Respiratory System- is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe.
helps your body absorb oxygen from the air so your organs can work.
It also cleans waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your blood.
Common problems include allergies, diseases or infections.
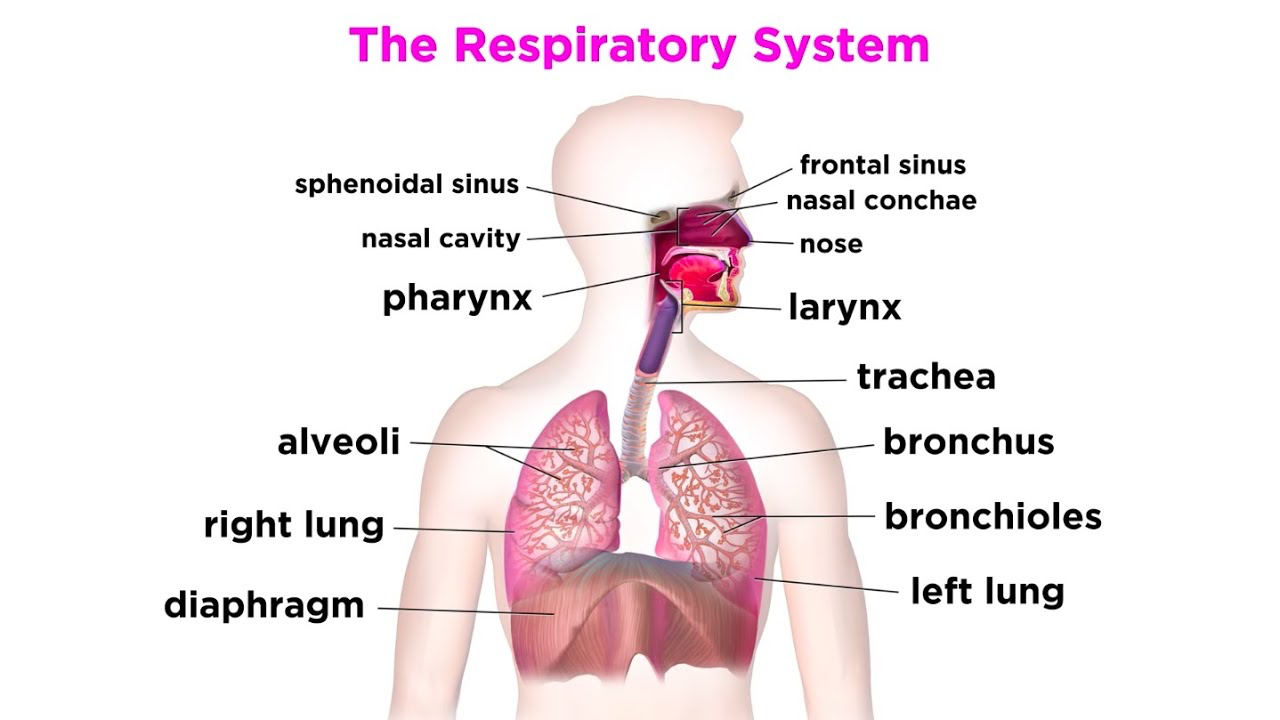
PARTS of RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Mouth and nose: Openings that pull air from outside your body into your respiratory system.
Sinuses: Hollow areas between the bones in your head that help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air you inhale.
Pharynx (throat): Tube that delivers air from your mouth and nose to the trachea (windpipe).
Trachea: Passage connecting your throat and lungs.
Bronchial tubes: Tubes at the bottom of your windpipe that connect into each lung.
Lungs: Two organs that remove oxygen from the air and pass it into your blood.
Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and push it out.
Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and heart.
Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
Bronchioles: Small branches of the bronchial tubes that lead to the alveoli.
Lung lobes: Sections of the lungs — three lobes in the right lung and two in the left lung.
Pleura: Thin sacs that surround each lung lobe and separate your lungs from the chest wall.
Cilia: Tiny hairs that move in a wave-like motion to filter dust and other irritants out of your airways.
Epiglottis: Tissue flap at the entrance to the trachea that closes when you swallow to keep food and liquids out of your airway.
Larynx (voice box): Hollow organ that allows you to talk and make sounds when air moves in and out.