Common Injuries in the Foot
- Fractures
- Mechanism of Injury (MOI): caused by direct trauma from contact with the ground or an opponent
- Fractures in specific areas of the foot that occur frequently are given particular names to designate the location of the injury
- Example- Jones Fracture: most common acute injury to the foot, occurs at the proximal base of the fifth metatarsal
- Signs and Symptoms (S&S)
- Pain and swelling at injury site
- Possible deformity of the bone
- Discoloration or redness
- Athlete heard a pop or snap
- Athlete unable to bear weight
- Hesitation to ambulate
- Treatment
- Depend on the location of injury
- Phalanx Fracture vs Metatarsal or Tarsal bone
- Immobilization: walking boot, crutches (NWB)
- Rehabilitation
- Stress Fracture
- MOI: overuse
- Can occur in any bone in the foot but most common in the metatarsals (2nd and 5th)
- March Fracture: stress fx to the 2nd metatarsal (high occurrence rate in the military during basic training
- S&S:
- Gradual onset of pain (achy)
- Sensation similar to a rock in their shoe while running or walking
- Can lead to Stress Reactions: bone attempts to repair healthy bone tissue to protect itself.
- This increases the stress fx stage as bone becomes weaker and eventually breaks down
- Treatment
- Immobilization
- Rest to bone stimulation
- Surgical intervention
- Orthotics to long term reduce forces or correct mechanics
- Rehabilitation
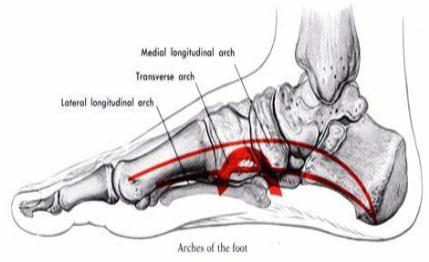
- Arch Strain/Sprain
- MOI: Hyperextension of the midfoot, often resulting from contact with an uneven surface or twisting motion during running
- Longitudinal arch most common one sprained/strained
- Damage to the muscles, ligaments and/or fascia that assist in the formation of the arch
- Because multiple structures are damaged we use sprain and strain
- S&S:
- Pain and tenderness over injury site
- Swelling (usually seen on medial aspect of arch)
- Pain with running and cutting
- Treatment:
- RICE
- Arch tape, orthotics
- Return to Play (RTP)
- Spring Ligament Sprain
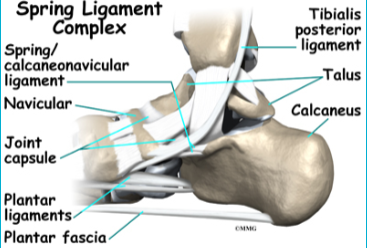
- Plantar Calcaneonavicular Ligament (Spring Ligament)
- Important component of the longitudinal arch and assists in the shock absorption and maintaining the integrity of the arch
- MOI: running on uneven surfaces and stepping in holes or divots
- S&S
- Pain and tenderness distal to the heel of the foot on the medial aspect of the arch
- Pain with weight bearing
- Slight swelling over injury site
- Treatment:
- RICE
- Orthotics or padding to provide support
- RTP as tolerated
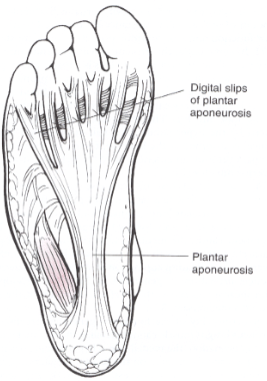
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fascia: fibrous tissue on the bottom of the foot that runs the length of the foot to help strengthen the arch complex
- The fascia can become inflamed as a result to chronic stress.
- The initial stress causing the fascia to tighten, which decreases range of motion (ROM) and increases the stress on the tissue.
- As the stress increases, the tightness and inflammation increases causing more damage to the fascia.
- MOI: overuse/chronic, anatomy
- S&S
- Pain most often at the distal aspect of the heel on the lateral side
- Pain that is most severe with the first steps out of bed in the morning
- Tightness and decreased ROM at the midfoot
- Slight swelling at injury site
- Treatment:
- Ultrasound therapy
- Ice massage
- Friction massage (tennis or lacrosse ball) -> break down scar tissue
- Stretching
- Medication
- Night Splint (keep dorsiflexed position)
- Heel Contusion
- MOI: stepping on a hard object or jumping from a high height
- Injury may also develop chronically from repetitive compression (worn down shoes without proper cushioning)
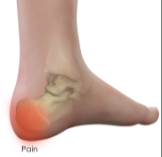
- S&S
- Point tender on heel
- Slight discoloration
- Pain with ground contact
- Treatment
- RICE
- Heel cup or heel taping when playing sports
- X-ray to rule out fx
- Turf Toe
- Sprain of the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint
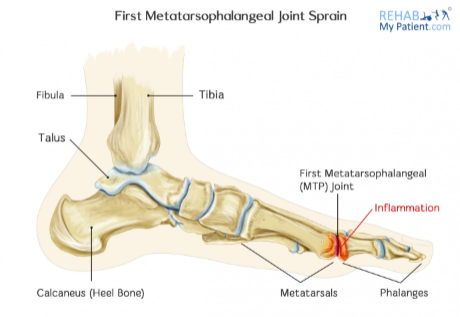
- MOI: hyperextension or hyperflexion motion of the joint
- S&S
- Pain at 1st MTP joint
- Pain with flexion or extension of 1st MTP
- Pain and discomfort with running, especially push off
- Slight swelling and discoloration
- Treatment
- RICE
- Referral to physician to rule out fx
- Turf toe tape or steel insole to decrease motion
- Bunion and Bunionette
- Bunion: protrusion medially from 1st metatarsal head, inflammation of the synovial bursa resulting in the enlargement of the joint and lateral displacement of the toe
- Bunionette: similar injury expect it occurs at the 5th metatarsal
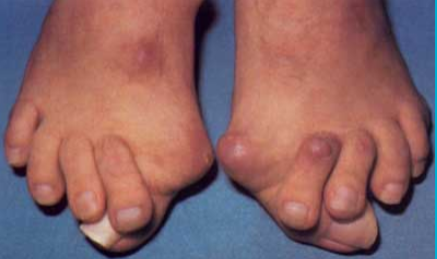
- MOI: chronic and increases in size over time, 1st metatarsal head moving medially causing inflammation in surrounding tissue and forcing the first toe in the opposite direction
- S&S
- Pain, especially with shoes on
- Redness and swelling
- Obvious protrusion of the 1st or 5th metatarsal with opposite movement of the associated toes
- Treatment of Bunions/Bunionettes
- Ice
- Shoe change
- Surgical intervention
- Padding





