Unit 10.2 Introduction to Abstract Data Types
Aims
Know what is meant by the term abstract data type.
Know what is meant by the term stack and be able to add and remove data from a stack.
Know what is meant by the term queue and be able to add and remove data from a queue.
Know what is meant by the term linked list and be able to add and remove data from a linked list.
Abstract Data Types (ADT) refers to: the collection of data organised in some way and the different operations that can be used to manipulate the data.
Stacks
Queues
Linked Lists
Stacks - LIFO (Last in, First Out)
Data held in array and a stack pointer is used to indicate position where data is added/removed. Operations that can be performed on stack:
Push - Used when adding data to stack
Pop - Used when you remove data from stack.
Example
Stack with 1D array: theStack with 8 positions, currently holds 3,4,5 in that order.
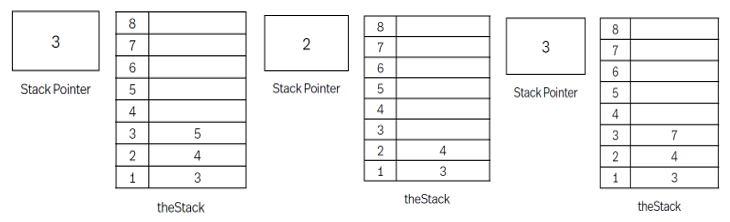
Pop - Goes to stack and locates position indicated by stack pointer - 3 (Og) and removes the item - 5. Stack pointer is reduced by 1 to look like image 2 (Pop)
Push - Goes to stack pointer - 2 (Pop) and inc by 1, then goes to stack and locates position from stack pointer - 3 and adds data 7 (given in e.g.) to look like image 3 (Push)
How Stacks work
Array sizes have to be declared so only a limited number of elements are available. If all are used and more info is added an error is returned (stack overflow), same as if it was empty and trying to delete info (stack underflow).
When an item is pushed onto the stack:
Check if stack pointer is = to max
If it = max it reports the stack is full.
If not, it inc’s stack pointer by 1
Then add’s new data to stack indicated by pointer.
When an item is popped from the stack:
Check if stack pointer = 0
If it =0 it reports the stack is empty
If not, it outputs data from stack in position of pointer
Then reduces stack pointer by 1
Stack Uses e.g.:
Storing instructions that can be used in undo mechanisms.
To reverse word/numbers e.g. ABC to CBA, 123 to 321
Recursion to store variables within each recursive call.
Keeping track of code lines when subroutines/interupts are used in a program.
Queues - FIFO (First in, First out)
Data held in array and two pointers manipulate the data
Head Pointer-States beginning of queue where data will be removed
Tail Pointer - States end of queue where data is added
Push (aka enqueue) - used when add data to queue
Pop (aka dequeue) used when data removed from queue.
Example
1-D array theQueue with 5 positions - holds A (1st), B, C (last), head pointer at 1 and tail at 3
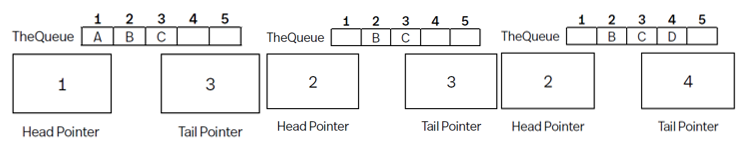
Pop - Go to queue and locate position indicated by head pointer (1), and remove the item. Head pointer then inc by 1, contents of queue after is image 2 (Pop). (Remember FIFO!)
Push - Go to tail pointer (3) and inc by 1, goes to location indicated (now 4) and then add value (D), contents of queue after is image 3, (Push).
How a queue works
Make use of arrays to store data, size is predetermined so only a limited amount of elements can be held, head determines if queue is empty and tail determines if full.
Can do circular queue, back pointer points to front of array when space has ran out
Push
Check if tail pointer is = to max
if tail = to max it outputs queue is full
If not, tail pointer inc by 1 then
Insert data into queue in position of updated tail pointer.
Pop
Check if head pointer = to tail pointer
If head > than tail , it outputs queue is empty.
If not, output the data from queue in position of head pointer then
Inc head pointer by 1.
Queue Uses:
An O/S may use queue to schedule tasks i.e. print jobs
In data communications to queue data packets that need to be streamed.
Breadth first searching of trees and graphs.
Linked List
Data is stored in order of its input and pointers used to link data in desired order- (data not modified).
Linked Lists used because:
Data can be processed in the order they are in the list
New data added can be given priority by updating pointer values
Data can be deleted from any position in list once its become redundant
Setting up Linked List
Start pointer and end pointer show start and end of list respectively.
State start pointer, this points to the first item that will appear in the list.
Then add pointer from each item to point to the next item in list.
Add end pointer, which has a pointer of null to indicate end of list.
Example
Linked list of names, 2D array and a start pointer, data is saved in order it was input however pointer values can be used to output the data from the linked list in alphabetical order.
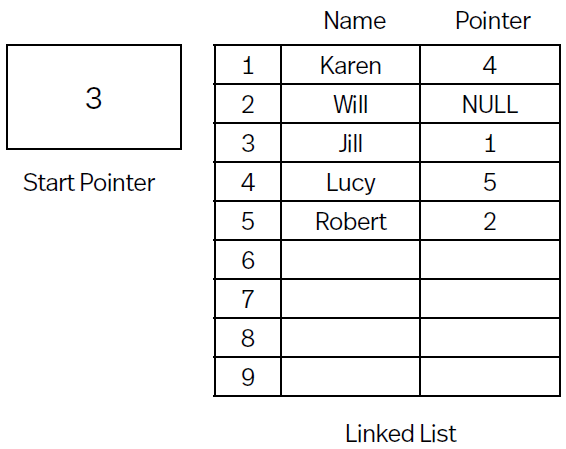
Data output - Start pointer 3, go to box 3 and output the name (Jill), then look at that elements pointer (1) and go to that box and output the name (Karen) and look at that pointer, Go to pointer, output value and look at associated pointer, repeat the 3 steps until Null pointer in reached.
Free storage in a Linked List
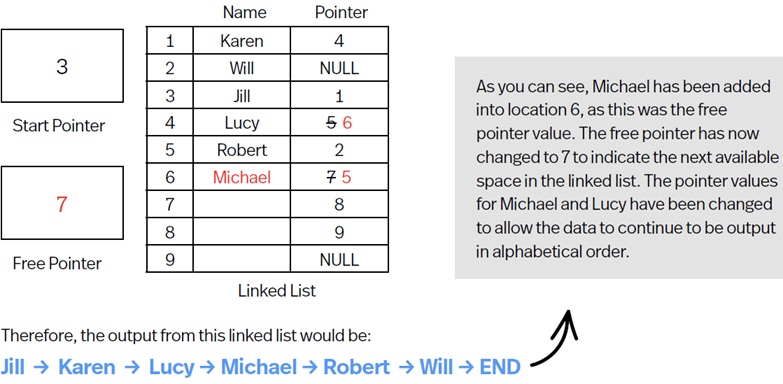
Free Pointer can indicate 1st of available positions, this list is also stored as linked list, when data is added to the linked list, its added to the position indicated by the free pointer. e.g.
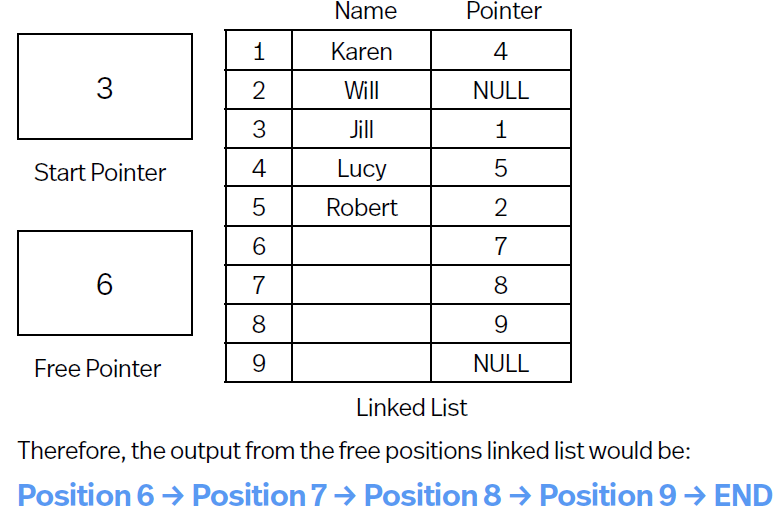
Adding data to Linked List
Store data in position indicated by free pointer.
Alter free pointer to next free position.
Update the pointer of data that goes before the new data.
Set the pointer of new data to next data item.
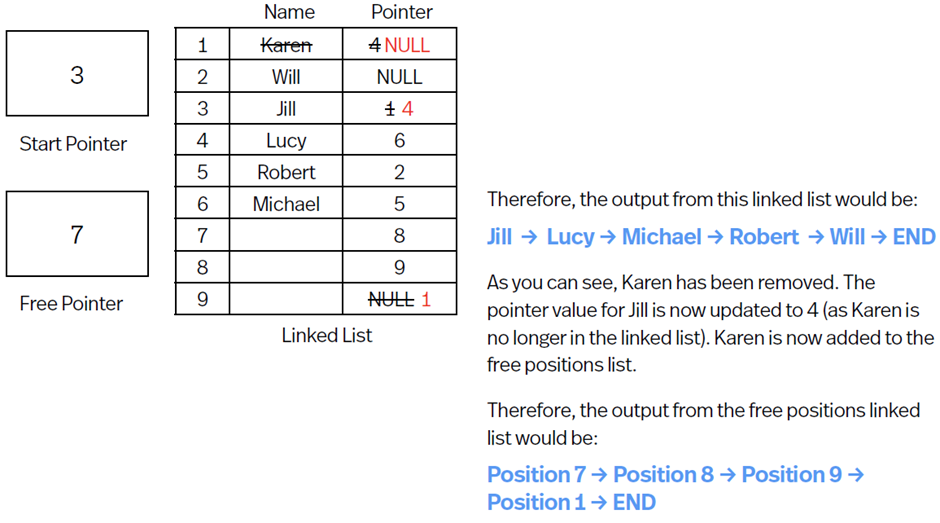
Deleting data from Linked List
Pointer for the previous item is changed to pointer of the item to be deleted.
Pointer for the data to be deleted is removed.
Position of deleted item is added to the free positions list.
Linked list uses:
Implementing an undo function
Allowing operating system to store job queues.
Image viewing such as moving between previous and next images.
Music players, to store tracks in a playlist that allows users to add or remove songs in any position
Store web browsing history, allowing for back and forward mechanisms.