Variation and Selection (3.22-3.26)
Variation: differences between individuals within the same species
Variation is defined as differences between individuals within the same species
Genetic variation – The differences in genetics among individuals within the same species (mainly due to sexual reproduction & mutation)
Phenotypic variation – The variability of phenotypes within a population (influenced by both the genetic & environmental factors)
Continuous Variation - When there are very many small degrees of difference for a particular characteristic between individuals and they are arranged in order and can usually be measured on a scale (Quantitative)
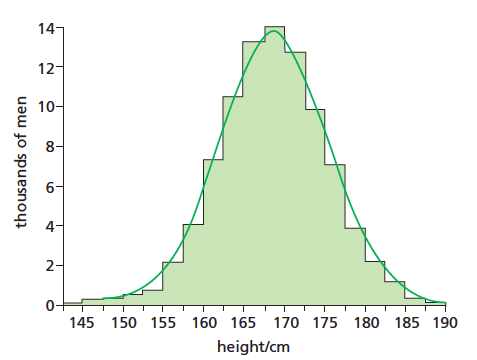
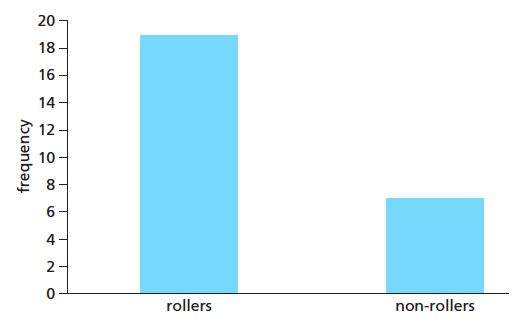
Discontinuous Variation - When there are distinct differences for a characteristic (Qualitative)
Mutations
Mutations: random genetic changes
→They could cause the development of new alleles and so new phenotypes
Mutations happen spontaneously and continuously
Sickle cell anemia: caused by the mutation in a gene that codes for hemoglobin
The abnormal base sequence of the hemoglobin gene causes sickle-shaped red blood cells
Sickle celled RBCs are less efficient at carrying oxygen, and more likely to become stuck in capillaries preventing blood flow
Individuals with two A alleles (HbAHbA) have normal haemoglobin, and therefore normal RBCs
Those with two S alleles (HbSHbS) develop sickle cell anaemia
Those who are heterozygous for sickle cell (HbAHbS) produce both normal and abnormal haemoglobin (codominance)
Heterozygous individuals are said to be ‘carriers’ of the sickle cell gene and are said to have ‘sickle cell trait’
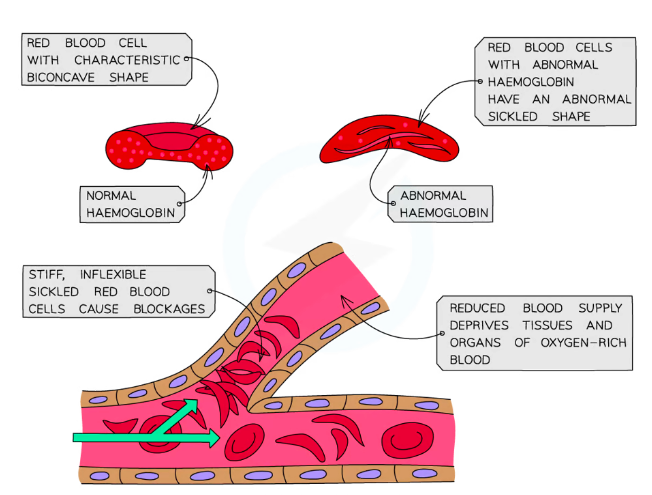
→The normal Hb allele is dominant to the sickle cell Hb allele
Sickle-cell anemia provides protection against malaria, because the parasites cannot penetrate sickle-celled RBCs.
- A person with sickle cell anemia will be fully protected against malaria, but likely to die from sickle-cell disease
- A person that has no sickle cell anemia has no protection from malaria, and is therefore likely to contract the disease
- A person that is a sickle-cell carrier has malarial protection, and will not die from sickle cell disease
Adaptation
Adaptive Features: Inherited functional features of an organism that increase its fitness
Fitness: Probability of an organism surviving and reproducing in the environment in which it is found
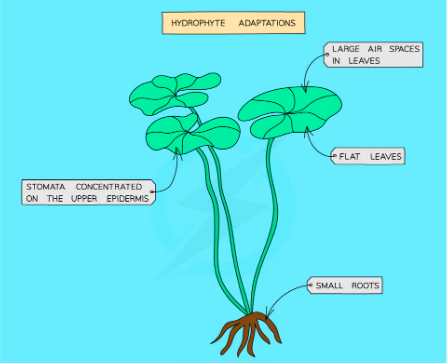
Hydrophytes: Plants adapted to live in extremely wet conditions
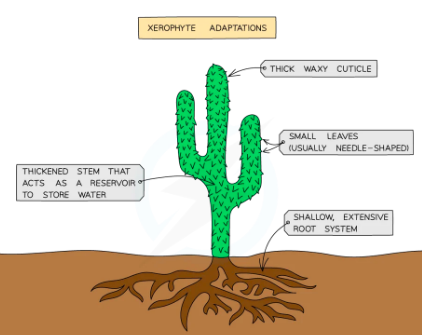
Xerophytes: Plant adapted to live in extremely dry conditions
Selection
Natural selection:
Natural Selection is the concept that for a given environment, organisms with the most beneficial features are ‘selected’ to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation
- Individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment have a higher chance of survival and more chances to reproduce
- Alleles resulting in these characteristics are passed to their offspring at a higher rate than those with characteristics less suited to survival
- There is variation within a population (could be due to mutation)
- Many offspring are produced
- Competition for resources among individuals within the population
- Struggle for survival
- The most ‘fit’ individuals that are more adapted to the environment will survive and reproduce
- Fitter individuals pass on their alleles to their offspring
Artificial Selection
Artificial selection: the intentional reproduction of animals and plants by humans that have desirable traits
Organisms can pass down favourable traits to their offspring to produce more organisms with desirable characteristics
Desirable characteristics in plants:
- disease resistance in food crops
- increased crop yield
- hardiness to weather conditions (e.g. drought tolerance)
- better tasting fruits
- large or unusual flowers
Desirable characteristics in animals:
- produce lots of milk or meat
- chickens that lay large eggs
- domestic dogs that have a gentle nature
- sheep with good quality wool
- horses with fine features and a very fast pace
Process
- decide which characteristics are important enough to select
- choose parents that show these characteristics
- choose the best offspring from parents to produce the next generation
- repeat the process continuously until a new breed will reliably show the characteristics