Organisms and their Environment (4.1-4.9)
^^Ecosystem: ^^a unit containing all of the organisms and their environment, interacting together, in a given area
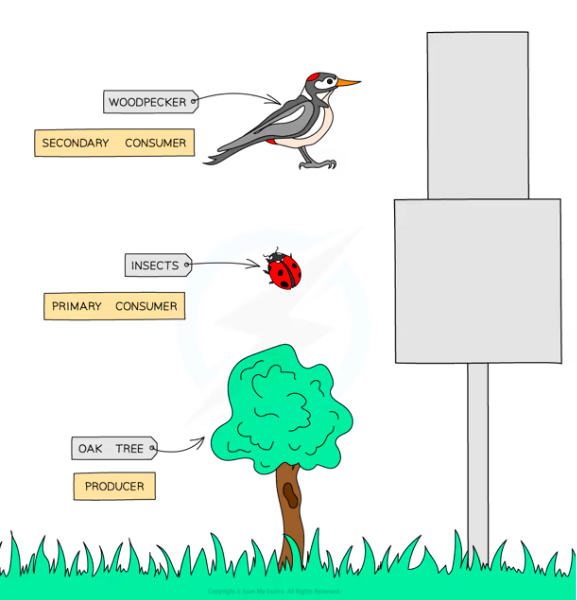
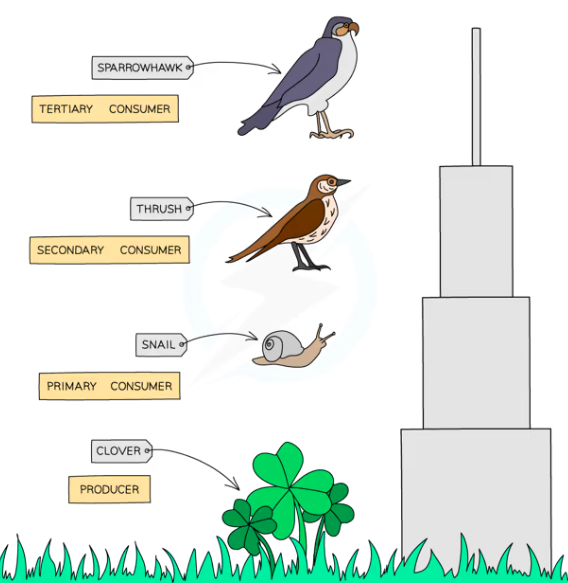
Food Chain - shows the transfer of energy from one organism to the next, beginning with a producer
Food Web - A network of interconnected food chains
Producer - An organism that makes its own organic nutrients, usually from sunlight via photosynthesis
Consumer - An organism that gains energy by feeding on other organisms. They can be further classified into primary, secondary, tertiary consumers
Herbivores - Animals that gain energy by eating plants
Carnivores - Animals that gain energy by eating other consumers
Decomposers - Organisms that gain energy by breaking down dead, or organic waste material
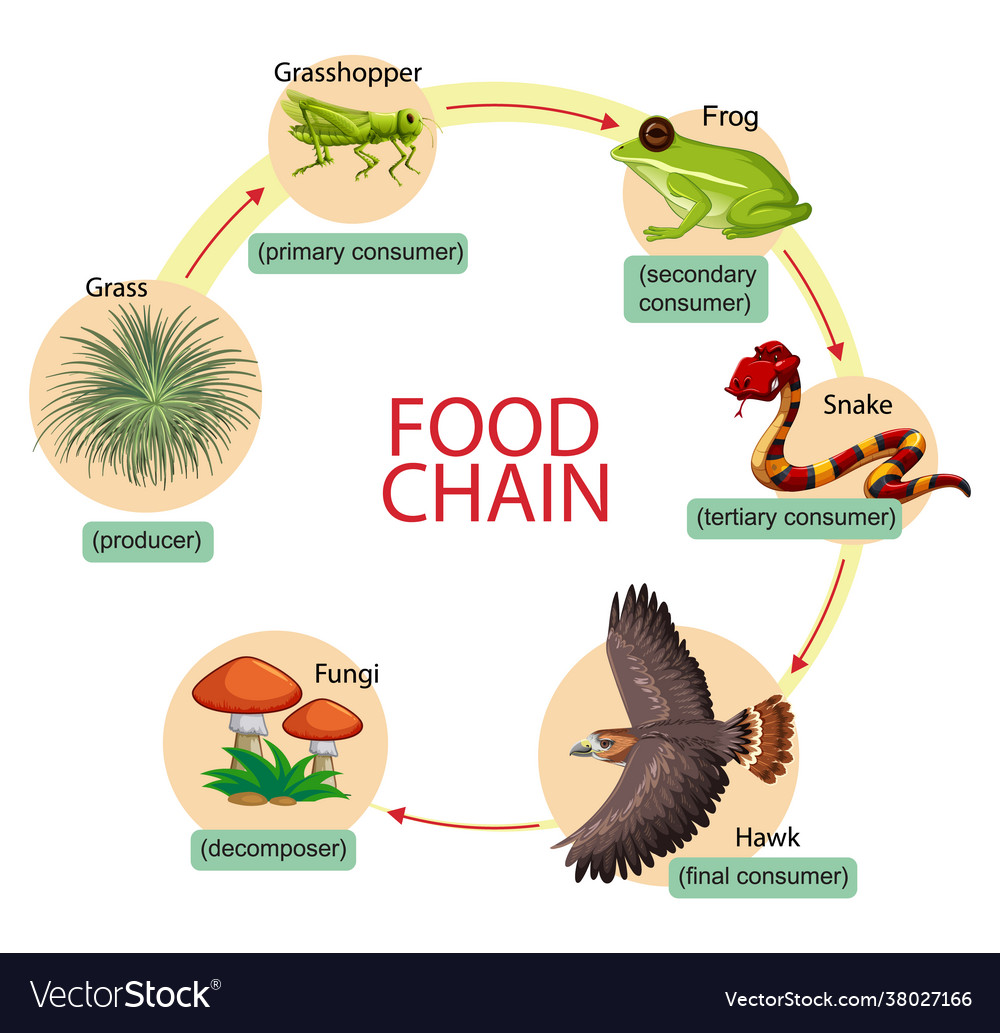
Light energy from the sun is the source of all energy
The arrows in a food chain show the transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next
Energy is transferred from one organism to another by ingestion (eating)
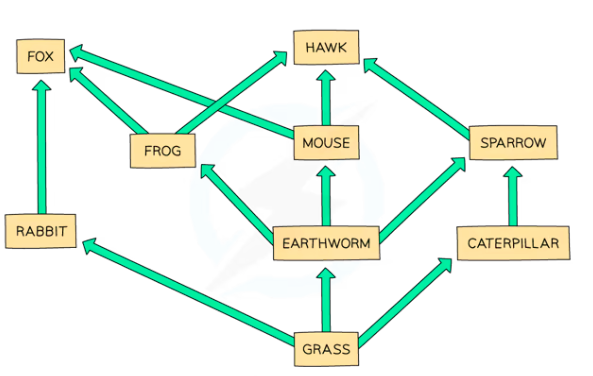
Shows interdependence - how the change in one population can affect others within the food web \n
^^Trophic Levels^^
Trophic Level: the position of an organism in a food chain, food web, pyramid of numbers, or the pyramid of biomass
^^Primary producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers^^
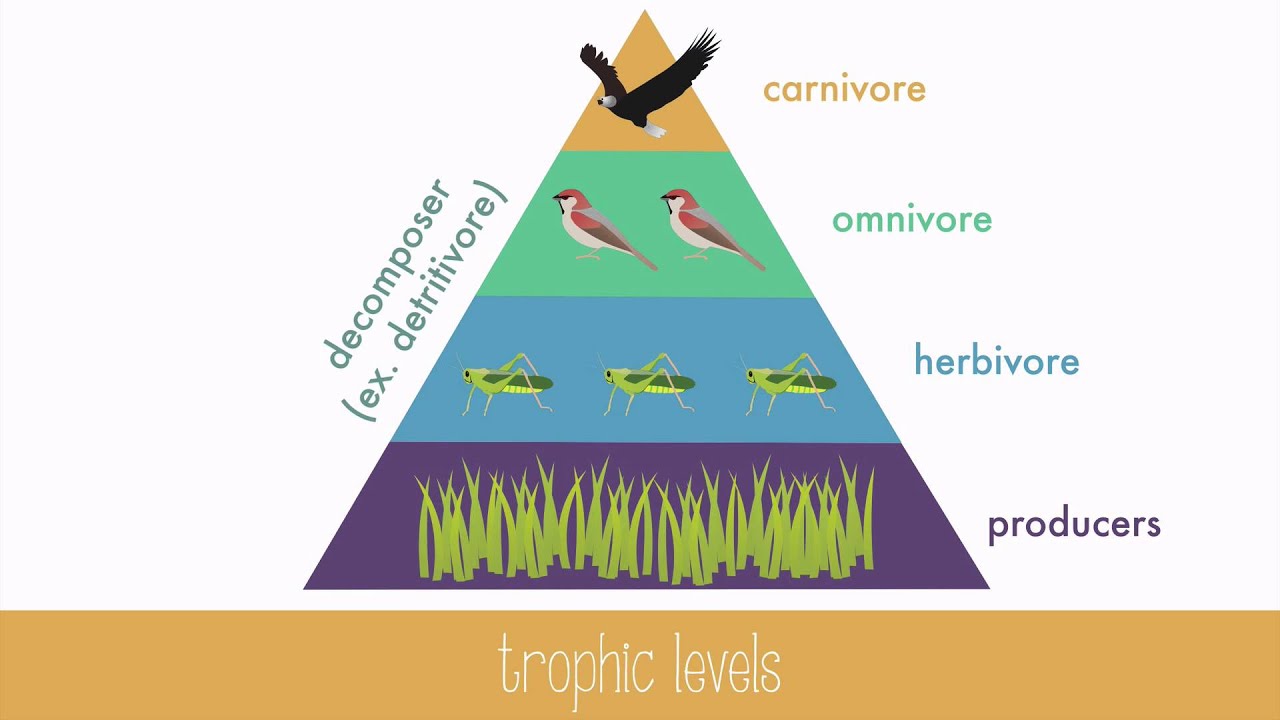
Energy transfer
^^At each level, 90% of the original energy is lost^^
- Respiration – Energy is used to respire
- Movement – Energy is used for movement
- Maintenance of body temperature – Energy is used in homeostasis
- Indigestable material within an organism – Some parts of eaten marterial cannot be digested or used by the consumer
^^→The higher the trophic level, the smaller the amount of energy transferred^^
Pyrimads
^^Food Pyramids^^: graphical representations that show feeding relationships of organisms at each trophic level
Pyramid of Number - A pyramid of numbers shows ^^how many organisms^^ we are talking about at each level of a food chain.
→The width of the box shows the number of organisms at that trophic level
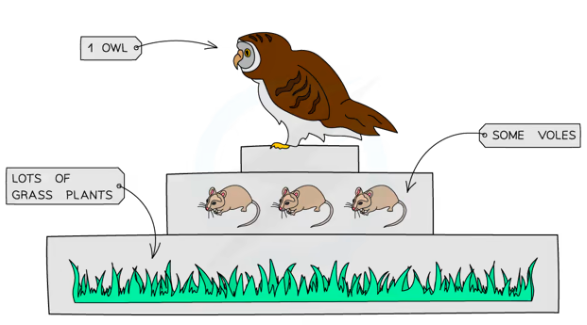
Could also be irregulary shaped
Pyramid of Biomass - shows how much dry mass the organisms have at each trophic level
→Always pyramid shaped
Nutrient Cycles
^^Nitrogen Cycle^^
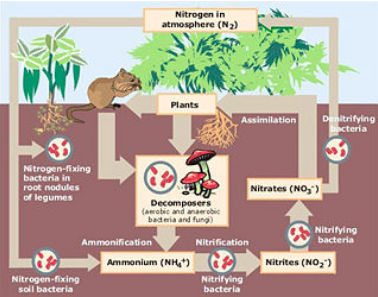
- Nitrogen-fixation: Legume plants contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These bacteria live in swellings in the plant roots called nodules. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas from air into a form that plants can use to make proteins
- Production of nitrogenous waste products: Animals cannot store excess protein in their bodies. They break it down and turn it into waste products and excrete them from their bodies.
- Decomposition: Decomposers break down animal and plant proteins and nitrogenous waste products to into ammonium
- Nitrification: nitrifying bacteria convert ammonium into nitrates in order to obtain energy.
- Uptake of nitrates: Plants absorb nitrates from the soil into their roots and use the nitrates to produce their proteins.
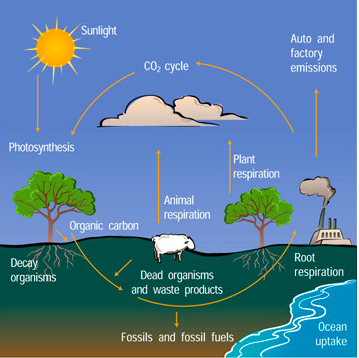
^^Carbon Cycle^^
^^Water Cycle:^^
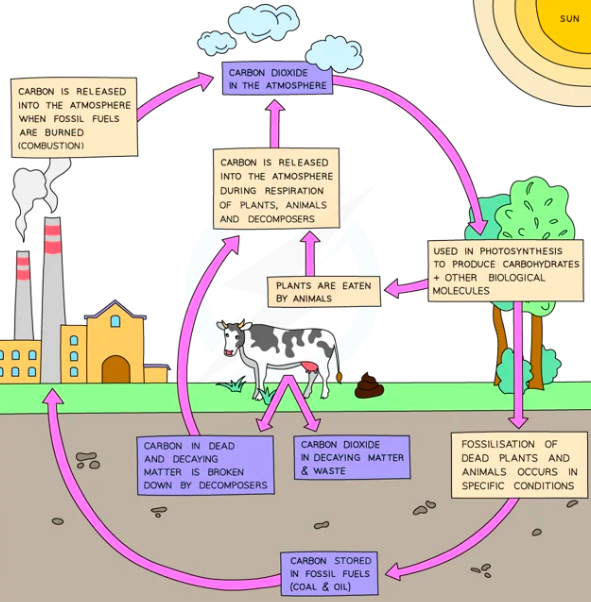
Population
Population: All the members of a single species that live in a habitat
Community: A combination of all populations of different species in an ecosystem
Ecosystem: A unit containing the community of organisms and their environment, interacting together
^^Factors Affection population size:^^
Food supply
Predation
Disease
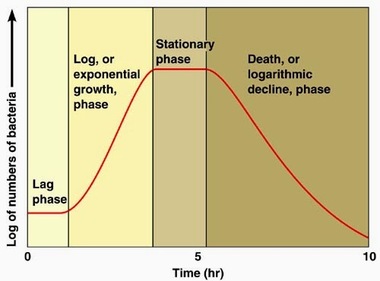
Lag phase
The population growth begins slowly from a few individuals
Log phase
Exponential growth due to ideal conditions and maximum growth rate is achieved
Stationary phase
The carrying capacity of the environment is reached
Limitation of resources such as food
Death phase
Sudden environmental change causes an inability of the environment to support the population