parts of the brain
old brain “reptilian brain”
the brainstem
connects your brain to your spinal cord
sits near the bottom of your brain
helps regulate vital body functions that you don't have to think about, like breathing and your heart rate
medulla oblongata
reticular activating system (ras)
in charge of arousal (awake and alert)
cerebellum “little brain”
process our voluntary movements
“you can do anything that you set your mind to”
limbic system
amygdala
plays a central role in emotion and in the evaluation of stimuli (fear and aggression)
thalamus
in order for the brain to communicate with another part of the brain it must go through the thalamus
serves as a major relay and integration center for sensory information
grand central station!
hypothalamus
the brain of the endocrine system
in charge of the emotion of reward; feeling of accomplishment
helps with homeostasis (body being in balance); controls hunger, thirst, body temperature, and etc.
hippocampus
short-term memories —> long-term memories
gives us our internal map (navigation skills)
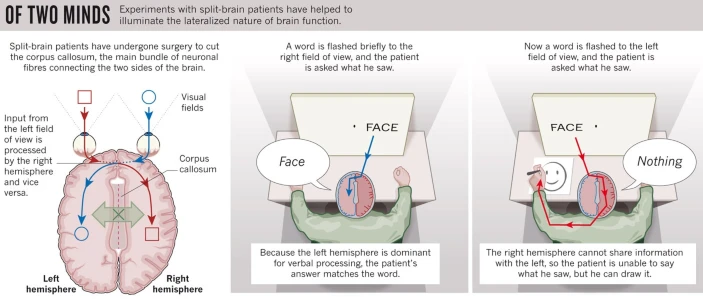
corpus callosum
band of neural fibers that connect the two hemispheres of the brain allowing them to communicate with one other
they transfer information and synchronize the activity between hemispheres
cerebral cortex
occipital lobe
processes our vision
temporal lobe
processes our hearing
parietal lobe
processes our sense of touch
frontal lobe
in charge of fine motor movement (growing ability to write, draw, etc.)
helps with emotion regulation (demure!)
help with planning and judgement
brain’s contralateral hemispheric organization
right side of the brain (hemisphere) controls the left side of the body and vice versa
split brain research:
Mike Gazzaniga and Roger Sperry
hemispheric specializations
Left | Right |
|
|
association areas/functions
multiple regions of the brain that have very specific tasks
Broca’s Area: in the left frontal lobe and it is in charge of the motor movement of the mouth while speaking; specific to that region as he is still able to write
Wernicke’s Area: in charge of language expression and comprehension (auditory and visual)
brain plasticity
the brain's ability to change its structure by creating new neural connections allowing the brain to fix/cope with brain damage
age plays a part because young people’s brains are still developing