Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cell structure
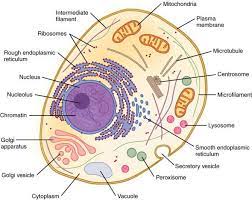
}}Nucleus}}
- Nucleus = surrounded by double membrane called the nuclear envelope
- Nucleus = Contains nuclear pores to allow molecules to enter and leave
- Nucleus = Contains chromatin and a nucleolus (where ribosomes are produced)
}}Rough endoplasmic reticulum}}
- RER = series of flattened sacs enclosed by a membrane with ribosomes on the surface
- RER = It folds and processes proteins made by ribosomes
}}Smooth endoplasmic reticulum}}
- SER = series of membrane bound sacs
- SER It synthesise and processes lipids and steroids
}}Golgi apparatus}}
- Golgi = stacked fluid filled, flattened and curved sacks called cisternae
- Golgi = Has vesicles surrounding the edges
- Golgi = Sorts, processes and packages proteins and lipids
- Golgi = Produces lysosomes
- Golgi = Also modifies proteins into lipo/glycoproteins
}}Centrioles}}
- Centrioles = hollow cylinders containing a ring of micro tubules arranged in a 9+2 arrangement
- Centrioles = Involved in cell division (pull chromosomes apart from the equator)
}}80s ribosomes}}
- 80s ribosomes = composed of a large 60s subunit and a small 40s subunit
- 80s ribosomes = Where protein synthesis occurs
}}Lysosomes}}
- Lysosomes = vesicles containing digestive enzymes
- Lysosomes = Bound by a single membrane
}}Mitochondria}}
Mitochondria = bound by a double membrane called the envelope
Mitochondria = Inner membrane is folded into cristae
Mitochondria = Has a matrix on the inside containing enzymes needed for aerobic respiration
Prokaryotic cell structure
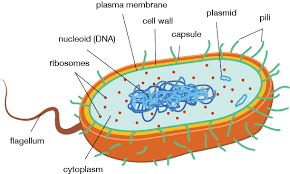
<<Cell wall<<
- Cell wall = ridged outer covering made of peptidoglycan
- Cell wall = Provides cell with support and strength
<<Slime capsule<<
- Capsule = protective slime layer which helps cells retain moisture
- Capsule = Helps adhere to surfaces
<<Plasmid<<
- Plasmid = circular piece of extra DNA
<<Flagellum<<
- Flagellum = tail like structure that rotates to move the cell
<<Pili<<
- Pili - hair like structures which attach to other bacterial cells
- Allow plasmids to move from cell to cell
<<70s ribosomes<<
- 70s ribosomes = composed of a large 50s subunit and small 30s subunit
- 70s ribosomes = Site of protein synthesis
- 70s ribosomes = Smaller than the eukaryotic ribosomes
<<Mesosomes (artefact)<<
- Mesosomes = in folding of the inner membrane which contain enzymes needed for respiration
Bacterial cell wall
bacteria can be classified according to their shape and their reaction to gram stain
Gram positive
- cell wall made of a thick layer of peptidoglycan, and an inner plasma membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
- Will stain violet after having gram stain put on it as the crystal violet stain binds to the peptidoglycan cell wall
Gram negative
- cell wall made of a thin layer of peptidoglycan with an outer lipopolysaccharide membrane and an inner phospholipid bilayer
- Wont stain with gram stain as the peptidoglycan isn’t available to bind to
- Will stain pink after washing with ethanol and using red Safranin
Bacteria and medication
- different antibiotics are needed for gram positive and gram negative bacteria
- Gram positive bacteria release exotoxins whilst alive and make you feel ill quicker
- Gram negative bacteria release endotoxins when dead and make you feel ill after a while