Chapter 3: Federalism
Dividing Power Between the National and State
Section 1: Boundaries of Power
1. Who has more control?
State governments cannot hold most of the power in an efficient government
The national government cannot hold most of the power in a non-tyrannical government
GOAL: reduce the ability of tyrants to hold power but maintain efficiency in governance
2. Conflict over Medical Marijuana
The Supreme Court often settles disputes between the national government and the states by defining the ambiguous implied powers of Congress
When the court rules it either:
EXPANDS national power and WEAKENS state power
WEAKENS state power and EXPANDS state power
Gonzales v. Raich (2012)
Problem: at the federal level Medical Marijuana is illegal but increasingly most states have legalized it
Section 2: Federalism and the Constitution
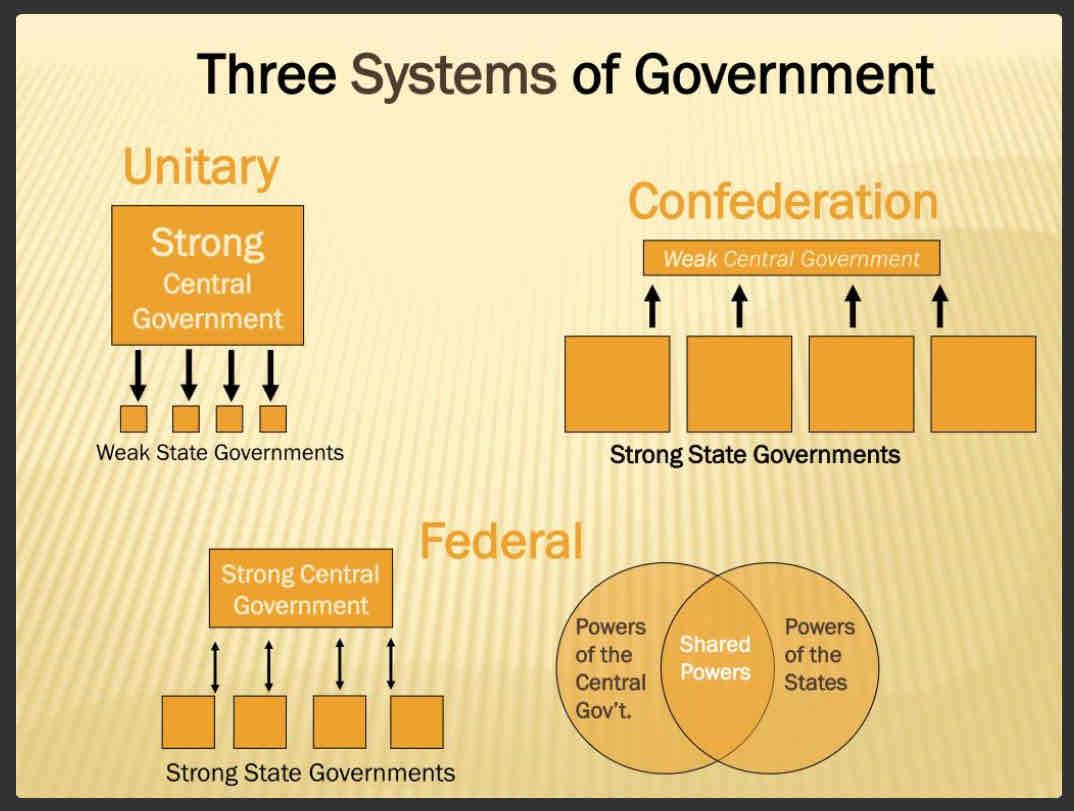
1. Types of Governance
Expressed/enumerated powers: powers explicitly given to a certain authority in the Constitution
Commerce Clause: grants Congress the power to “regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes”
Congress has repeatedly claimed this authority in cases that do not seem to be productive commerce
Necessary and Proper Clause: also called the elastic clause, a critical source of power for the national government
Congress can do extra things needed to execute the powers it explicitly has
Supremacy Clause: “This Constitution and the Laws of the United States shall be the supreme Law of the Land.“
The states must abide by the laws passed by Congress
Even if the state constitutional provisions conflict with them
The Constitution are much less specific about state powers
2. Division of Power With States
10th Amendment: anything not listed here, than it is the power of the state
Concurrent Powers: granted in the Constitution to both National and State Governments
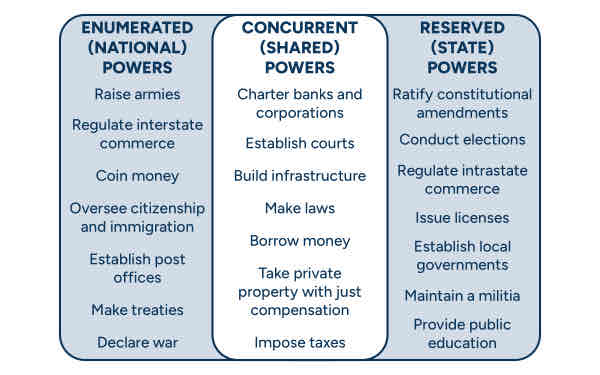
Full faith and credit clause- requires states to recognize the public acts, records, and civil court proceedings from another state
Extradition- you cannot flee from a crime by simply going to a state with different laws
Privileges and Immunities- states cannot discriminate against out-of-state individuals
Section 3: The Future of Federalism
1. National Equality Amendments
Thirteenth: outlaws slavery
Fourteenth: person born in the United States are citizens
Fifteenth: gave African American males the right to vote
2. Federal Models
Dual Federalism: layer cake, states and national governments work independently of one another
Cooperative Federalism: swirled cake, states and national governments work together with powers shared/mixed more evenly
3. National Expansion
The Great Depression
States could not deal with the crisis
Turned to national policy for help
Accepting finically aid had strings
Permanently altered the relationship between the states and national government
Gave the national gov more power, created a legacy of gov involved programs
Section 4: The Cost of Federalism
1. Fiscal Aid
Grants in aid: tool used to achieve policy objectives within states
Categorical: provided to states with specific provision on their use
Limited in how states can spend funding
Have conditions on their use
Fiscal Federalism: the whole process of using grants in aid to influence state policy
Unfunded Mandate: the national government but requires states to pay for programs without providing funds
American Disabilities Act (1990), government provided guidelines but not money
Block Grant: gives states more authority in how they use their money “blocking” money without assigning specific mandates
2. The Drinking Age
1920: banned alcohol in the 19th amendment
18 year olds were given the right to vote, some states also gave 18 year olds the right to vote
Fatalities were very high from drunk driving, often in states with teens drinking
Especially dangerous for teens driving to states that allowed alcohol
Federal government helped with high way funds
Withholding funds in the drinking age was the condition upon which the funds were dispersed
Does an older drinking age actually save lives?
Probably, maybe, still debated
2. Federalism and Public Education
Starting in the 1960’s, the national government provided grant money to states to create more opportunity for low-income areas
No Child Left Behind (NCLB) provided states with grant money if they agreed to give standardized assessment tests to students at certain grade levels
Led to “teaching to the test” and controversy about how to obtain funding
Section 5: The Supreme Court and Modern Federalism
1. US v. Lopez
Alfonso Lopez brought a gun to school and was charged with violating the Gun-Free School Zones Act
Question: Is the Gun-Free Zones Act unconstitutional because it exceeds the power of Congress under the Commerce Clause?
Majority: 5-4
Involves the 10th Amendment: reserving power for states
2. Same-Sex Marriage
Edith Windsor and Thea Spyer’s marriage was not recognized by federal law
She had to pay $350,000 of federal estate taxes that she would have been exempt
Is DOMO (Defense of Marriage Act) which defined marriage as between a man and a woman, constitutional?
5-4 decision for Windsor
James Obergefell and John Arthur were married in Maryland, but in their home state Ohio, their marriage was not legal
James could not be listed as the surviving spouse of Arthur’s death certificate
Can states deny same-sex couples the same legal rights as opposite-sex couples?
The right to marry is a fundamental right inherent to the liberty of a person
2. Marijuana: Gonzales v. Raich
Background: Angel Raich and Diane Monson grew medical marijuana in their homes under the supervision of a doctor under a California law
6-3 against States rights and in support of the federal government controlling the market for marijuana