Lecture 11 Algae
Oxygenic Photosynthetic protists that do photosynthesis via primary or secondary endosymbiosis.
Primary production of O2 on earth
30% by algae
20% by prokaryotes (cyano)
50% by land plants
What are Algae?
Algal blooms are places in water bodies where the growth of algae is excessive, those places often have chemical contamination which in turn decreases oxygen levels and causes lots of harm to aquatic life.
Definitions
Classification
Food
What are some examples of what it can do and connections to their various supergroups
Red tide (Alveolites (SAR)) cause by: photoautotroph dinoflagellates
What are Haptophytes
Definition: Unclassified, marine unicellular organism
What is the classification
Eukarya
Physicals
2 flagella (movement)
Haptonema (prey and surface attachment)
What is it food?
photoautotrophs and sometime mixotrophs
What is it capable of doing?
Their dead bodies make haptophytes (hard calcified scale
What are Stramenopiles?
Definition: straw hair, fine hairlike projections,
What is its classification?
Physicals
1 flagella
What is its food source?
What are some examples?
Diatoms
What is it capable of doing.
Forensics
Brown algae
Multicellular photoautotrophic
Plant like reproduction cycle
Explain the sexual reproduction cycle
Human example
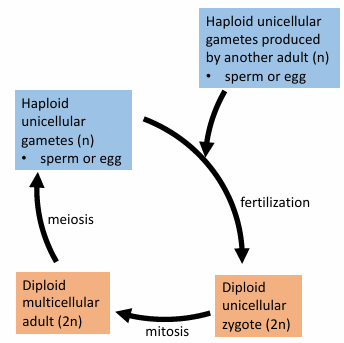
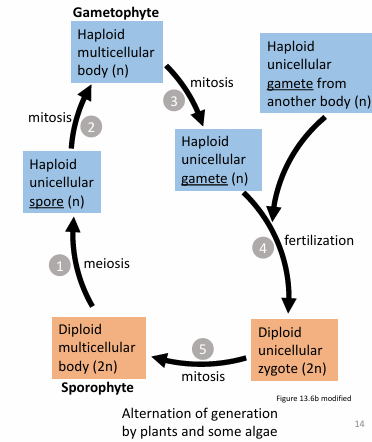
What is Alternation of generation
The production of gametes in algae involves both haploid and diploid stages, where the organism alternates between these phases throughout its life cycle.
Sporophytes:
diploid
make spores using meiosis, which results in the formation of
haploid spores that can grow into gametophytes.
Gametophytes
haploid
produce gametes through mitosis, leading to fertilization and the formation of a new sporophyte generation
Archaeplastida
Definition:
Direct ancestors of primary Endosymiosis
The source organism of secondary endosymbiosis, which led to the evolution of red and green algae, as well as land plants.
Green Algae
Paraphylectic group (a grouping that excludes some members)
Missing embryophytes
What are the two types of algae
Chlorophytes
sister group to streptophyta (charophytes +plants)
Charophytes (closest relative to land plants)
Relations to plants include
Morphological traits
Molecular phylogeny of nuclear
Mitochondrial and plastid DNA
Things they have in common,
Flagellated sperm
Both synthesize cell wall using ring-like protein structure, embedded in plasma membrane (Create their cell wall in a similar manner.
Chloroplast DNA, Mitochondria and Nuclear
Sporopollenin
A though layer which surrounds charophytes zygotes to keep moisture in.
This allowed them to live on land
Encase plant Spore !!
Encases charophytes Zygotes!!
 Knowt
Knowt