Organic Chemistry
Polymer
The process of joining single monomer together to form longer chain polymers is known as polymerisation
Propene (C3H6) → Polypropylene or polypropene 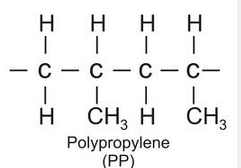
Chloroethene (vinyl chloride [C2H3Cl]) → Polychloroethene (PVC)
Condensation polymerisation
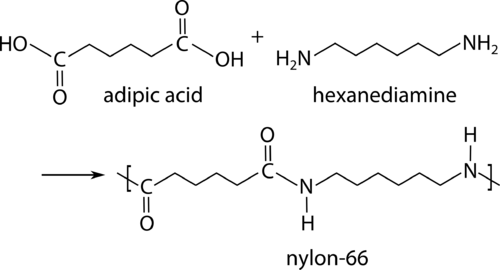
Monomer
Alkene - C2h4
Combustion - alkanes as fuels
Alkanes burn in the presence of excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water
C3H8(g) + 5O2 (g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O (g) ΔΗ= -2220KJmol-1
2C3H8(g) + 7O2 (g) 3CO (g) + H2O (g) (INCOMPLETE COMBUSTION )
C3H8(g) + 2O2 (g) 3C(g) + 4H2O (g) (Extreme Oxygen limitation)
Substitution reactions of alkanes: Halogens
Radical Symbol: .
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Steps: Free Radical mechanism of alkanes
Initiation: Cl2 → 2 Cl. radicals
Propagation (A continues chain reactions {doesn’t stop}): Cl. + CH4 → CH3 + Cl
CH3. + Cl2 → CH2Cl. + HCl
Termination: Cl. + Cl. → Cl2
CH3. + Cl.
Addition of Hydrogen (Hydrogenation)
CH3 CHCH2+H2 → CH3CH2CH3
(propane) (propane)
- Hydrogen reacts with alkenes to form alkanes in the presence of nickel catalyst.
- The process, known as hydrogenation is used in the margarine (oils) industry to convert oils containing many unsaturated hydrocarbon chains into more saturated compounds which have higher melting points.
Addition of halogens
Propene + Br2 → 1,2-dibromopropane
Halogens reacts with alkenes to produce dihalogeno compounds.
These reactions happen quickly at room temperature,
accompanied by lose of color of reacting halogen.
Addition of hydrogen halides
Ethene +HCl → Chloroethane
Hydrogen halides, such as HCl an HBr react with alkenes to produce Halogenoalkanes
Addition of Water
Ethene → Ethyl Hydrogensulfate → Ethanol
This reaction with water is known as hydration and coverts the alkenes into alcohol.
Conditions : Heat with steam and catalyst of conc. Sulphuric acid
The reaction involves an intermediate in which both h+ and HSO4 -ions are added across the double bonds, but this is quickly followed by hydrolysis with replacement of HSO4- by HO- and reformation of H2SO4.