MHF4U - Unit 1 - Practice Questions
Lesson 1 - Power Functions
Predict the end behaviour of a polynomial function
Identify if the equation is even or odd by observing the highest degree
Determine if the leading coefficient is positive or negative
Use end behaviour to state which quadrants the ends are in
Use approaching notation to indicate which direction the ends are going in
Ex. Predict the end behaviour of y = x3 - 2x3 - 3x
The equation is odd because of the degree of 3
The leading coefficient is positive 1
Quadrant 3 to quadrant 1
y → -∞, as x → -∞; y → ∞, as x → ∞
Sketch a graph, given an equation
Determine end behaviours
Factor the equation
Using each factor, determine the zeroes
Substitute 0 for x to find the y-intercept
Plot all solved points, and connect with curved line, and add arrows
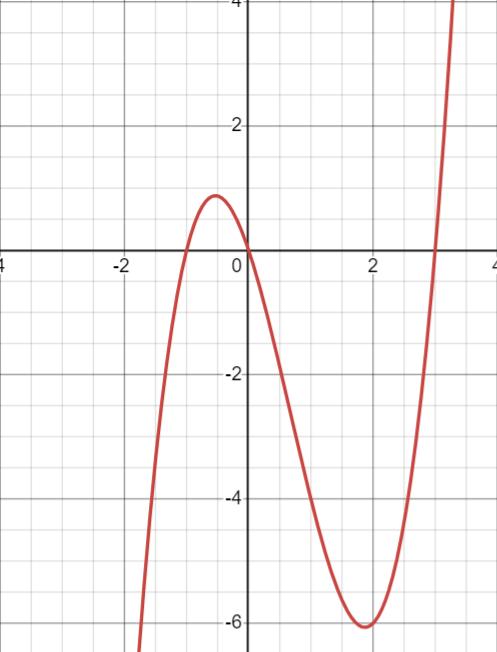
Ex. Sketch y = x3 - 2x3 - 3x
Quadrant 3 to quadrant 1
(x)(x + 1)(x - 3)
x=0 x + 1=0 x - 3=0
The zeroes are 0, -1, and 3
y = (0)3 - 2(0)3 - 3(0) = 0
The y-intercept is 0
Describe a set using interval notation
Any value that is a clear, defined point uses [ ]
Any open/infinite points use ( )
Ex. Describe the parent quadratic function in interval notation
domain: (-∞, ∞) range: [0, ∞]
identify if it is a polynomial question, justify (pg 11)
state the degree and leading coefficient (pg 11)
describing graphs (pg 12)
identifying end behaviours (Pg 12)
graphing (pg 12)
identifying graphs as powers, exponential, periodic, or none
Pg 26 - 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13