Bacteria and Viruses
^^Domain Archaea^^
- Cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan
- They contain different amino acids and lipids
- They were first discovered in extreme environments
Ex: swamps, hot springs, salt lakes
| Group 1: Methanogens | Group 2: Halophiles | Group 3: Thermoacidophiles |
|---|---|---|
| Convert hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide into methane. | name translates out to “Salt loving” | Serve as producers for communities living at great depth |
| Live in anaerobic environments | Halo: “salt” and phile: “loving” | Acidic environments with high temperatures |
| Habitats: Deep fresh water, marine mud, swamp mud, sewage, cow and termite intestinal tract | Habitats: Great Salt Lakes and Dead Sea | Habitats: Hot springs of Yellow Stone, volcanic vents, hydrothermal vents |
Domain Bacteria:
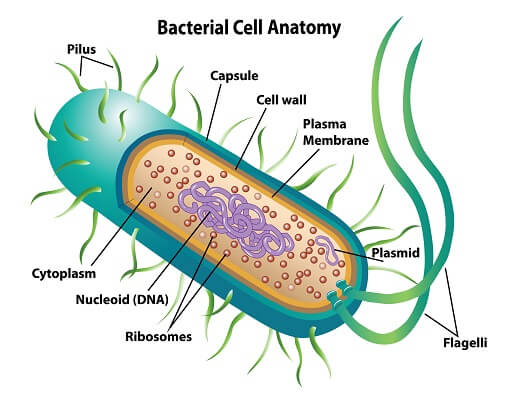%%Endospores%%: contains DNA; is thick coated, resistant structure ( in unfavorable environmental conditions)
Classification of Bacteria:
- Shape: Bacilli (rod shaped), Coccus (spherical), and Spirilum (Spiral shaped)
- Arrangements: Diplo ( in pairs), Strepto (in links), Staphylo (in clusters)
Ex: Streptococcus (spherical, found in links)
Gram Stains:
- Smudge bacteria (dry and fix by heat
- Smear Crystal Violet Dye
- Mordant: smear Iodine
- Decolorize: add Ethanol
- Secondary Stain: add Safarin
- Gram Positive: Purple, blue, or black
- Gram Negative: Pink or Red
^^Gram Positive^^^^:^^ the bacteria is of a simpler makeup; has more peptidoglycan; stains purple
**==Gram Negative: ==**the bacteria is more complex; has an outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane on the bottom; has less peptidoglycan; stains pink
Movement in Bacteria:
Taxis: movement toward or away from a stimulus
Positive taxis: towards the stimulus
Negative taxis: away from the stimulus
Chemotaxis: react to chemical
Nutrition and Metabolism (what they eat):
- Photoheterotroph: uses light energy, but gets carbon by eating other organisms
- Chemoheterotroph: obtains energy and carbon from other organisms
- Photoautotroph: uses light energy and gets carbon from carbon dioxide
- Chemoautotroph: extracts energy from inorganic compounds and uses carbon dioxide as a carbon source
Habitats:
- Obligate anaerobes: cannot live where oxygen is present
- Falculative anaerobes: can live with or without oxygen
- Obligate aerobes: need oxygen to live
Reproduction and Recombination:
- Binary Fission: production of two identical cells (asexually)
- Conjugation: exchange of DNA between prokaryotes through the sex pilus
- Transformation: prokaryotes take in DNA from outside environment
Bacteria + Human Health:
Exotoxins: toxic substances that bacteria secrete to environment (from inside to leaving outside)
Endotoxins: lipids and carbohydrates in cell membrane of gram negative bacteria (These are the lipid portions that are apart of the outer membrane of the cell wall and are released when the bacteria dies)
Ex: Streptococcus
Important Bacterial Groups
- Proteobacteria (major phylum of Gram Negative bacteria): largest and most diverse group; live symbiotically with other organisms
Ex: Nitrogen fixing bacteria (Rhizobium) in legume roots that transform Nitrogen usable for plants
Gram Negative Bacteria:
- \
Chlamydia: live inside animal cells; no peptidoglycan in cell walls
- Spirochetes: Spiral shaped bacteria; live freely as pathogens; include syphilis and lime disease
Gram Positive Bacteria:
- Streptococcal species: Botulism (in bad canned foods)
- Streptobacilli species: Includes anthrax and lactobacilli (makes milk sour)
- Actinomycetes: these make antibiotics
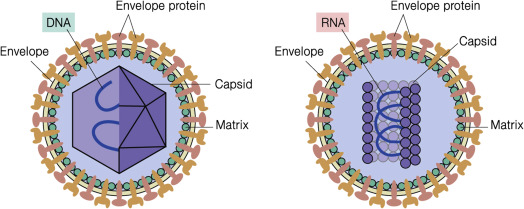
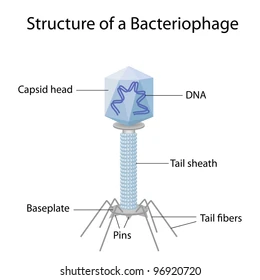
Viruses:
Why Are They Not Alive?
- They have no cytoplasm or organelles
- They use no energy so they have no metabolic or homeostatic processes
- They don’t grow by division
- They have DNA and RNA, but they can’t reproduce by themselves (they use a host cell)
Viral Size and Structure:
Smallest particles that can cause disease
Capsid: protein coat; causes different shapes; helps bond virus to specific host cells
Helix: (rabies and measles)
Icosahedron: 20 triangular faces and 12 corners (chicken pox, adenovirus, and polio)
Spherical: influenza virus