: Explains behavior by internal factors (character traits)
Situational Attributions: Explains behavior by external factors (dog ate hw)
Explanatory Style: Optimistic (I can study harder) Pessimist (Nope)
Locust of Control: (Internal or External)
Attribution Bias: Tendency to attribute causes of behavior to character/internal
Fundamental Attribution Error: Blame internal factors of others
Actor-Observer Bias: Own actions are external but others are internal
Self-Serving Bias: Personal success internal but failures are external
Mere-exposure effect: More exposed to thing = More positively viewed
Self-fulfilling prophecy: Your expectation of someone influences their actions which only reinforce your expectations
Relative Deprivation: Dissatisfied cuz u compare w other ppl
Prejudice: Bad belief Discrimination: Actually taking action abt neg. belief
Implicit Bias: Unconscious stereotyping towards a group/race
Cognitive Dissonance: Beliefs contradict; Either change mindset or behavior
Persuasion
Elaborative Likelihood Model: Persuasion theory that explains persuasion through:
Central Route: Method that involves logical arguments and evidence
Peripheral Route: Method that involves attractiveness/visual cues
Foot in the door: First small request for a larger later
Door in the face: First huge request for a more reasonable request
Solomon Asch’s conformity experiment: Which line is longer?
Stanley Milgram’s obedience: Shocking ppl w/ a researcher next to them
Individualism: Culture w/ independence and self goals
Collectivism: Culture with group harmony and needs of group
Group polarization: Talking w a similar opinion group will lead to stronger view
Groupthink: Desire for harmony leads to bad ideas
Social loafing: Doing jack shit on a group project
Deindividuation: Loss of self accountability in group settings
Prosocial Behavior: Good voluntary actions without a reward
Altruism: Selfless concern without personal gain
Social Debt: Helping someone out cuz u “owe them one”
Social Reciprocity Norm: Expectation of ppl “paying u back” when u do them a favor
Personality
Sigma Freud:
Conscious: Conscious shyts and perceptions
Preconscious: Not actively in mind like memories and info
Unconscious: Outside of conscious awareness like unresolved conflicts
Ego defense mechanisms: (that i don’t know already)
Displacement: redirecting shyt (like throwing beer bottles at your child)
Regression: Going back to childish behaviors (tantrums)
Sublimation: Channeling emotions to a productive behavior (like gym)
Projective test: “What do you see” to uncover unconscious thoughts
Social cognitive theory: How thoughts behaviors and environment shape us (Albert Bandura)
Reciprocal Determinism: Personality is shaped by behavior, thoughts, environment
Self-Efficacy: Belief in ability to succeed which affects motivation
Trait theory: Trait is a consistent pattern of thinking/feeling
OCEAN: Openness, Conscientiousness (Responsible/Dependability), Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism (Stress under pressure)
Self Report Inventory: Type of psych assessment for trait evaluation
Factor Analysis: Ensures a test measures the right traits by looking at patterns of responses
Motivation:
Drive reduction: Biological needs motivate (Needing to piss or eat)
Arousal theory: Motivation to seek stimulation when bored & reduce stimulation when too much
Yerkes-Dodson Law: there is an optimal level of stress for motivation
Lewin’s Motivational Conflict theory:
Approach-Approach: Choose between two desireable options
Avoidance-Avoidance: Choose between two bad options
Approach-Avoidance: Drawn & Repelled to one option cuz theres both + and - effects
Unit 5: Mental & Physical Health
Health Psychology
Stress
General Adaptation Syndrome: Model of stress response (Hans Selye)
Alarm: Pupils dilate, fight/flight, adrenaline kicks in
Resistance: Body tries to keep up w/ stress, can’t stay this way forever
Exhaustion: Body gives up
Stress Related Illnesses:
Weakened immune system (T & B Lymphocytes, NK Cells)
Risk of heart disease
Anxiety
Oxytocin: “Love hormone” helps reduce stress
Coping:
Problem Focused/ Emotion Focused
Subjective Well Being: Self evaluation of self happiness/satisfaction
Positive Subjective Experience: Personal internal feelings of joy/happiness (How you see urself)
Positive Objective Experience: External life circumstances: Relationships, good health (How u are)
Psychological Disorders
3 D’s (Distress, Dysfunction, Disorder)
Biopsychosocial Model: Looking at behavior/processing through the interaction of biological, psychological, and social-cultural factors
Anxiety Disorder: ANS is constantly aroused (Imbalance of brain chemicals)
Mood Disorder: Imbalance/low level of brain chemicals (dopamine, serotonin)
Dissociative Disorder:
Fugue: Forgetting identity
DID/MPD: Multiple personalities
Schizophrenic Disorder: Too much dopamine receptors
Personality Disorders:
Weird: Type A (Eccentric/Odd)
Wild: Type B (Dramatic/Impulsive)
Worried: Type C (Anxious/Fearful)
Histrionic Personality Disorder (needs to be the center of attention; impulsive actions)