12-05: Trigonometric Equations
Trigonometric Functions
- Periodic function: a function where the y values repeat over regular x value intervals
Key properties
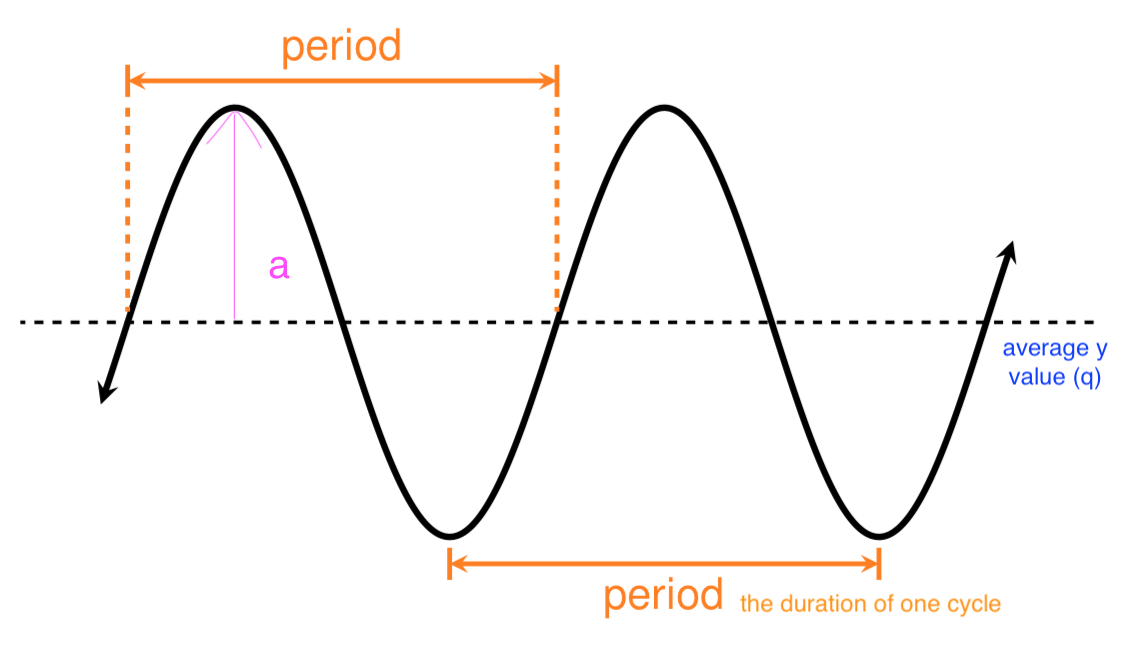
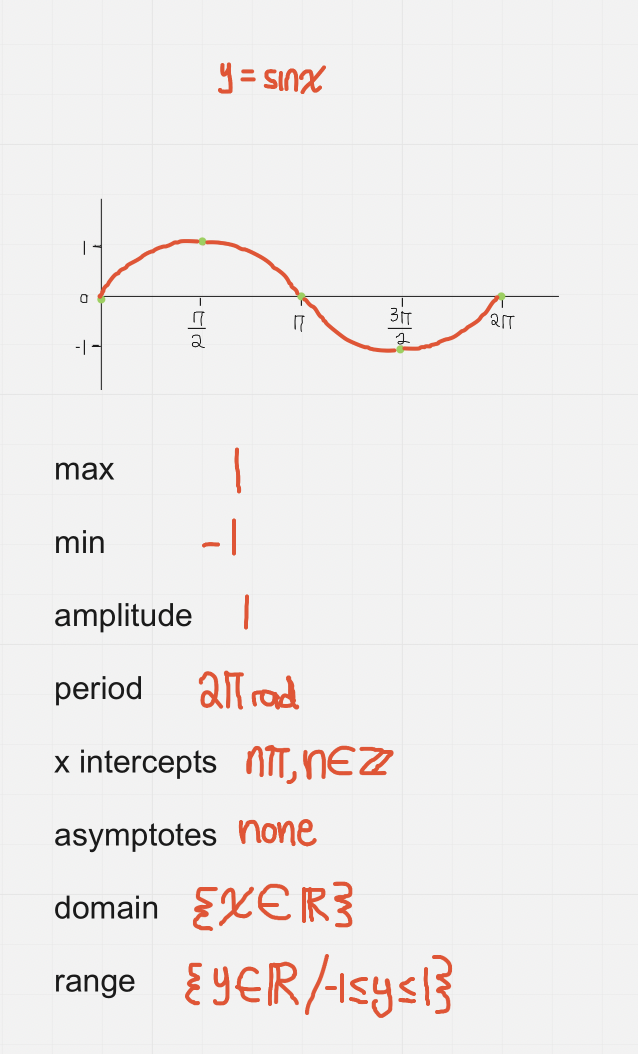
y = sinx
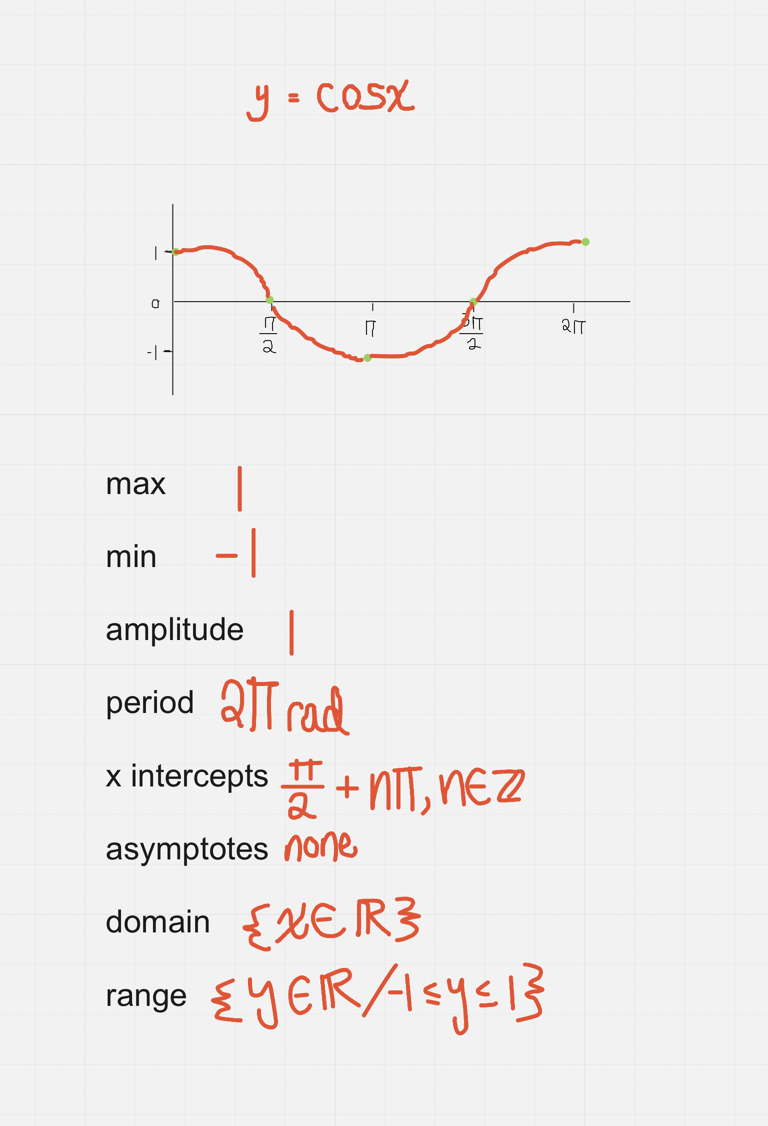
y = cosx
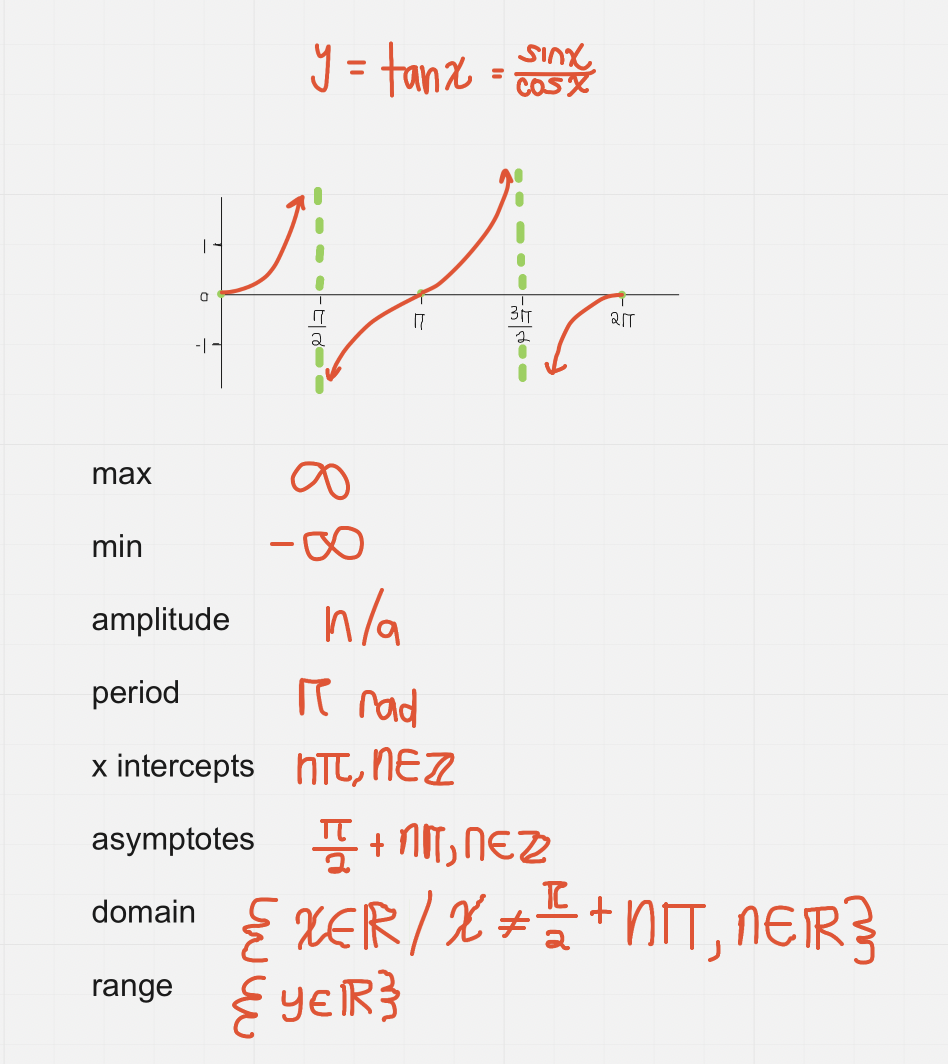
y = tanx
Properties of Secondary Trig Functions
y = cscx
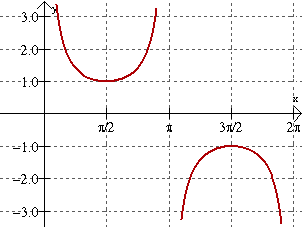

y = secx
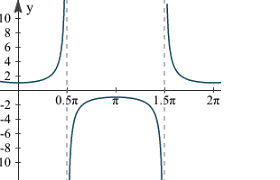

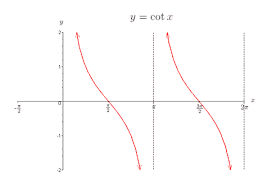
y = cotx

Transformations of Sine and Cosine
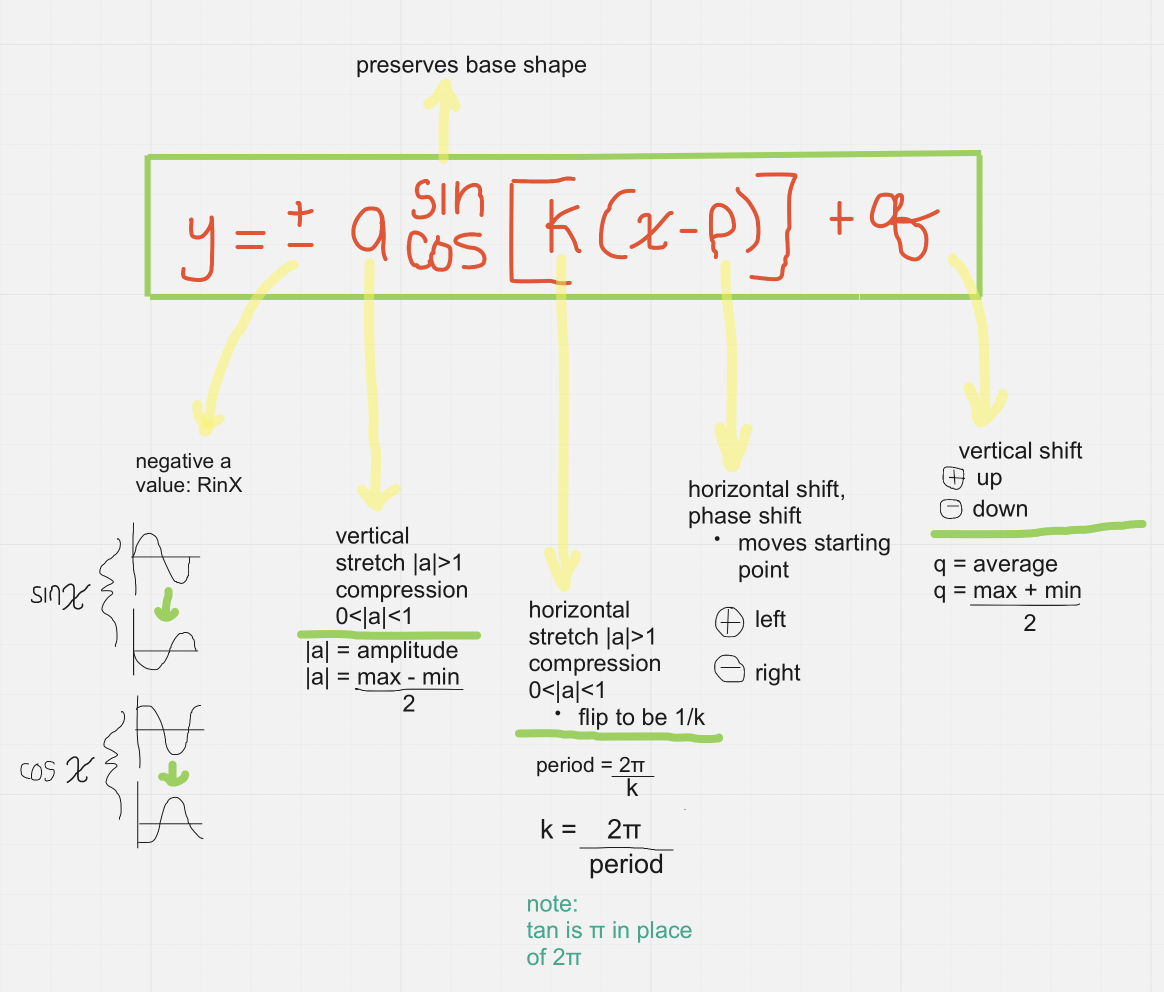
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
Mapping
(x,y) → (1/k x - p, ay + q)
| SINE | COSINE |
|---|---|
| (0,0) → ( _ , _ ) | (0,1) → ( _ , _ ) |
| (π/2, 1) → ( _ , _ ) | (π/2, 0) → ( _ , _ ) |
Average (sine), Max (cosine), Average, Min
Properties (Graph with x and y scale)
y-scale
avg = q
max = q + |a|
min = q - |a|
x-scale
period = 2π / k
QI (quarter intervals) = Period/4
avg (Sin), max (Cos), avg, min, (and so on)
Solving Trigonometric Equations
Strategies
Rearrange (isolate for trig ratio)
Factor (exponents, same ratios repeats)
Identities (multiple ratios)
- CAST rule must always be considered
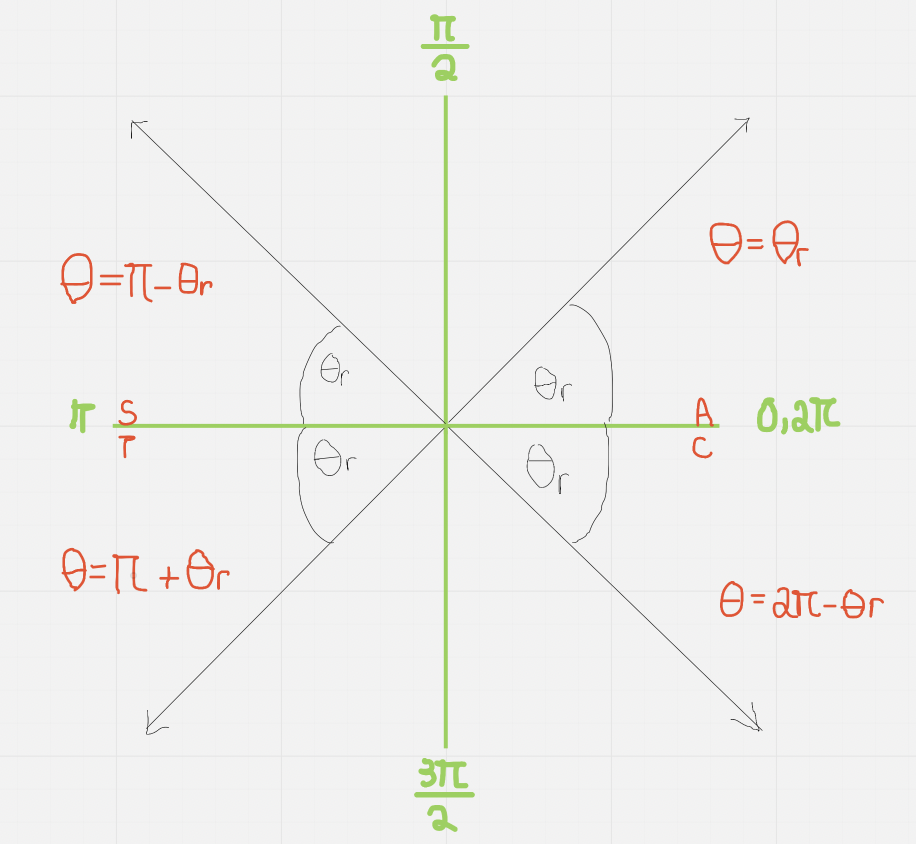
Solving for Angles:
| Approx. | Exact |
|---|---|
| Decimals | No decimals |
| Calculator: sin⁻¹( ), cos⁻¹( ), tan⁻¹( ) | Special Triangles, main coordinates |
Solving Trigonometric Equations
Strategies
- Rearrange - isolate for trig ratios
- Factor - exponents, same ratio repeats
- Identities - multiple ratios
In all cases: must consider CAST rule
Applications and IROC
AROC: average rate of change - slope of secant of curve
IROC: instantaneous rate of change - slope of tangent line (+ and - 0.001)
slope = ∆y/∆x
slope =( y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)