Molecular Bio Quiz 1
Organic Molecules
Molecules that exist in all living things
Life’s building blocks
Four types of organic molecules
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Proteins
All organic molecules are based on Carbon
Monomers are the building blocks of organic molecules when they are joined together, they form polymers
Organic Molecules share similar elements, but their shape and position of bonds determine what type of organic molecule they are
Carbohydrates
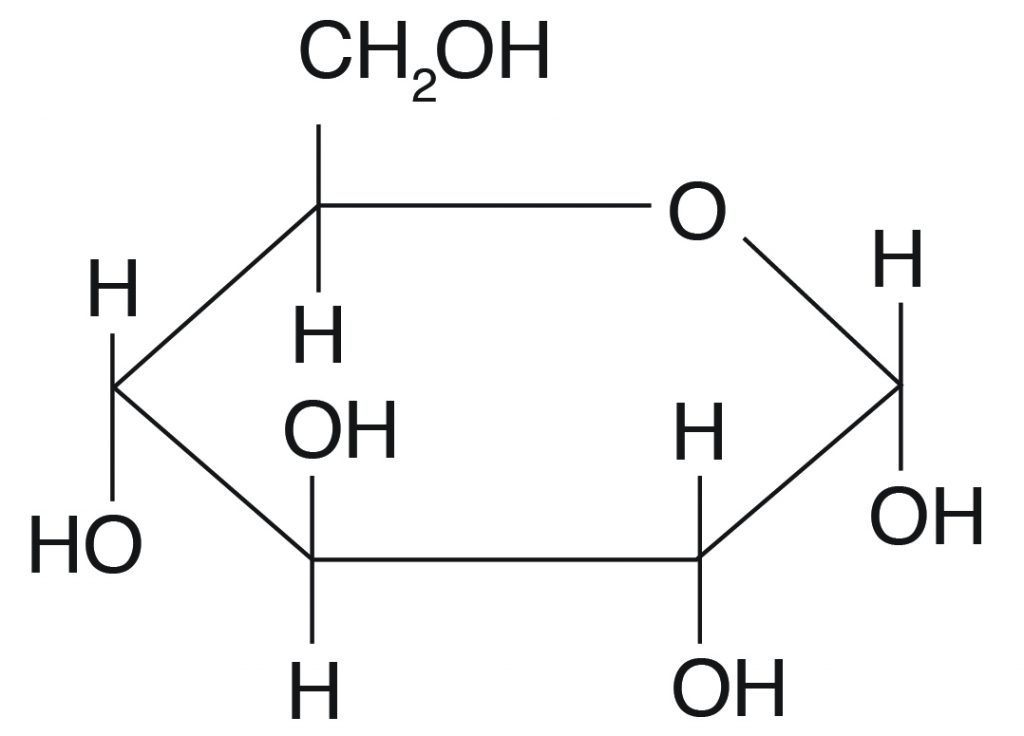
Elements: CHO
Monosaccharides are the building blocks of a carb
Disaccharide: two monosaccharides bonded together
polysaccharides: many monosaccharides bonded together
Monosaccharides are bonded together by glycosidic linkage
Fructose and Glucose are examples of carbs
Three main categories of carbs
Starch: Storage form of carbs in plants
Glycogen: Storage form of carbs in animals
Cellulose: Structural support in plants (leaves and stems)
Proteins
Elements: CHON
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins
20 types of Amino Acids
Peptide bonds bond them together
Functions:
Transport
recognition
structural support
message transport
Nucleic Acids
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
Elements: CHONP
DNA and RNA are two types of nucleic acids
DNA: Blueprint, store genetic info
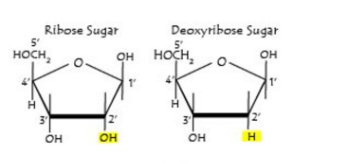
Deoxyribose
RNA: Codes for amino acids, translates genetic code into protein
Ribose
DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded
DNA and RNA differ in 2’ carbon
DNA is missing an OH(hydroxyl), but ribose has it
Nucleotide is a monomer
Sugar, Phosphate, Base
Sugar: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Adenine and Thymine bond together, have two bonds
Guanine and Cytosine bond together, and have three bonds
Adenine and Guanine are purines, which means they have two rings
Cytosine and Thymine are pyrimidines, which means they only have one ring
Phosphate attaches to 5’ carbon of a nucleotide, 3’ carbon of nucleotide will attach to another phosphate, and a chain will be created

5’ end will be on top with a phosphate group, 3’ end will be bottom with free OH(hydroxyl group), which is not attached to anything
One side will be 5’ to 3’, while other side will be 3’ to 5’, this is known as complementary base pairing
Nucleotides are bonded together by a phosphodiester bond
Lipids
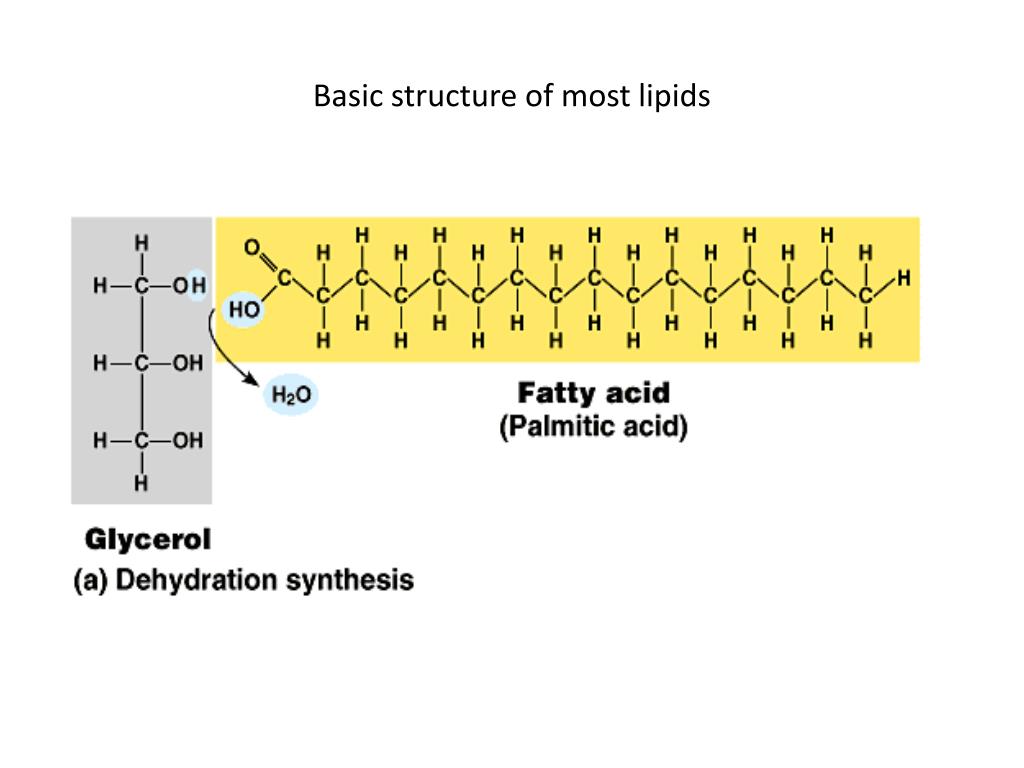
Elements: CHO(P)
Fatty acids are the building blocks of lipids
Phospholipids, triglycerides, steroids, and cholesterol are examples of Lipids
Basic structure
Chain of hydrocarbons with carboxyl tail, looks like a long chain
Saturated vs Unsaturated
Saturated: Most hydrogens possible, straight tail
Unsaturated: Kinked tail, double bonds
 Knowt
Knowt