pathophys midterm
Exam Units
Content areas:
Infection, inflammation, immunity 8 questions
Neural function 10 question
Sensory function 10 questions
Hematopoietic system 10 questions
Arterial Blood Gas (ABGs)
Lab Values
Antibiotics Overview
Penicillins
Uses: Treats streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, syphilis, gonorrhea
Naming: Ends in "-cillin" (e.g., piperacillin, amoxicillin)
Side Effects: Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain
Cephalosporins
Uses: Treat varied infections, including urinary tract and respiratory infections
Naming: Starts with "cef-" (e.g., ceftriaxone, cefepime)
Caution: Contraindicated for those allergic to penicillin
Aminoglycosides
Uses: Treat Gram-negative bacterial infections
Examples: Gentamicin, tobramycin
Adverse Effects: Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity
Tetracyclines
Uses: Treats various infections
Naming: Ends in "-cycline" (e.g., doxycycline)
Contraindications: Not for pregnant individuals or children under 8
Macrolides
Uses: treat Mild to moderate respiratory infections
Example: Azithromycin
Contraindications: Lactating individuals or those with hepatic (liver) dysfunction
Fluoroquinolones
Uses: Treats Gram-negative and Gram-positive infections of urinary/respiratory tracts
Naming: Ends in "-floxacin" (e.g., levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin)
Adverse Reactions: Tendon rupture, CNS effects
Isolation Precautions
Contact Precautions: Wear gloves and gowns to prevent spreading infections through touch.
Droplet Precautions: Use masks to protect against germs from coughs and sneezes.
Airborne Precautions: Wear special masks to guard against germs that linger in the air.
Pharmacological Treatment - Analgesics
Function: Drug Decrease or eliminate pain without loss of consciousness
Analgesics do NOT cure UNDERLYING cause
Purpose: Allows mobility post-surgery for necessary exercises like coughing or deep breathing
Special Types of Pain
Neuropathic Pain: Chronic pain due to nerve damage, often described as burning/stabbing/tingling
Neuralgia: Sharp, sudden pain along a nerve path due to irritation or damage
Phantom Limb Pain: Sensations or pain felt in an amputated limb
Spinal Cord Function
Function: Transmits signals between brain and body; controls reflexes
Structure: Long, cylindrical structure from brainstem to lower back
Function in Neural: Basic motor control and sensation; damage leads to paralysis or sensation loss
Brain Stem Function
Function: Regulates life functions (heart rate, breathing, swallowing)
Structure: Includes midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Function in Neural: Communication pathway for brain and spinal cord; controls autonomic functions, manages reflexes
Motor Cortex Function
Function: Responsible for Voluntary movement control
Structure: Located in frontal lobe, specifically in precentral gyrus
Function in Neural: Signals to muscles for voluntary movements; damage can lead to motor issues or paralysis
Cerebellum Function
Function: Coordinates movement and maintains balance
Structure: Back of the brain, below occipital lobes
Function in Neural: makes sure of smooth, coordinated movements; damage can cause ataxia (loss of coordination)
Skeletal Muscle Disorders
Muscle Atrophy: Weakening/shrinking due to disuse/injury/disease
Muscular Dystrophy: Genetic disorder causing progressive muscle weakness
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Median nerve compression in wrist causing pain/numbness
Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Immune system attacks peripheral nerves, causing weakness
Herniated Disk: Ruptured/slipped spine disk causing pain and nerve compression
Parkinson's Disease: Neurodegenerative disorder with tremors and rigidity due to dopamine loss
Spinal Cord Injury Effects
Injury Levels
Cervical (C1-C7): Paralysis below the neck.
Quadriplegia (all four limbs paralyzed)
breathing = IMPAIRED (life threatening; happens to a lot of sports figures)
C = cervical & C= CAN’T MOVE
Thoracic (T1-T12): Paraplegic (lower body 2 legs, pelvic organs)
think T for trunk of the body (lower end)
T = Thoracic injury & T = trunk & legs
Lumbar (L1-L5): Think of double L’s = legs & leaky bladder
L = legs & L = leaky bladder
Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction
Vasovagal Response: Sudden heart rate and blood pressure drop; may cause fainting
triggers: stress, pain, standing too quickly
Autonomic Dysreflexia: High blood pressure spike in individuals with spinal cord injuries
triggers: overstimulation of autonomic nervous system
Postural Hypotension: Blood pressure drops upon standing; may lead to dizziness or fainting
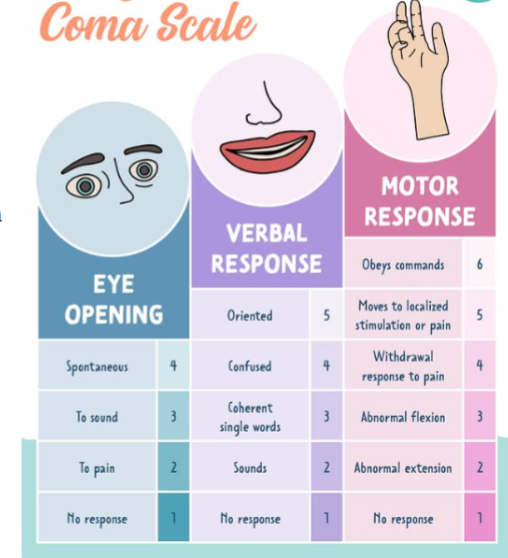
Glasgow Coma Scale - assess level of consciousness
Eye Response (4): Indicates alertness and awareness
Verbal Response (5): Assesses brain function, memory, and awareness
Motor Response (6): Evaluates muscle movement control; checks brain-body connections
max points is 15
7 is comatose
Posturing Types
Flexed, Extended, Adducted, Plantar Flexed: Various postures that reflect neurological status
decerebrate - arms flexed away from core
decorticate - arms flexed into core
Stroke Types
Ischemic Stroke: Result from a blockage (clot)
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Involves bleeding in/around brain, often with increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma: Increased intraocular pressure can lead to glaucoma, a condition that damages the optic nerve and can result in vision loss if not managed effectively.
Primary open-angle glaucoma is a common eye condition where the eye's pressure increases, damaging the optic nerve and possibly causing vision loss. It develops slowly and often has no early symptoms. Risk factors include age, family history, and other health issues. Regular eye check-ups are important for early detection and treatment.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma: This type occurs when the iris is very close to the drainage angle in the eye, leading to a sudden increase in intraocular pressure. Symptoms may include severe eye pain, headache, nausea, and vomiting. It is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent vision loss.
Eye Movements
**Amblyopia:** Lazy eye; one eye has reduced vision because the brain favors the other eye.
**Nystagmus:** Uncontrolled eye movements that can affect vision and balance.
**Strabismus:** Crossed eyes; eyes do not align properly, which can cause double vision.
**Myopia:** Nearsightedness; distant objects look blurry while close objects are clear.
**Astigmatism:** Blurred vision caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
**Hyperopia:** Farsightedness; distant objects are clear, but close objects look blurry.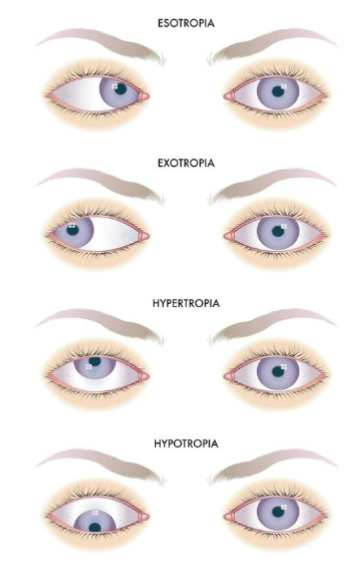
Hearing Loss Types
Conductive Hearing Loss
Definition: Problems in outer/middle ear preventing sound waves from reaching the inner ear
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Definition: Damage to cochlea or auditory nerve pathways
Diagnostic Tests
**Romberg Test**: A clinical diagnostic assessment used to evaluate an individual's balance and proprioception (the body's ability to sense its position in space). During the test, the patient stands with their feet together and arms at their sides, first with their eyes open and then with their eyes closed. The test checks for swaying or loss of balance, which can indicate issues with the vestibular system or sensory input. A positive Romberg sign (failure to maintain balance) may suggest neurological conditions that affect balance.
External Ear Disorders
Impacted Cerumen
Definition: Blockage from accumulated cerumen in ear canal
Causes: overproduction of cerumen, use of cotton swabs, narrow ear canal, hearing aids
Symptoms: Hearing loss, ear fullness/pressure, pain, tinnitus (ringing in ear), dizziness, balance issues
Management: Professional removal, ear drops, irrigation
Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Definition: Infection/inflammation of the external auditory canal
Causes: water exposure (swimming, bathing), mechanical injury (scratching, use of cotton swabs), allergies or skin condition (eczema, psoriasis)
Symptoms: Itching, pain, redness, discharge (clear, yellow pus like)
Management: Antibiotic/fungal ear drops, pain relief, avoidance of moisture
Barotrauma
Causes: Rapid ascent/descent or Eustachian tube dysfunction
Symptoms: Ear pain, hearing loss, pressure, possible bleeding or rupture of ear drum
Management: prevention: yawning, swallowing, chewing gum, use nasal decongestants prior to flying/diving, if rupture occurs seek medical attention for possible ear drops or antibiotic treatment
Otosclerosis
Causes: Genetic factors, more common in women
Symptoms: Gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, difficulty in hearing in loud noisy environments
Management: Hearing aids, possible stapedectomy (removal of affected bone), a prosthetic device can SOMETIMES replace the stapes
Disorders of inner ear: Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Causes:
Exposure to loud noise (e.g., concerts, machinery)
Ear infections or blockages (e.g., impacted cerumen)
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis)
Ototoxic medications (e.g., certain antibiotics, anti-inflammatories)
Head or neck injuries
Medical conditions (e.g., Meniere's disease, acoustic neuroma)
Symptoms:
Ringing, buzzing, hissing, or roaring sounds in the ears
Sounds may vary in pitch and volume
May be perceived in one or both ears
Can interfere with concentration or sleep
Diagnosis:
Medical history assessment
Physical examination (head, neck, ears)
Hearing tests (audiometry)
Imaging tests if needed (e.g., MRI, CT scan) to rule out underlying conditions
Management:
Sound therapy: Use of white noise machines or hearing aids to mask tinnitus
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps manage the impact of tinnitus on quality of life
Medications: Antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs for associated conditions
Lifestyle changes: Stress management techniques, avoiding loud noises, and limiting caffeine
Hearing aids: If hearing loss is also present, they can help reduce the perception of tinnitus.
Disordered Hearing in Children
Even mild or unilateral hearing loss can affect a young child's language development, with 1 to 3 babies per 1,000 born with permanent hearing loss.
Causes of Hearing Impairment
Hearing loss in children can be conductive or sensorineural. Genetic causes contribute to about 50% of sensorineural hearing loss.
Postnatal Causes
After birth, sensorineural hearing loss can be caused by infections like bacterial meningitis or sepsis, toxins (e.g., ototoxic drugs), or trauma. Congenital cytomegalovirus is a leading cause of hearing loss in newborns.
Screening and Intervention
The AAP recommends universal screening for all infants before 1 month of age, with intervention by 6 months. Children with risk factors for delayed hearing loss should receive ongoing monitoring, and a developmental and speech evaluation is needed once hearing loss is identified.
Hearing loss in Older Adults
Presbycusis refers to age-related degenerative hearing loss, affecting approximately 45% of individuals aged 65 and older. It is a common social and health issue due to its high prevalence.
Characteristics:
Gradual, bilateral hearing loss.
Typically involves high-frequency loss.
Leads to difficulty in understanding speech, especially in noisy environments, and challenges with sound localization.
Causes and Symptoms:
Likely resulting from a combination of aging, auditory stress, trauma, and otologic diseases.
Common complaint: difficulty understanding speech rather than the inability to hear, particularly for high-frequency sounds like beepers or alarms.
Screening and Treatment:
Annual screening recommended for older adults, often involving the question, "Do you have a hearing problem?"
Effective treatments include hearing aids, lipreading, and assistive devices.
Cochlear implants are recommended for severe hearing loss unresponsive to hearing aids.
Vestibular System Disorders
Peripheral Vestibular Apparatus
What they are: The peripheral vestibular apparatus includes structures in the inner ear that help maintain balance and spatial orientation.
Vertigo
Symptoms: Sensation of spinning or dizziness, balance issues, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Treatments: Treatment options include medications (antihistamines, anticholinergics), vestibular rehabilitation therapy, and in some cases, surgery if caused by specific disorders.
Motion Sickness
Symptoms: Dizziness, sweating, nausea, vomiting, and general discomfort when traveling.
Treatments: Antihistamines (like dimenhydrinate), prescription medications (like scopolamine patches), and behavioral techniques (such as looking at stable objects).
Meniere Disease
Symptoms: Episodes of vertigo, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), fluctuating hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Treatments: Diet changes (low salt), diuretics, medications for vertigo, and in some cases, surgical options to relieve pressure in the inner ear.
vertigo
motion sickness
Meniere disease
Red Blood Cell Disorders
Normal CBC Levels
WBC: 4,500–11,000
Hemoglobin: 11–18 g/dL
Hematocrit: Women 36-44%, Men 41-50%
Platelets: 150,000–450,000
Lab Work Types
Complete blood count (CBC): red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelets
hemoglobin & hematocrit: H&H tests are performed to rule out anemia
Type & Screen: Identifies blood type and antibodies for transfusions
blood type: patient’s red blood cells are typed for their ABO and Rh (D) blood type
antibodies: the patient’s plasma is screened for the presence of antibodies that could cause a transfusion reaction
Blood Transfusion Reactions
Monitoring: Start slow, watch for adverse reactions, and replace with normal saline if needed
Start administration slowly (approximately 2–3 mL/min for the first 15 minutes).
Stay with the patient for the first 15 minutes of transfusion.
Assess the patient at least every 30 minutes for adverse reactions.
Stop the blood transfusion if you suspect a reaction.
Quickly replace the blood tubing with a new administration set primed with normal saline for IV infusion.
Initiate an infusion of normal saline for IV at a keep open rate, usually 40 mL/hr.
Obtain vital signs.
Notify the health care team and the blood bank/transfusion service.
Blood Disorders
Anemia: Deficiency in red blood cells, leads to fatigue & weakness
Sickle Cell Disease: Genetic disorder causing abnormal blood cells [cause blockage in blood flow]
Thalassemia: Reduced hemoglobin production, leads to anemia
Polycythemia: Overproduction of red blood cells [can lead to blood clots]
Neutropenia: Low neutrophil counts increasing infection risk
Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas group of cancers originating from the lymphatic system, affecting white blood cells
Leukemias: cancers of the bone marrow and blood, leads to overproduction of abnormal white blood cells
Multiple Myeloma: Cancer of plasma cells in bone marrow affecting production of normal blood cells