Chapter 1 - Introduction
Chemistry - The study of matter and its changes
- Matter - Anything that has mass and takes up volume
Composition vs. Structure
- Composition - What something is made of
- Structure - What something is made of and how the components are arranged
Atom - The fundamental unit of matter
Element - Made of only one type of atom
Compounds - Composed of more than one element; bound in fixed ratios
Molecules - Groups of atoms that bind tightly together, and behave as a single unit
- Diatomic molecules - an element bound to another of itself
Pure substances - Composed of one element or one compound ONLY
Mixtures - contain more than one substance, not bound in a fixed ratio
- Alloys - mixtures of metals
- Homogenous - components mix evenly
- Heterogenous - component do not mix evenly
- Mixtures can be - separated into their components without changing the identity of the substance, unlike compounds
Matter -----> Pure Substances vs. Mixtures
Pure Substances -----> Elements (Gold) vs. Compounds (Water)
Mixtures -----> Homogenous (Air) vs. Heterogenous (Salt and Water)
The Three States of Matter
Solid - Definite volume and shape
Liquid - Definite volume, but no definite shape
Gas - No definite anything
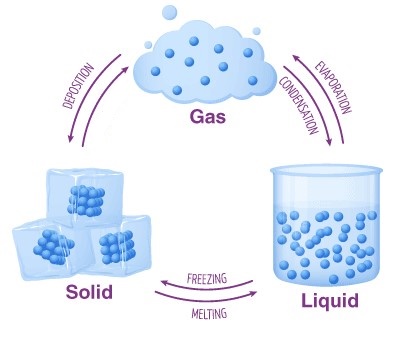
Deposition = Condensation
The behavior of any substance is determined by the arrangement of the particles that compose the substance.
Properties and Changes
- Physical properties - Can be measured without changing the identity of the substance
- Physical changes - Don’t change the identity of the substance
- Phase Changes are Physical Changes
- Chemical properties - Can NOT be measured without changing the identity of the substances
- Chemical changes - Change the identity of the substances
- Chemical Reactions
Elements combine to form new substances - A chemical change
A change that forms new compounds - A chemical change
CHEMICAL CHANGES IDENTITY, PHYSICAL DOES NOT CHANGE IDENTITY
Energy and Change
Energy - the ability to do work
- Potential energy - Stored energy
- Kinetic energy - Energy of motion
Heat energy - Involved kinetic energy of the particles in a substance
Physical and Chemical involve changes in energy
High energy or stable?
High energy - brings changes
Stable - no reaction
Exothermic change - Releases heat energy (Unstable Product)
Endothermic change - Absorbs heat energy (Stable product)
The Scientific Method
Make observations, formulate ideas, test ideas with experiments, and repeat
Hypothesis - A tentative explanation that has been tested
Theory - Idea supported by experimental evidence, or a paradigm
- Paradigm - A way of thinking about a topic
Scientific law - A statement that describes observations that are widely varying circumstances
A theory is how or why it happens, A law is what happens