Cyber Security Day 3 Final
Cyber Security Incident Responses & Frameworks
Introduction to Incident Response
Definition: A structured approach to managing and mitigating cybersecurity incidents.
Key Objectives:
Minimize damage and downtime.
Preserve forensic evidence for investigation.
Ensure swift recovery and communication.
Stakeholders Involved:
IT/Security Operations Center (SOC)
Legal, Compliance & PR Teams
Executive Management
Incident Response Lifecycle - NIST Framework
Preparation
Identification, Detection and Analysis
Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
Post-Incident Activity
Incident Response Lifecycle – NIST Framework Details
1. Preparation
Develop and update incident response (IR) policies and playbooks.
Conduct regular simulations and staff training.
2. Identification, Detection & Analysis
Monitor alerts using SIEM and log analysis.
Validate and classify the incident.
3. Containment, Eradication & Recovery
Containment:
Short-term: Isolate affected systems.
Long-term: Prevent further spread and establish control.
Eradication:
Remove malware and patch vulnerabilities.
Restore systems from clean backups.
Validate system integrity before full re-deployment.
Recovery:
Restore systems from clean backups.
Validate system integrity before full re-deployment.
4. Post-Incident Analysis
Importance of learning from previous incidents to improve processes:
What happened, and when?
How effectively did the incident response team respond?
What information was needed sooner?
Were there any wrong actions taken?
What improvements can be made for future incidents?
What tools or resources are needed to prevent future incidents?
Use Case: JP Morgan Chase Cyberattack (2014)
Hackers accessed sensitive banking data of 76 million households.
Poor segmentation allowed attackers to move across systems undetected.
Post-attack improvements: Stronger authentication and network segmentation.
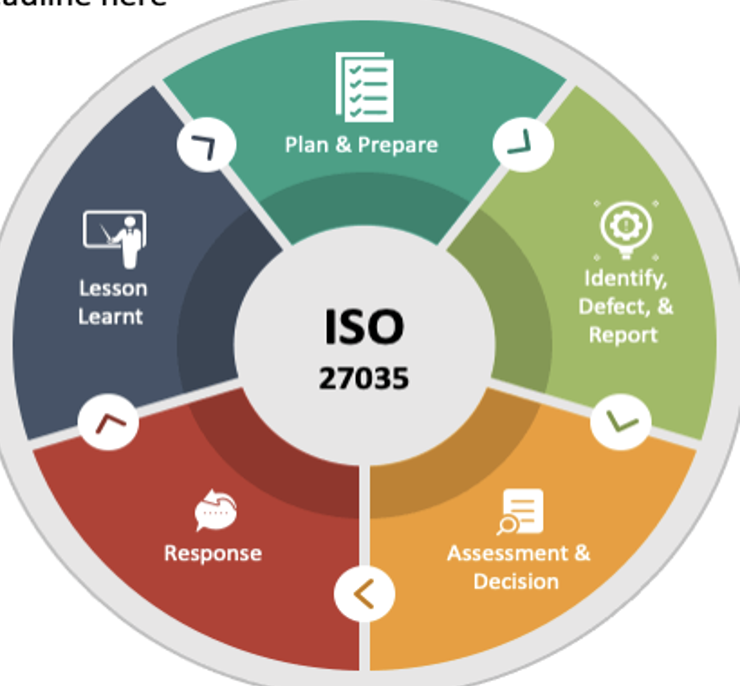
Introduction to ISO 27035
What is ISO 27035?
An international standard for managing information security incidents.
Provides a structured approach to detect, assess, respond, and learn from incidents.
Importance of ISO 27035:
Minimizes downtime and reduces damage.
Enhances incident response efficiency.
Promotes continuous improvement in security practices.
Incident Response Phases
Phase 1 — Detection & Reporting
Objective: Identify incidents early and ensure proper reporting.
Key Activities:
Implement continuous monitoring tools (SIEM, IDS/IPS).
Define incident criteria to differentiate between regular events and security breaches.
Train employees to recognize suspicious activities.
Centralize incident logging for real-time tracking.
Outcome: Faster detection, clear reporting channels, and immediate escalation.
Phase 2 — Assessment & Decision Making
Objective: Analyze incidents and determine response strategy.
Key Activities:
Assemble the Incident Response Team (IRT).
Classify incidents by severity (Low, Medium, High, Critical).
Assess potential impact on data, operations, and finances.
Develop communication plans for stakeholders.
Outcome: Informed decision-making and structured response planning.
Phase 3 — Response Actions
Objective: Contain the incident and eliminate threats.
Key Activities:
Containment: Isolate affected systems.
Eradication: Remove malicious code and close vulnerabilities.
Communication: Keep stakeholders informed.
Outcome: Neutralized threat and minimized damage.
Phase 4 — Recovery
Objective: Restore systems and ensure business continuity.
Key Activities:
Restore affected systems from backups.
Validate system integrity and monitor for abnormalities.
Test functionality to ensure correct operations.
Outcome: Systems restored with normal operations resumed.
Phase 5 — Post-Incident Activities
Objective: Learn from the incident and strengthen security measures.
Key Activities:
Conduct post-incident reviews and lessons-learned sessions.
Update incident response plans and security policies.
Provide additional training based on vulnerabilities identified.
Outcome: Enhanced security posture and continuous improvement.
Compliance Considerations – PCI DSS & GDPR
PCI DSS
Requirement 12.10: Mandates an incident response plan for payment data security.
Focus on transaction monitoring and fraud detection.
GDPR
Requires data breach notification within 72 hours.
Imposes penalties for inadequate personal data protection.
Banking Relevance: Protects financial and customer data, ensures regular compliance audits, and reporting.
Use Case Examples
Capital One Data Breach (2019)
Misconfigured firewall exposed sensitive credit card data.
Resulted in an $80M fine for non-compliance with PCI DSS.
Bangladesh Bank SWIFT Heist (2016)
Poor monitoring caused unauthorized SWIFT transactions worth $81M.
Simulation: Test rapid detection and containment of fraudulent transactions.
Incident Response Planning
Purpose:
Minimize damage and downtime during incidents.
Ensure coordinated, effective response across teams.
Why It Matters for Banks:
Protects sensitive customer data and transactions.
Ensures regulatory compliance (PCI DSS, GDPR).
Preserves trust and reputation.
Incident Classification
Definition: Categorize incidents based on impact and urgency.
Classification Criteria:
Low Impact: Minor issues with no data loss.
Medium Impact: Potential data exposure, limited system impact.
High Impact: Critical systems compromised, significant data loss.
Importance: Prioritizes response actions and ensures appropriate team engagement.
Escalation Matrix
Purpose: Ensure prompt escalation to appropriate teams.
Key Elements:
First Responders: IT helpdesk or SOC for initial detection.
Incident Manager: Coordinates response and communication.
Executive Notification: Informs management for high-impact incidents.
Banking Relevance: Provides clarity during critical incidents like fraud or ransomware.
Communication Strategy
Internal Communication
Inform relevant teams (IT, Security, Compliance).
Provide clear instructions to avoid panic and misinformation.
External Communication
Prepare press statements and customer notifications.
Comply with breach notification laws (e.g., GDPR requirements).
Importance: Ensures consistent messaging, reduces reputational damage.
 Knowt
Knowt