1: Intro to Human Resources Management
Human resources management: An integrated set of systems, practices and policies in an organization that focuses on the effective development and deployment of its employees; critically to follow business strategy.
Systems, practices & policies
Health and safety through culture
Define, analyze and design work
Plan, recruit, select employees
Orient, train, develop, on-board employees
Manage and assess employee performance
Reward & recognize employees
“Employees need to know why their work is valuable and needed”
Employee & employer rights and responsibilities
Labour relations and collective bargaining
International HRM
Professionals
Managers are critical towards connecting employees and organizations.
They are principally responsible for identifying skillsets, gaps in skillsets. Ultimately, managers are responsible for the development of workplace culture in a more accessible way that HR professionals cannot do.
Managers determine the characteristics of the workplace; HR aids in achieving this through an organization’s people.
HR professionals are necessary to equip managers with “best people practices” to ensure organizational success.
e.g. policy formation, employee advocacy
Ongoing HRM issues
Global economy
Many companies have worked collaboratively to expand global operations to sell Canadian products.
Companies that had been doing business in Canada can move to countries with lower production costs.
HRM must evolve to address different legal, political and cultural requirements.
We’re presently watching the dismantling of globalization.
Business Sector & Firm Changes
Canada’s economy is primarily comprised of housing and consumer spending. Oil and mineral exports must be expanded to create economic growth — but fluctuations in natural resource prices add risk.
Downsizing: strategy to decrease the number of employees in a company, e.g. Bell Media.
Outsourcing: hiring a person who does not work for the company to perform work that would’ve normally been performed by someone employed for the company.
Independent Contractors: someone hired for a specific job at a specific time, who is not subject to tax deductions such as EI and income tax.
Technology
Technology has enabled the vast improvement of processes.
The advent of “telecommuting” work from home processes has also grown in popularity following COVID-19.
e.g. advent of AI recruitment and HR
Quality management
Six sigma: a process used to translate customer needs into a set of optimal tasks performed with oneanother.
Lean: an organizational system of improvements that maximize customer value and minimize waste
Benchmarking: finding the best practices in other organizations that can be brought into a company to enhance performance
Human capital
Human capital: the value that employees provide to an organization through their knowledge, skills and attributes
Core competencies: a combination of knowledge, skills and characteristics needed to effectively perform a role in an organization
Emphasis on knowledge workers. What does the work of the future look like?
Dave Ulrich proposes that employee attitude is critical towards customer satisfaction. When employees care about their work, they invest time to developing competencies associated with their work.
Demographics
Canada’s overall population is changing. Companies must adapt their hiring practices to reflect this overall diversity.
Generationally, age is more diverse in the workplace. Peoples of different backgrounds are entering the workforce. Indigenous employees are finding their way.
Skills in the labour force are evolving. There is a concern about skills and labour shortages in the workplace; will there be enough people to satisfy corporate needs?
“She-cession”: a term coined in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic to reflect female disparity in the workplace.
Educational attainment is rising in the workplace.
Employee Expectations
Rights, ethics & privacy as legislation changes
Fulfilling and meaningful work with supportive and inclusive corporate culture.
Work-life balance has become important as employees view life satisfaction as derived from balancing the challenges and rewards of work with those of their personal lives.
RBC and World Vision offer their employees alternative work arrangements to accommodate young families.
Gig economy: working 2 or more part time jobs to supplement income.
CIBC increases the value employees add to the bottom line and customer satisfaction. Employees are involved in decision making and steps necessary to reduce customer complaints.
Canada’s family physician shortage
Medicine’s bureaucratic systems; doctors run small businesses. Recruitment & business management is somehow integrated.
‘unpaid work’ when not seeing patients.
burnout & employee value.
Clinics have become a popular business model by sharing overhead and costs.
Underfunded primary care networks
Employee Lifecycle
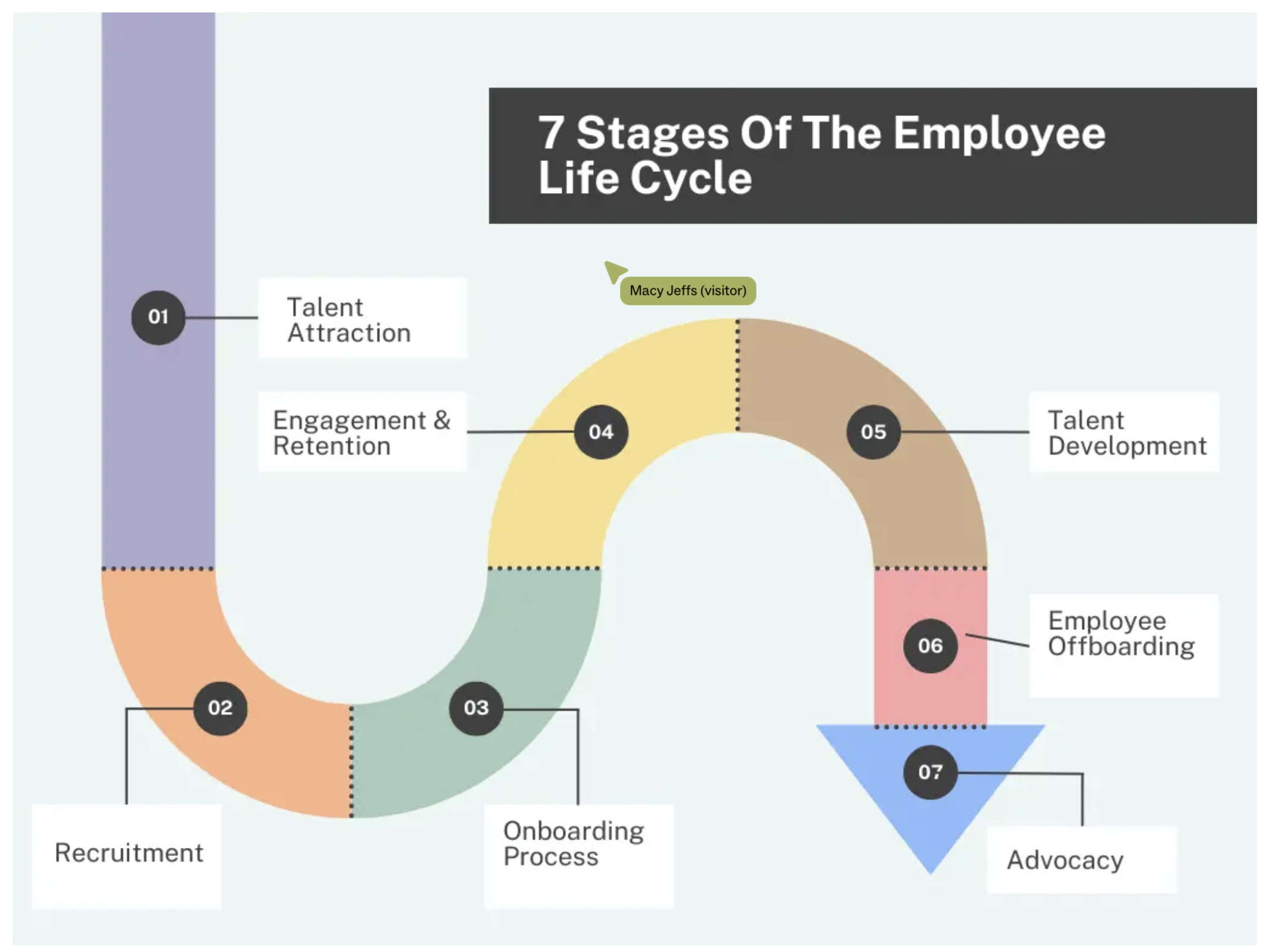
Importance of HR
Delta CRJ rollover
crews will likely have to be placed on some form of leave
compliance with investigations — HR’s responsibility is to ensure that crews have appropriate certification; prevent negligence.
Health & safety issues: injury compensation?
HR is critical towards building a cohesive safety culture and attracting skilled talent towards this purpose.
Workplace conflicts:
Various forms; sometimes managers may involve HR or a third party investigator.