5.1 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
Common symptoms
Power-on-self-test (POST) beeps
POST is designed to test major system components before booting the operating system. It checks:
CPU
CMOS
Video
Memory
Storage
+ more components
If any component isn’t working correctly, this is indicated with beeps and codes displayed onscreen.
Check the manufacturer documentation for the different beeps/error messages, and what they are associated with.
Blank screen on boot
Listen for POST beeps
Typically indicates a bad graphics card, bad RAM, or a bad CPU
Boot to an incorrect device
Some external storage devices can attempt to boot before the primary internal storage device - check the device for the external storage media and remove it.
Proprietary crash screens/Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
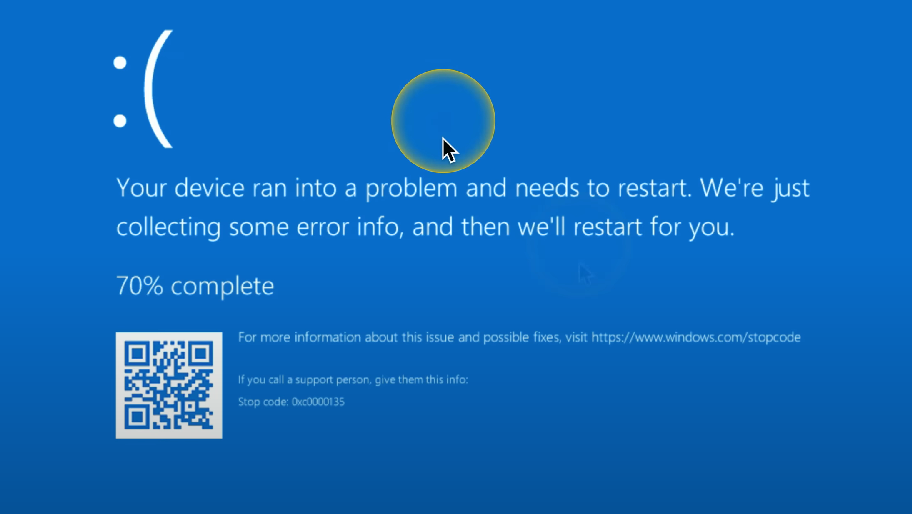
Occurs when a serious problem causes Windows to shut down or restart unexpectedly to prevent data loss.
Contains valuable information that is written to Event Viewer.
Contact the computer/hardware manufacturer to run debugs/narrow problems
Startup and shutdown BSOD:
Bad hardware
Bad drivers
Bad application installation
Solution: Use a Last Known Good Configuration, run a System Restore, a Rollback Driver, or run Windows in Safe Mode
macOS X Spinning Wait Cursor/Spinning Ball of Death
The spinning wait cursor indicates that a process needs to be completed before the user can resume using the OS.
Possible reasons for a never-ending spin:
Application bug
Bad hardware
Slow paging to storage disk
Solution: Restart the computer - also check for details in system logs.
Black screen
Check if the monitor is connected - if the power and signal cables are both connected.
Check the input selection on the monitor - is the monitor configured to accept the input (i.e., if you’re plugging an HDMI cable, the monitor should be set to accept HDMI input).
For dim images - check the brightness controls on the monitor
Swap the faulty monitor for a monitor you know is good - this checks if the problem is specifically the monitor or concerns the computer.
No video immediately after Windows loads - use VGA mode (F8) to check if the issue concerns a driver or the monitor.
VGA mode: Generic video startup mode compatible with nearly all Windows machines/connected monitors.
Proprietary crash screens
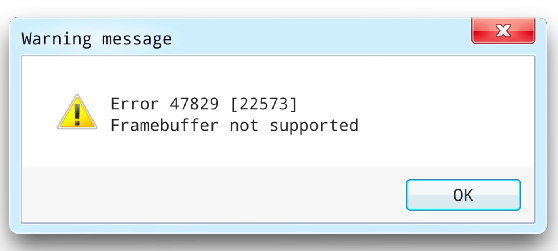
Every application has proprietary crash screens that display specific error messages or codes relevant to the software.
Some error messages provide more information than others.
Gather as many details about the error as possible (e.g., screenshots) and contact the application manufacturer for more information about crash screens.
No power
Typically due to:
No power from the outlet
No power from the device power supply/device cord
If fans are spinning, fans are functioning, but no power is reaching other components. Check:
Where your fan power is connected
A bad motherboard (lack of POST beeps/messages)
Power supply output for the system - check the power supply output voltage. Case fans typically have lower voltage requirements.
Sluggish performance
Typically due to:
High CPU usgae for some applications - check Task Manager
Out of date OS - update the OS with the latest patches and drivers
Lack of disk space - check for available space and clear/defrag if necessary
Defrag/defragmentation: The process of rearranging the data on a storage medium so that related data pieces are stored on a small number of contiguous blocks.
Check for power saving mode - this throttles the CPU
Scan for malware - malicious software can occupy system resources
Overheating
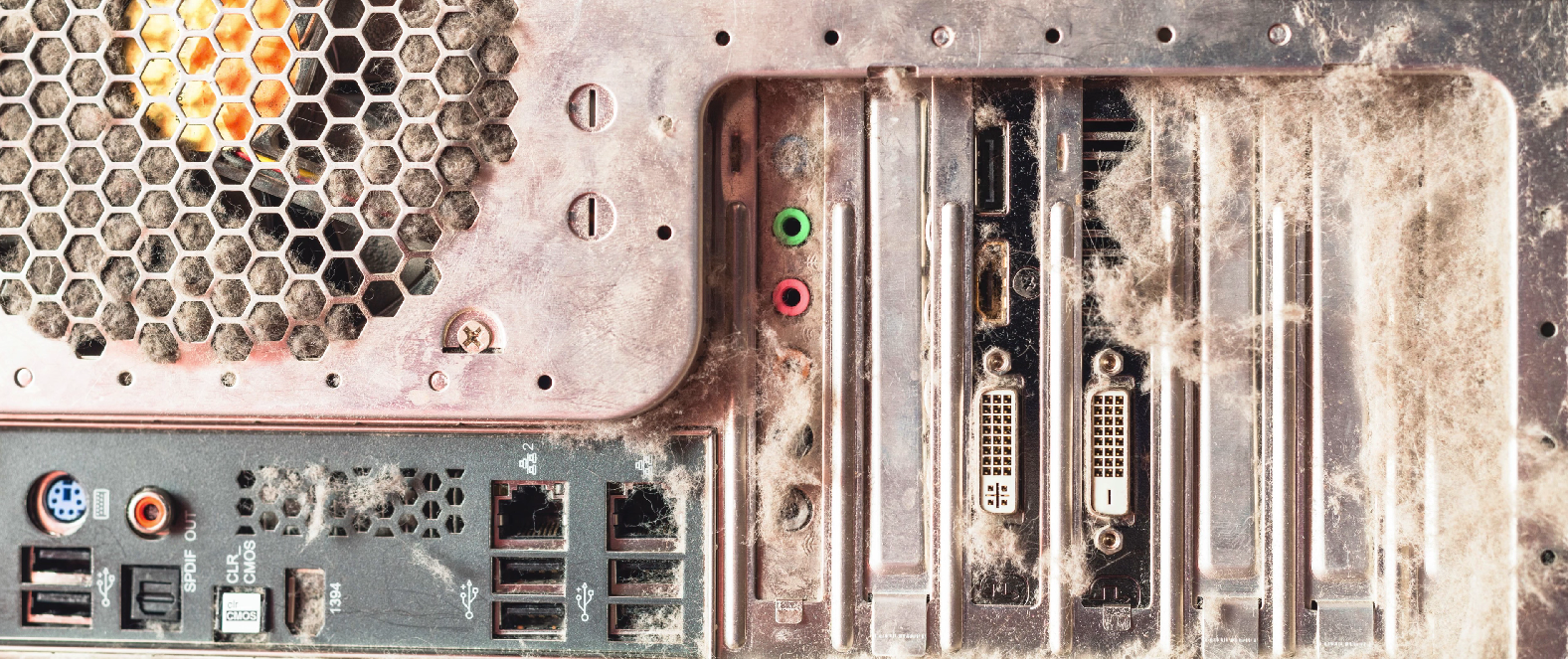
Check for dust on case fans or other cooling component
Burning smell
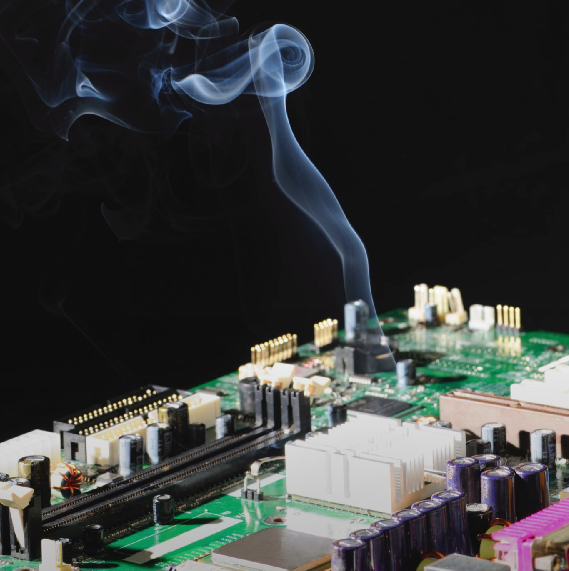

Disconnect the computer from any power source, located the burned components, and replace all the damaged components.
Random shutdown
Check for faulty hardware
Check Event Viewer for Mesages just before the computer shuts down
This may also be a heat-related issue:
Check for high CPU usage
Clear fans and check heat sinks
Check the BIOS for fan status and high temperatures
Check for failing hardware - has anything been disabled? Also check Device Manager
Slowly eliminate hardware components that are working to narrow down a faulty component
Application crashes
Screenshot any error messages
Check Windows Event Viewer for application logs
Check Windows Reliability Monitor
Delete and reinstall the application to ensure the correct app version has been installed
Contact application support
Unusual noise
Depends on the noise:
Rattling: Loose components - typically a heat sink
Scraping: Issues with a hard disk drive
Clicking: Issues with fan airflow
Pop: A blown capacitor
Capacitor swelling
Capacitors are found on the motherboard - when capacitor swelling occurs, the capacitor appears bulged, and is near exploding.

Inaccurate system date/time
Due to a faulty CMOS battery - the system may fail to retain the correct date and time settings.
This can be resovled by replacing the old CMOS battery. For older comptuers, this may reset the BIOS, but this is not a problem on newer systems.