Skin - "The jack of all trades" (bio chem ch 13)
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN
Protection
Sensation
Temperature regulation
Storage of food
Grip
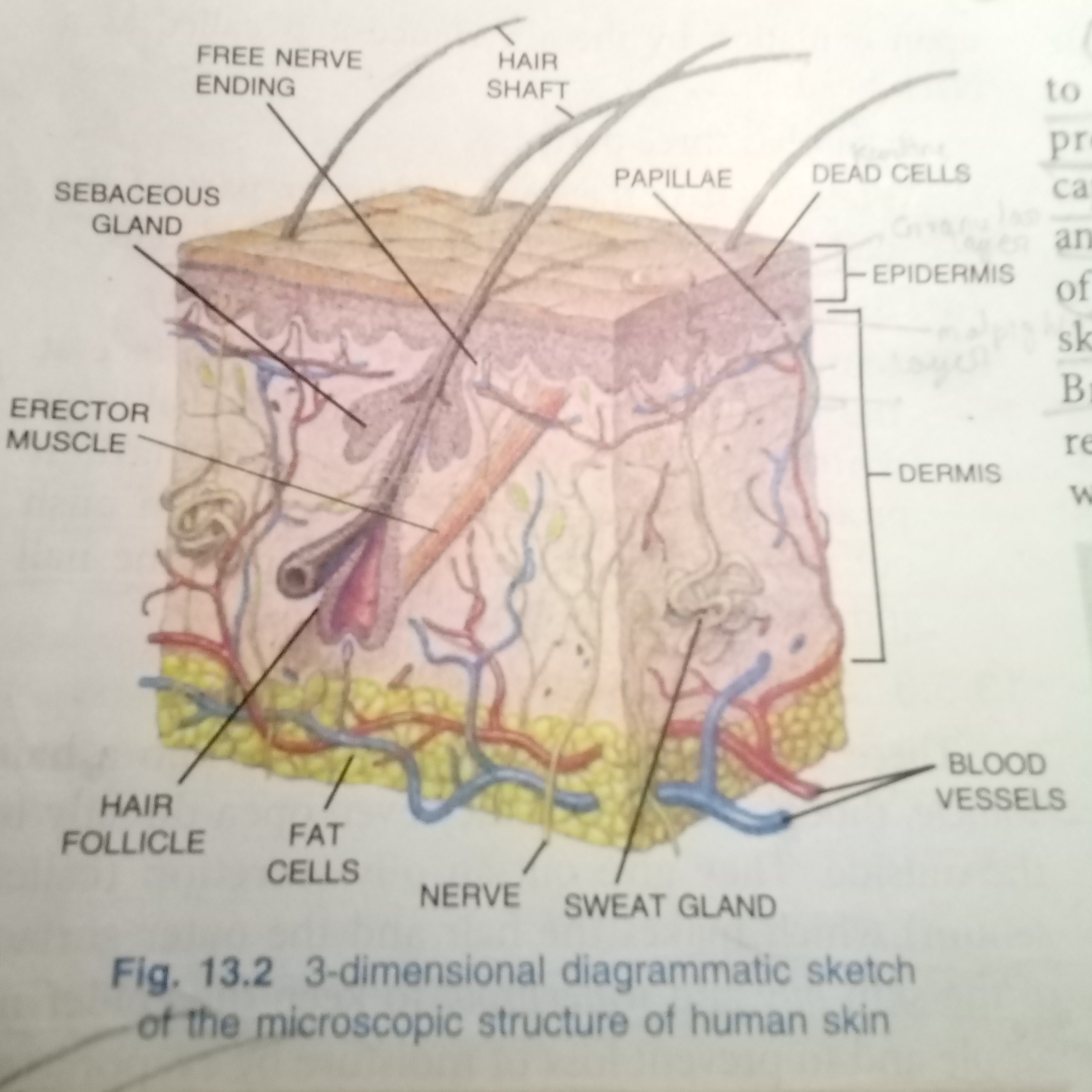
Epidermis.
The epidermis is the outer thinner part of the skin. It is formed of stratified epithelium piled up layer after layer.
The cornified layer (stratum corneum) is the outermost layer consisting of several piled up layer of flattened dead cells. These are made of a fibrous structural proteins called keratin also found in nails, hairs, horns, hooves and silk.
The granular layer is a very thin middle layer consisting of two or three sub layers of flattened cells.
The malpighian layer (stratum malpighi, also called germinative layer) is the innermost region of the epidermis
Colouration of the skin (e.g. the complexion of the face) is due to a pigment melanin contained in the cells of the malpighian layer. But revert to original condition when the exposure is cut down.

 The skin pigment acts like an umbrella to protect inner part of the body from the harmful effects of the ultraviolet rays of sunlight, which can cause skin cancer.
The skin pigment acts like an umbrella to protect inner part of the body from the harmful effects of the ultraviolet rays of sunlight, which can cause skin cancer.
Two abnormal conditions of skin pigmentation :
Leukoderma also called “vitiligo” : skin pigmentation (melanin) is lost from smaller or larger patches at different regions of the body; exact cause of this disease is not yet known.
Albinism : Complete loss of pigmentation of the skin all over the body including hair, eyebrows, eyelashes and even the iris. The skin of affected individuals appears pinkish because of the underlying blood capillaries. Albinism is a recessive trait caused due to inheritance; an albino couple would produce all albino children.
Dermis.
The dermis is the inner thick layer of connective tissue made of elastic fibers. It is rough and flexible.
Define papillae
The outer region of the dermis which lies next to the epidermis is raised into numerous small processes called papillae. Which contain blood capillaries and nerve endings.
Hair shaft is the part which projects from the skin and may extend slightly below the surface of the epidermis.
Hair bulb which contains a projection of the dermis called hair papilla, with capillary blood supply.
Hair follicle is a structure enclosing the hair root. It is composed of an epithelial and a connective tissue sheath.
There are hairs along the edges of the eyelids (eyelashes) to help prevent the entry of foreign particles. Similarly, there are hairs in the nose, again to prevent dust particles from entering nasal passages. Facial hairs in the human males, i.e. moustaches and beard, help in distinguishing the male sex (sexual dimorphism)
Three parts of nail :
Plate
Bed (root)
Matrix
Meibomian glands : these are modified sebaceous glands which open on the margins of the eyelids. Their secretion is oily and serves to lubricate the margins of the lids and to prevent the overflow of tears.
Ceruminous glands : these are modified sebaceous glands found in the auditory canal and secrete wax like substance called cerumen or earwax which lubricates and protects the delicate eardrum from dust particles and germs.