⚠️chem midterm study guide
[[1- states of matter[[
- solid- fixed shape and volume, particles touching, not moving
- ^^liquid- fixed volume, unfixed shape, particles touching and moving a little^^
- %%gas- no fixed volume or shape, particles far apart and moving a lot%%
- @@plasma- no fixed volume or shape, particles far apart and moving a lot@@
| shape | volume | particles | particles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| {{solid{{ | {{fixed shape{{ | {{fixed volume{{ | {{touching{{ | {{not moving{{ |
| <<liquid<< | <<unfixed shape<< | <<fixed volume<< | <<touching a little<< | <<moving a little<< |
| }}gas}} | }}unfixed shape}} | }}unfixed volume}} | }}far apart}} | }}moving a lot}} |
| ]]plasma]] | ]]unfixed shape]] | ]]unfixed volume]] | ]]far apart]] | ]]moving a lot]] |
]]1- properties of and changes in matter]]
==physical property==
anything you can see without changing the substance
ex. transparency, boiling point, density, elasticity, malleability, brittleness, melting point
==chemical property==
- you can only see by changing the substance
- ex. flammability, ability to rust, reactivity with vinegar
@@physical change@@
- when the identity of the substance doesn’t change (reversible)
- ex. shattering, melting, separating (sand from gravel), dissolving, mixing, evaporating
@@chemical change@@
- when the identity of the substance changes (irreversible), during a chemical reaction
- ex. rusting, bleaching, cooking, burning, exploding
extensive property
- depends on how much matter there is
- ex. mass, weight, volume
%%intensive property%%
- doesn’t matter how much matter there is
- ex. color, combustibility, density, melting point, malleability
^^chemical reaction^^
5 signs:
- formation of a gas
- color change/ emission of light
- odor change
- temp change
- formation of a precipitate
parts of a reaction
- reactant, yield arrow, product. the compound on top of the yield arrow is the catalyst- it speeds up the reaction time.
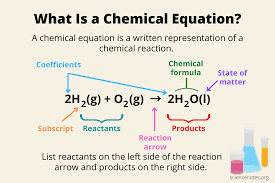
Law of conservation of mass: in a closed system, mass cannot be created or destroyed
{{1- elements, compounds, and mixtures{{
Matter is classified into ==Pure Substances== and ^^Mixtures.^^
==Pure Substance==- only one type of molecule, ex. water. can be @@elements@@ or compounds.
- @@element@@- an atom with specific characteristics, ex. hydrogen, iron, copper
- can be metals or nonmetals, can’t be broken down further
- compound- a molecule made of different atoms, ex. H2O, Na2
- can be broken down into molecules using chemical charges
- can be molecular, ionic, or intermetallic compounds
! ! pure substances can’t be broken down by physical means like distillation, filtration, chromatography, or evaporation ! !
^^Mixture^^- combo of 2 substances, not chemically bonded. can be %%solutions%% or heterogeneous mixtures. Can be separated through physical changes.
- %%solution (aka homogenous)%%- a group of molecules that are evenly distributed, ex. gasoline, air, and soda
heterogeneous mixture- a solution that is unevenly distributed, ex. cereal/ milk, raisin bread
~
~
}}2- precision and accuracy}}

- precision- the extent to which a series of measurements of the same quantity made in the same way agree with each other, not necessarily accurate.
- accuracy- the extent to which a measurement approaches the true value of a quantity
to find percent error: [(experimental - accepted) / accepted] * 100
![to find percent error: [(experimental - accepted) / accepted] * 100](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a83ee3a2fffd4826ac8eea206b9f89de.jpeg)
🔎 look at page #9 in binder
<<2- significant figures<<
any digit in a measurement that is known with certainty, plus one final digit that’s slightly estimated
- rule 1- all nonzero digits are significant, ex. 254 has 3 sigfigs
- rule 2- zeros in between nonzeros are significant, ex. 2001 has 4 sigfigs
- rule 3- trailing zeros are only significant with a decimal after, ex. 2000.0 has 3 sigfigs
- rule 4- zeros in front of a nonzero don’t count, regardless of decimal, ex. 00.0004 has 1 sigfig
rules of rounding
- round up if trailing # is above 5………….. so 4566.89 rounded to 4 sigfigs is 4567
- leave it alone if trailing # is below 5…… so 4564.45 rounded to 4 sigfigs is 4564
for math operations (x / + -)
- always round according to the # with the least amount of decimal places (least accurate)
(10.3) x (0.01345) = 0.138535 → 0.139
🔎 **look at binder page #6,7,8,10 for more examples
\n [[2- scientific notation[[
- used when numbers are super big or super small, like atoms or planets
- numbers are written as a product (multiply) of 2 numbers, a **coefficient
** and 10 raised to a power.4500 →**4.5
- \
- \
** x 10³, coefficient is4.5coefficient must be from 1 - 9.**can’t be 10!!***if the # is greater than 10, exponent is positive and is = to the amount of spaces the decimal is moved left to write the # in scientific notation4.500 → 4.5 x 10³⤴⤴⤴ (move 3 times right, so power of 3)if the # is less than 10, the exponent wll be negative and is = to the amount of spaces the decimal is moved right.00012 → 1.2 x 10⁻⁴12 → 1.2 x 10¹.000,0007 → 7 x 10⁻⁷490 → 4.9 x 10²1000 →1 x 10³.987 → 9.87 x 10-¹1000 000 → 1 x 10⁶0.0375 → 3.75 x 10⁻²0.01 → 1 x 10⁻²596 → 5.96 x 10².001257 → 1.26 x 10⁻³0.000595 → 5.95 x 10⁻⁴]]2- density]]
==mass==**:
- ** theamount of matter an object contains. Doesn’t change unless you add/remove matterfind with a balance, use ==grams==
volume**:
- ** theamount of space an object occupiesfind with liquid or a ruler, use mL for liquids or cm³ for solids or L for gases
@@density@@**:
- \
- \
** thecompactness of the molecules or particles of a substancemore compact molecules = greater densitythe relationship between an object’s mass and volume==mass== **/ volume = @@density@@
- \
- \
- \
- **remember:mL - volumeg - mass
g/mL org/cm³ org/L- density🔎 look at page # 17, 18, 19~~~~{{3- history of the atom{{
| scientist/s | experiment/model | year | description/ discovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Democritus/Dalton- the atom | n/a |  | **billiards ball- |
| ** small, hard sphereJJ Thompson- electrons | cathode ray tube | 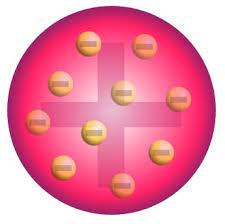 | **plum pudding- |
| ** electron “plums“ in a positive “pudding“Ernest Rutherford- atom mostly empty space, nucleus, protons on nucleus | 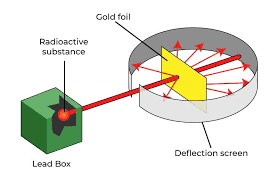 | 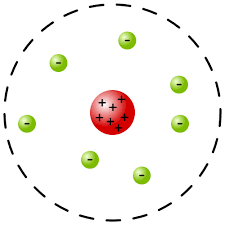 | **nuclear model- |
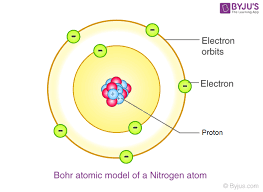 | ** nucleus with electron shellNiehls Bohr- atomic energy levelsBohr’s atomic model**planetary model- | ||
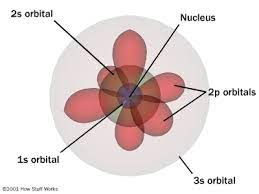 | ** electron shell is made of layers/orbitsHeisenberg & Schroedinger- electron cloud and orbitalsHeisenberg uncertainty principle**quantum model- | ||
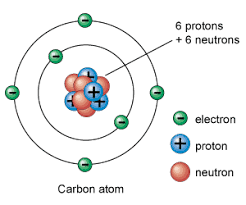 | ** (electron cloud)- there’s certain waves in the cloud?? what??James Chadwick- neutronsquantum model w/ neutrons**modern model- |
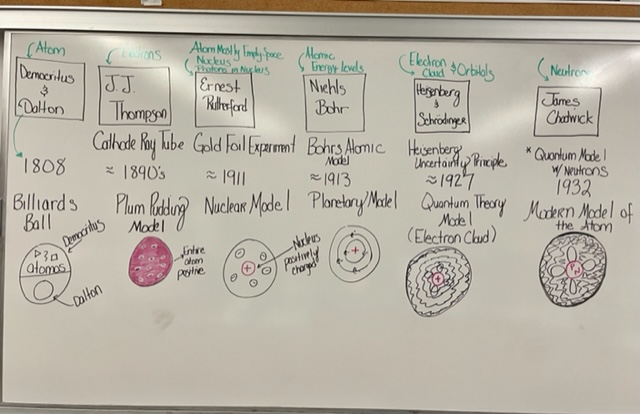
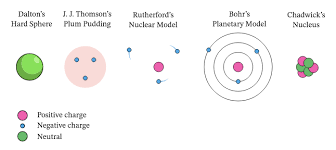
** discovered neutrons, current model used today🔎 look at page # 29}}3- atomic structure}}
==atom==
- the smallest particle of an element that still has the chemical properties of the element
@@nucleus@@
- very small thing @@in the center@@ of the atom
- made of at least one proton (p+) and usually at least 1 neutron (n*)
- surrounding the nucleus is a cloud of electrons (e-)
protons, neutrons, and electrons are called **Subatomic Particles
protons (p+)**
- located in nucleus, positive charge, big and heavy
%%neutrons (n)*%%
- located in nucleus, %%no%% charge, big and heavy
^^electrons (e-)^^
- outside the nucleus, ^^negative^^ charge, tiny and light
<<3- isotopes and ions<<
==isotopes==
- 2 atoms with different # of ==neutrons==
- \
# protons never changes - \
# neutrons can change - have the same atomic #, different mass #s
@@ions@@
- an atom with @@a charge@@, # of @@electrons@@ change
- if atom loses electrons, atom is + and (vice versa)
- protons, neutrons, atomic # and atomic mass stay the same
hyphen notation
- (element name) dash (mass number)
- ex. uranium-235
%%isotope notation (nuclear symbol)%%
- top - mass #……….. bottom - atomic #
- ex. %%U²³⁵₉₂%% (pretend like that’s lined up)
nuclide- general term for a specific isotope of an element (probably don’t need to know this)
[[3- atomic #, atomic mass, mass number[[
**atomic #
- \
** = protonsin a neutral atom, protons = electrons**mass #
** = protons + neutrons**atomic mass
** = the decimal in the element box**neutrons
** = mass # - atomic #]]electron configuration]]
periodic table
metals, nonmetals, and metalloids
periodic trends
valence electrons
cations and anions
nomenclature (ionic and molecular compounds; acids)
- **states of matter
- ****properties of and changes in matter
- ****elements, compounds, and mixtures
-
5.
-
7.
- precision and accuracysignificant figuresscientific notationdensityhistory of the atom
- ****atomic structure
-
11.
- isotopes and ionsatomic #, atomic mass, mass numberelectron configurationperiodic table
- ****metals, nonmetals, and metalloids
- ****periodic trends
-
17.
18.