Topic 1.1 - Properties of Water
Bonds
^^Covalent bond^^: Sharing of electrons by two atoms
- Forms molecules and compounds
- Single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds, etc … (how many pairs of electrons shared)
^^Nonpolar covalen^^t: Electrons are shared equally between the two atoms
^^Polar covalent^^: Electrons are not shared equally between two atoms
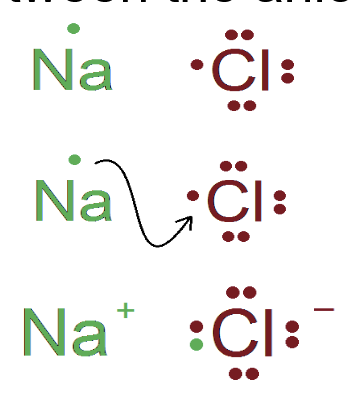
^^Ionic bond:^^ The attraction between oppositely charged atoms (ions)
- Forms ionic compounds and salts
- NaCl (sodium chloride)
- LiF (lithium fluoride)
Transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom forms ions
^^Cation^^: positively charged ion
^^Anion^^: negatively charged ion
- The attraction between the two ions forms the ionic bond
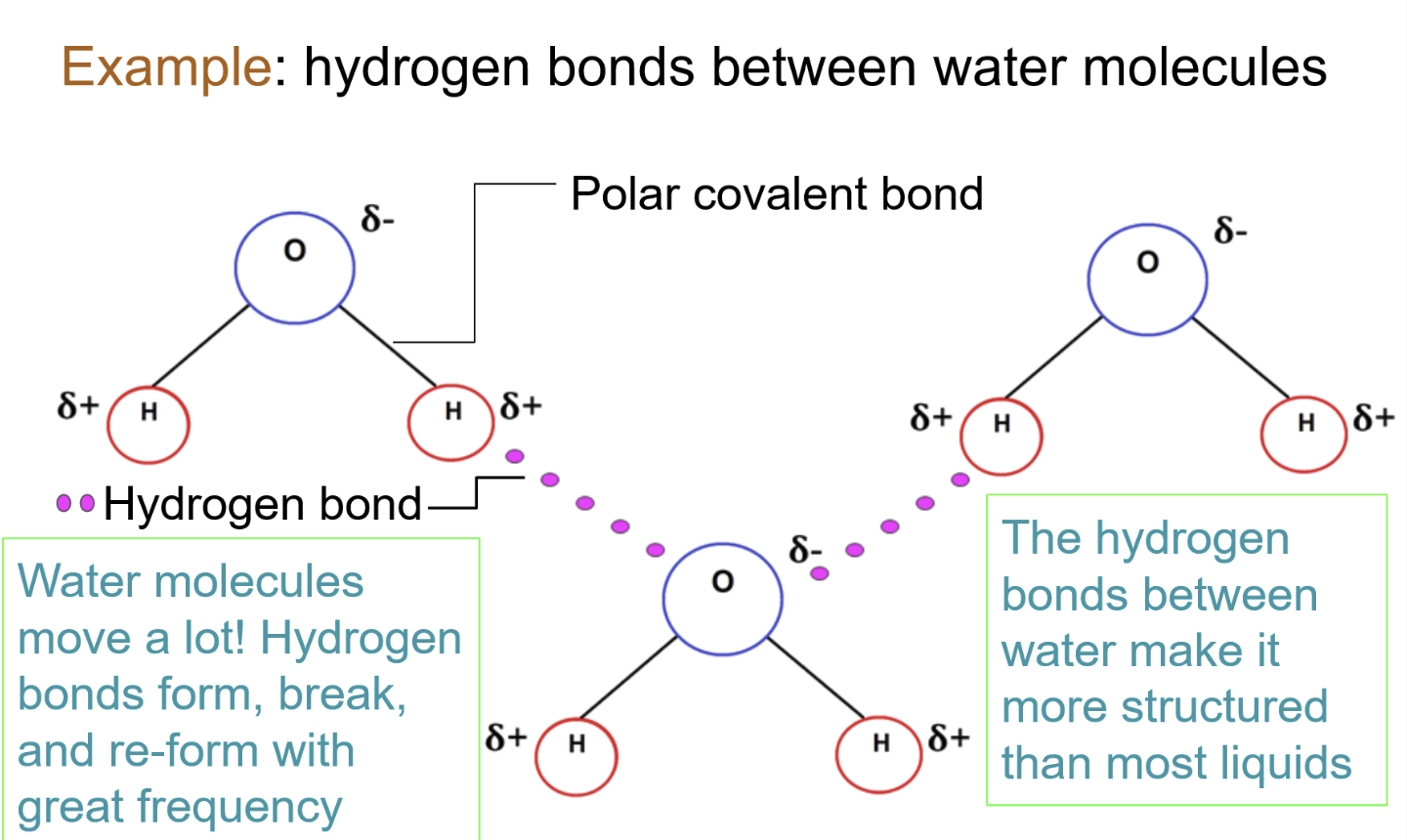
^^Hydrogen bonding^^
The partially positive hydrogen atom in one polar covalent molecule will be attracted to an electronegative atom in another polar covalent molecule. (negative + positive interaction). This forms a weak bond.
- ^^Intermolecular bond^^: Bond that forms between molecules
- This bond is typically formed with other water molecules
This happens because of the contrasting electronegativity between atoms, which causes polar covalent bonds.
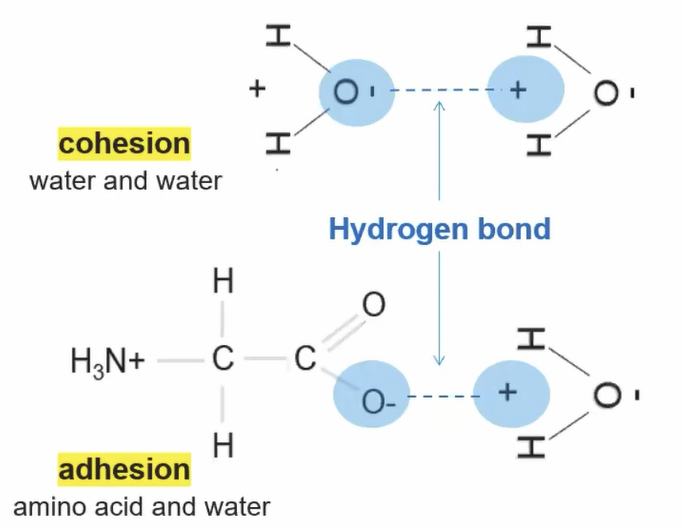
^^Cohesion^^: Two of the same molecules forming hydrogen bonds with each other.
^^Adhesion^^: Two different molecules forming hydrogen bonds with each other.
Cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension allow for water to show additional chemical behaviors known as emergent properties.
Properties of Water
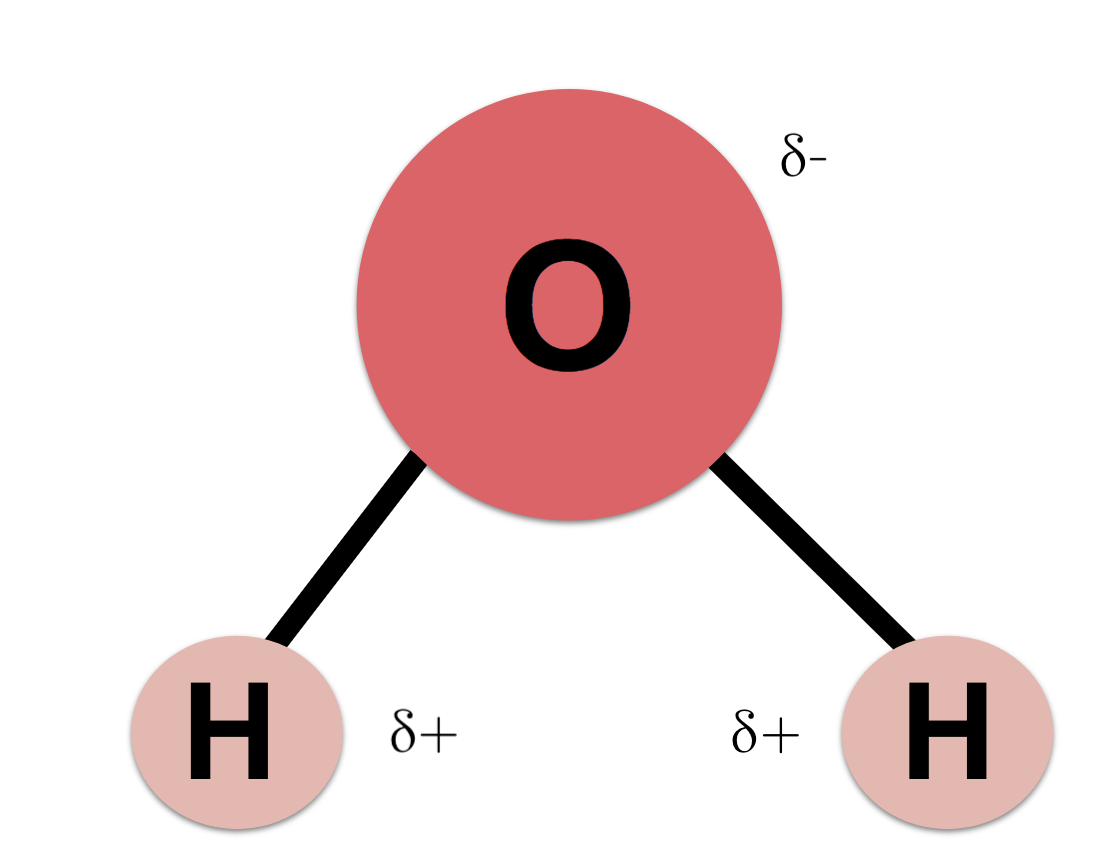
The unequal sharing of electrons in a water molecule makes water a polar molecule.
^^Cohesion^^: Hydrogen bonds between H₂O molecules told them together and increase cohesive forces.
- Allows for transport of water and nutrients against gravity in plants
- Responsible for surface tension (allows for liquid to resist external force)
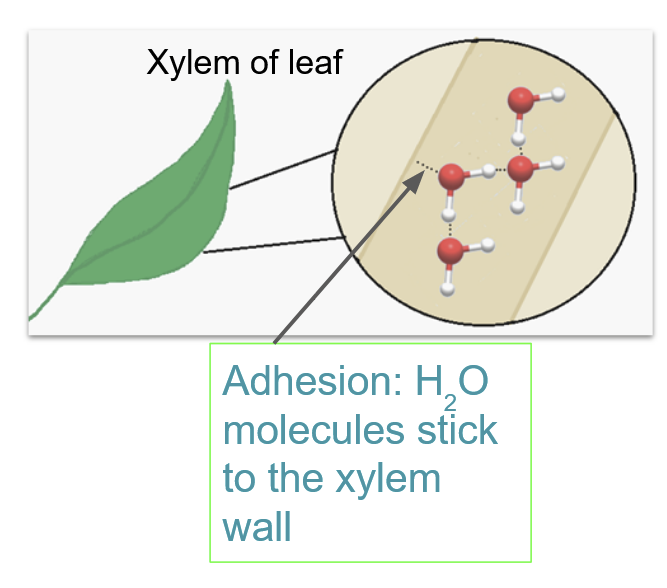
^^Adhesion^^: Caused by the polarity of H₂O.
- In plants, allows for water to cling to cell walls to resist gravity
^^Capillary Action^^: The upward movement of water due to the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension
- Adhesion > Cohesion
- Important for transport of water and nutrients in plants
^^Temperature control^^: H₂O resists changes in temperature through hydrogen bonds.
- Heat must be absorbed to break bonds, but heat is released when bonds form
Moderate air temperature
- Large bodies of water can absorb heat in the day and release it at night
Stabilizes ocean temperature
- Benefits marine life
Organisms can resist changes in their internal temperature
- Homeostasis
^^Evaporative Cooling^^: Water has a high heat of vaporization (b/c of hydrogen bonds).
The molecules with the highest kinetic energy leave as gas.
- Moderates the Earth’s climate
- Stabilize temperatures in lakes and ponds
- Prevents terrestrial organisms from overheating
- Prevents leaves from becoming too warm
^^Floating ice^^: As water solidifies, it expands and becomes less dense
- When cool, water moves too slowly to break its bonds
- Allows marine life to survive under ice sheets (ice floats to the top b/c of lower density)
Water is a ^^versatile solvent^^: its polar molecules are attracted to ions and other polar molecules it can form bonds with.
Water can interact with sugars/proteins containing oxygen and hydrogen
- Water will form hydrogen bonds w/ it to dissolve it.
^^Ionic compounds^^: Partially negative oxygen with interact with positive atoms and vice versa with hydrogen to dissolve the ions.