BIOLOGY
CELL STRUCTURE
2 types of cells are prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
PROKARYOTES
bacteria cells
cell wall doesnt contain cellulose
extra rings of DNA called plasmids
genetic material not in the nucleus
EUKARYOTES
animal or plant cells
genetic material enclosed in the nucleus
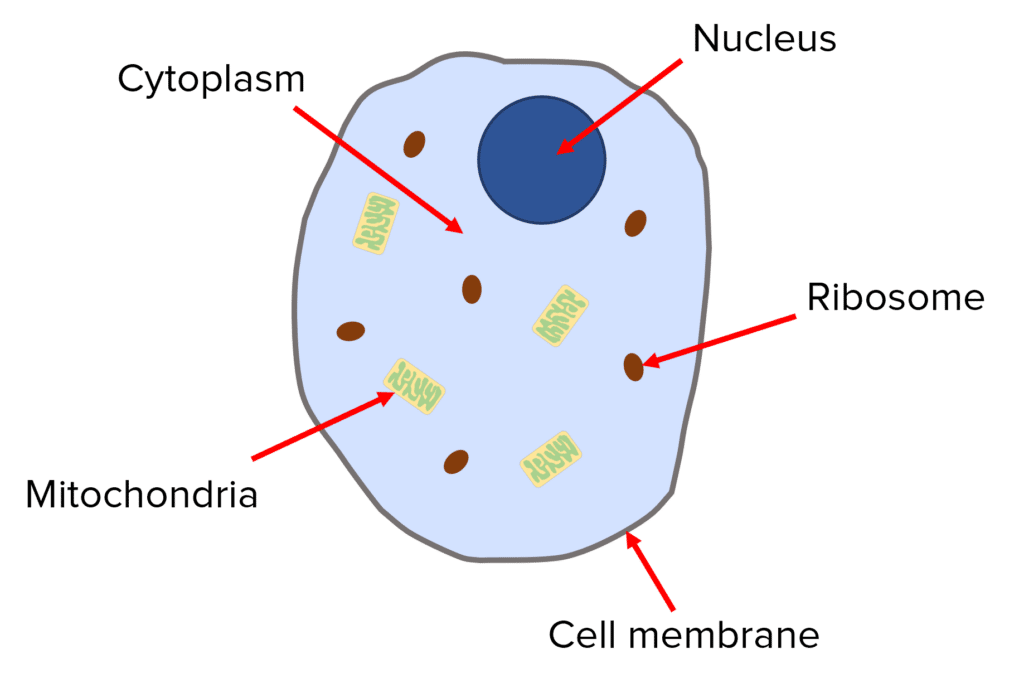
NUCLEUS - Surrounded by the nucleur membrane and contains genetic material which controls all of the activities of the cell
Ribosomes- Where protein synthesis takes place making all of the protein needed for the plant
Cell membrane - Holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out
Cytoplasm - a gel like substance where chemical reactions take place. Also contains enzymes that help control these chemical reactions
Mitochondria - where aerobic respiration takes place providing all of the energy needed for the cell
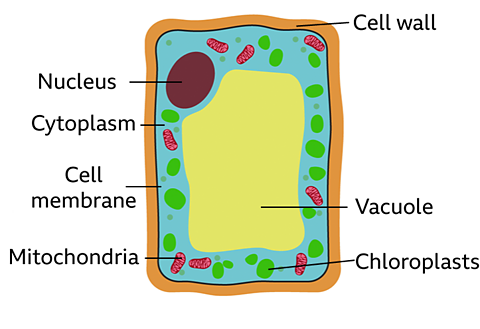
Vacuole - contains cell sap and a weak solution of sugars and salts. Also gives strength to the cell
Chloroplasts - where photosynthesis takes place providing all of the food needed for the plant. Also contains a green substance called chlorophyll providing all of the light needed for photosynthesis.
/
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - USING A LIGHT MICROSCOPE TO VIEW ONION CELLS
first add a drop of water to the middle of a clean slide.
Then cut up and onion and seperate it out into layers. Use tweezers to peel off some epidermal tissue from the bottom of one of the layers. Using the tweezers place the epidermal tissue into the water on the slide.
Add a drop of iodine solution which is a stain used to highlight any objects by adding colour to them. This helps to see parts of the cell.
Place a cover slip on top. To do this, stand the cover slip upright next to the water droplet. Then carefully tilt and lower so it covers the specimen. Try not to get any air bubbles underneath otherwise it will obstruct your view.
USING A LIGHT MICROSCOPE TO LOOK AT YOUR SLIDE
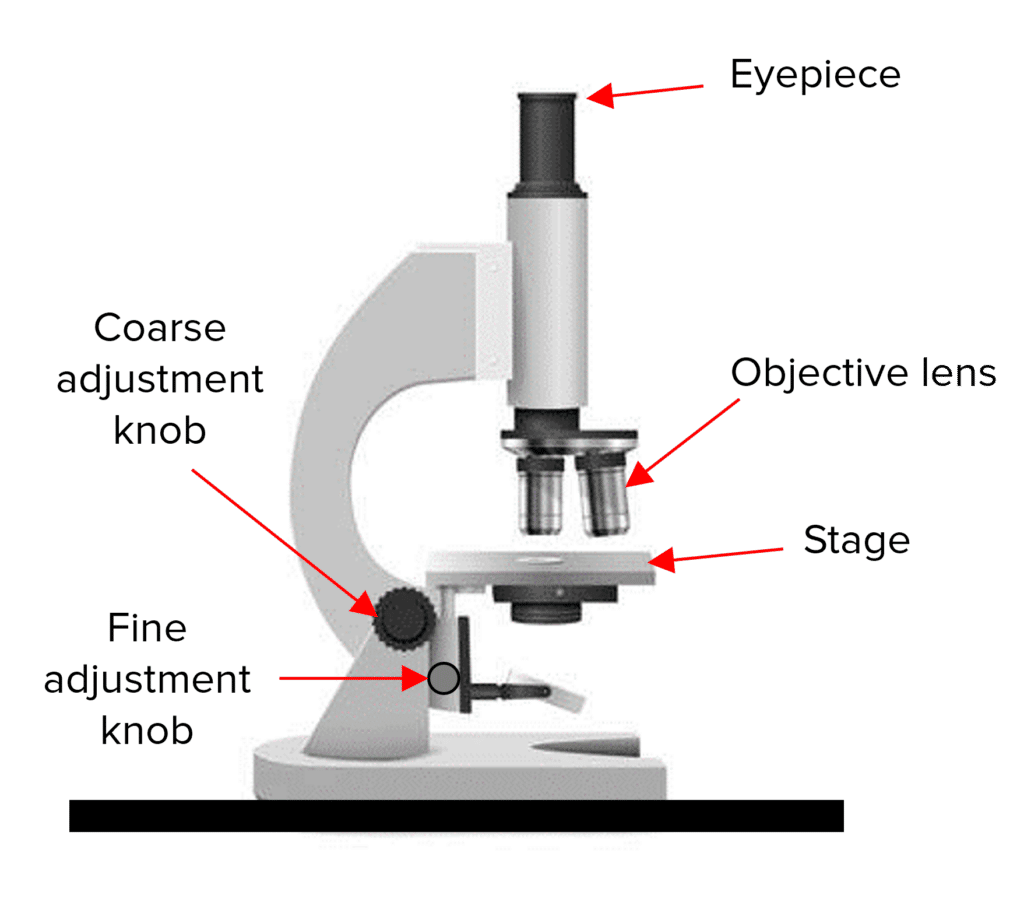
Place your slide on the stage
Select the lowest powered objective lens which is the one with the lowest magnification
Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the stage up until it is just below the objective lens
Look down at the eyepiece. Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the stage down until the image is roughly in focus.
Adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob until you get a clear image of whats on the slide.
HOW TO DRAW YOUR OBSERVATIONS
Make sure they are in pencil
include a title
label any subcellular structures
Specialised cells
Sperm cells - They are specialised for reproduction. Their function is to transfer the male DNA to the female DNA. They have a long tail and streamlined head to help swim to the egg. They also have lots of enzymes to help break through the egg cell membrane.
Nerve cells - They are specialised for rapid signalling. There function is to carry electrical signals from one part of the body to the other. They have branched connections to connect to other nerve cells and form a network around the body.
Muscle cells - Their function is to contract quickly. They are specialised for contraction. They are long to provide the space needed for contraction and have lots of mitochondria to provide the energy needed for contraction.
Root hair cells - Specialised for absorbing water and minerals. They are cells on the surface of plant roots which grow into long hairs that stick into the soil giving the plant a large surface area for absorbing more water and minerl ions from the soil.
Phloem and Xylem cells - Specialised for transporting substances. They form Phloem and Xylem tubes which transport food and water around the plant. To form the tubes the cells are long and joined end to end. Xylem cells are hollow in the centre whereas Phloem have very few subcellular structures so that stuff can flow through them.
1Cell differentiation
Cell differentiation is the process by which a cell becomes specialised for its job.
Cell differentiation in animals takes place in the very early stages of development being just the zygote after the sperm and egg cells fuse. They will then keep dividing until they are just a ball of cells called the embryo. Then once a baby is fully born they already have all of there specialised cells, this happens by genes being switched on off so that each specialised cell can produce a specific selection of protein. Specialised cells divide by mitosis to produce more of those specialised cells, but once you are an adult and fully grown, mitosis isnt for growth but for replacing and repairing worn out cells.
Cell differentiation in plants takes place throughout the life of a plant cells. It takes place in actively growing regions called the meristem and stems and roots are the meristem; mitosis often occurs here growth. This means that you can take a cutting from the tip of a root or a shoot, plant it in soil, and from that tiny cutting an entire new plant will grow.
Culturing microorganisms
Bacteria can be grown in a culture medium which contains all of the proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins that they need to grow.
The culture medium used can be nutrient broth solution or a solid agar jelly.
Bacteria grown on agar plates will form visible colonies on the surface of the jelly.
To make an agar plate, hot agar jelly is poured into a petri dish. Once it has cooled or set, Inoculating loops will will be used to transfer microorganisms to the culture medium. Or a sterile dropping pipette and spreader will create an even covering of bacteria. The microorganisms then multiply.
In labs at school, the cultures of microorganisms are not kept in temperatures above 25 degrees otherwise pathogens will grow.
In industrial conditions, the cultures are kept higher temperatures so that they can grow faster.
PRACTICAL : How to investigate the effect of different antibiotics on bacterial growth
First you place a paper disc soaked in different types of antibiotics on a agar place with a even covering of bateria. The antibiotic should then diffuse into the agar jelly. The antibiotic resistant bacteria will continue to grow however the non resistant strain will die. You must make sure you use a control, which is a paper disc not soaked in antibiotic and instead soaked in sterile water. You then leave it for 48hours at 25 degrees.

Answer to Q:
First the petri dishes must be sterilised before using, to kill any unwanted pathogens. Also the inoculating loop must be passed through a flame killing any bacteria. During the inoculation, the student should make sure the lid of the petri dish is opened as little as possible preventing microbes from the air entering. In addition, after the inoculation they should also incubate the culture allowing the growth of the bacteria.
Microscopy
Microscopes allow people to see things that cant be seen with the naked eye. extremely small structures such as cells cant be seen without a microscope meaning they enlarge the image.
LIGHT MICROCOPES
Light microscopes were first developed in the 17th century and their development has continued ever since.
They have a magnification of x2000
They are cheap
They can be used anywhere
They allow you to view specimens
They use a beam of light to an image of a specimen
ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
They were first developed in the mid 1900s and they allow biologists to view deep inside subcellular structures
They are large
They are expensive
They have a magnification of x2,000,000
They must be kept in special pressure , temperature and humidity controlled rooms
They use a beam of electrons to form an image
Magnification = Image size/real size
Cell division
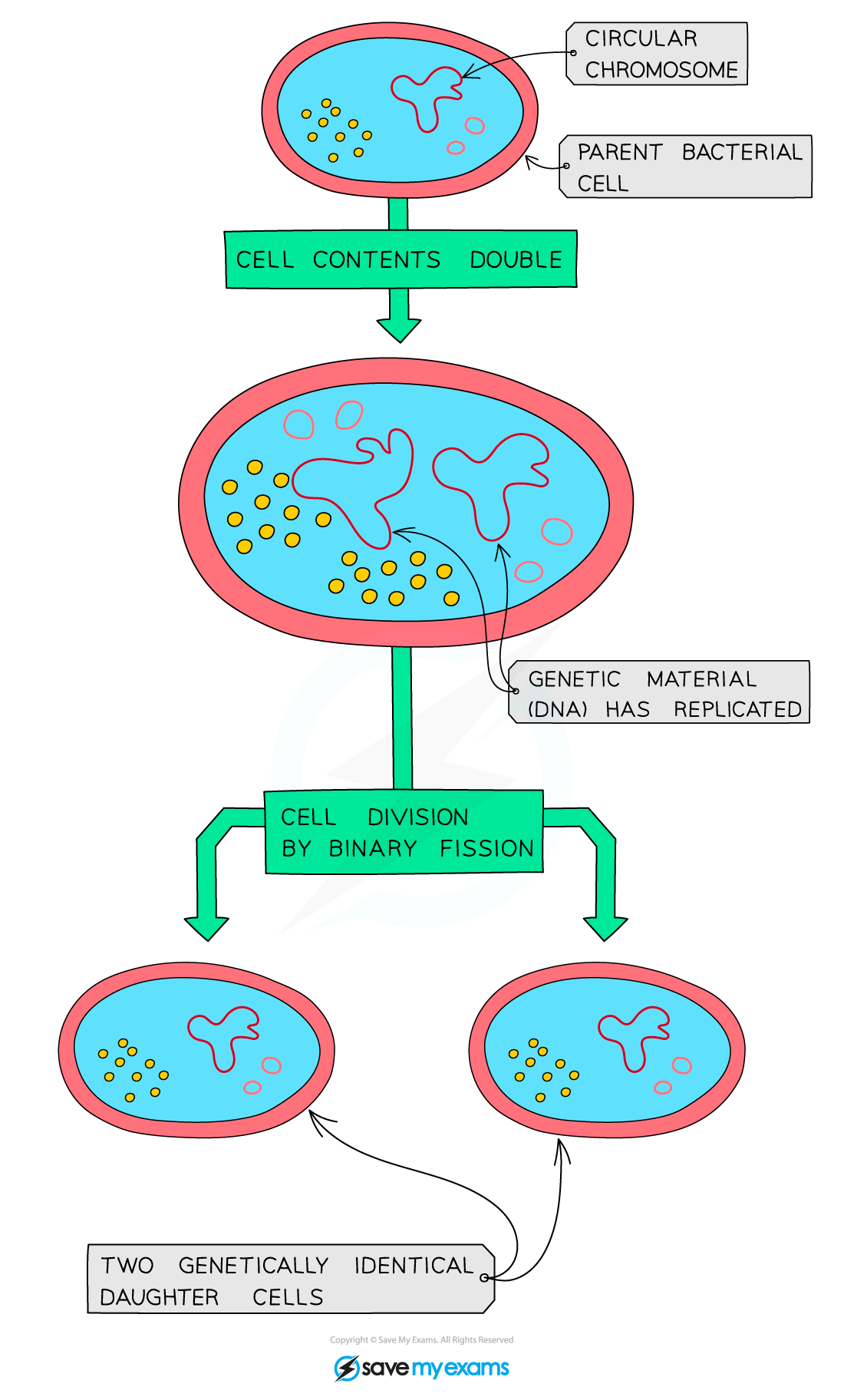
BINARY FISSION
Its the process by which prokaryotic organisms like bacteria divide and reproduce
First, the circular DNA and plasmids replicate. Then, the cell gets bigger and the circular DNA strands move to either poles of the cell. Next, the cytoplasm begins to divide and a new cell wall begins to form. Finally, the cytoplasm divides and two new 2 daughter cells are produced. They both have one copy of circular DNA but a variable number of Chromosomes.
Bacteria can only divide if they are kept in the right conditions like a warm environment. Some, like E coli can take as little as 20 mins to replicate in the environment. However if conditions are unfavourable then the bacteria will stop dividing and eventually die.
Cells contain a nucleus which contain chromosomes containing the genes that control a characteristic in your body.
There are 46 chromosomes in your body and 23 pairs. One is inherited from the mother and one is from the mother. However, in gametes chromosomes dont come in pairs meaning they only have 23.
Cell division involves a series of stages known as the cell cycle involving a process called mitosis which produces 2 identical daughter cells. This calls your body to have the same chromosomes and genetic material.
Mitosis is important for producing the additional cells needed for the growth and develepment multicellular organisms and for replacing worn out cells. Its also important for asexual reproduction.
STAGE 1 - This is the longest stage. This cell increases in size and carries on with its normal activities. The DNA then replicates to form two copies of chromosomes ready for cell division. It also increases in the number of subcellular structures ready for cell division.
STAGE 2 - Mitosis takes place. This is the process by which one set of chromosomes pulls to each end of the dividing cell and the nucleus divides.
STAGE 3 - The cytoplasm and cell membrane also divide producing two identical daughter cells.
STEM CELLS
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that divide to produce more of those undifferentiated cells
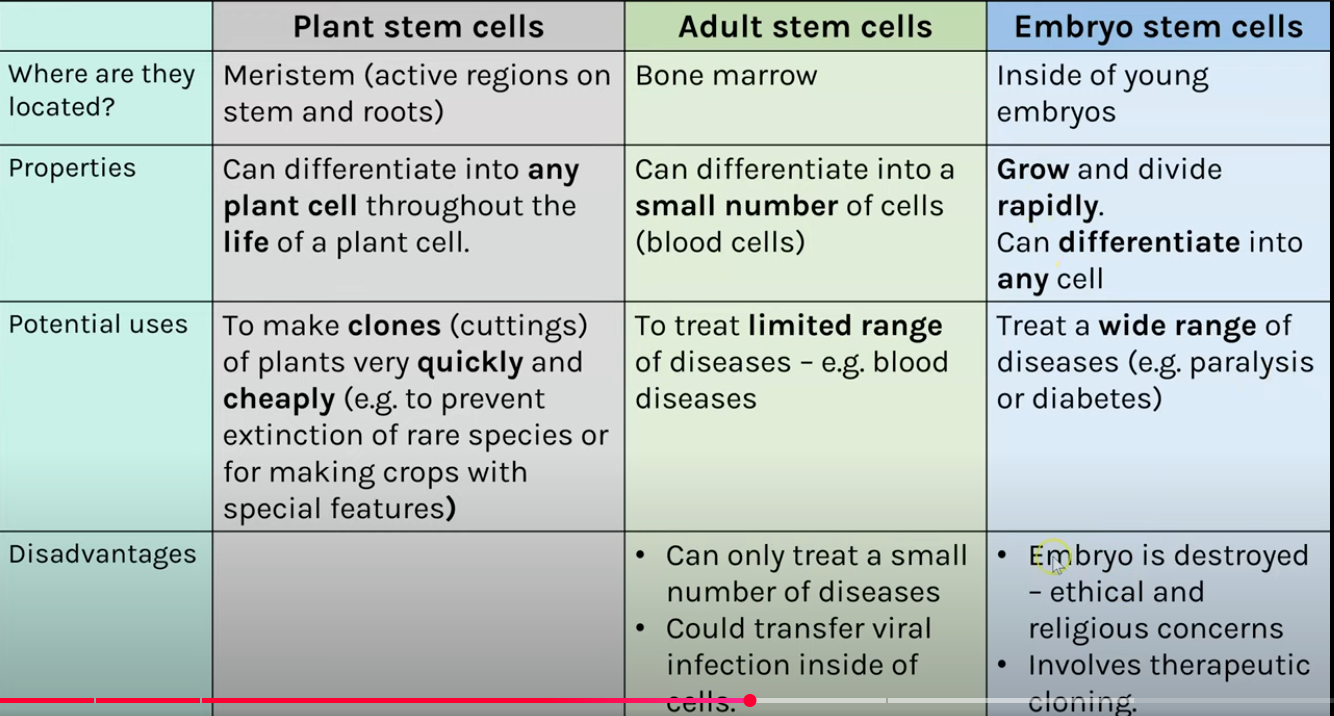
Therapeutic cloning is when an embryo is produced with the same genetic info as the patient meaning they can be used to treat diseases. However, A risk to stem cells is that they may transfer viral infections to the patient and people may have ethical or religious concerns.
DIFFUSION
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
If there is more particles on one side of the membrane than the other then there is a net movement overall from that side.
Factors affecting the rate of diffusion :
The bigger the concentration gradient the faster the rate of diffusion
The higher the temperature the faster the rate of diffusion because the particles have more energy meaning they move around faster
The bigger the surface area the faster the rate of diffusion because more particles will be able to pass through at once
OSMOSIS
The movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration across a partially permeable membrane.
A partially permeable membrane is a membrane with tiny holes in it. They are large enough to let tiny molecules like water through but not large enough to let larger molecules like sucrose.
The water molecules actually pass both ways during osmosis. This is because they are moving randomly all the time. But because there are more molecules on one side of the membrane than the other then there is a net flow of water molecules into the region with fewer water molecules (the stronger sugar solution). This means that the stronger solution becomes more dilute and acts as if its trying to even up the concentration either side of the membrane.
Required practical activity 3: investigate the effect of a range of concentrations of salt or sugar solutions on the mass of plant tissue.
You start by cutting a potato into identical cylinders. You then get some beakers with different sugar solutions. One should be pure water and the other should be a very concentrated sugar solution like 1 mole/dm. You then get a few others with concentrations in between like 0.4. Now you measure of the cylinders and leave them in a beaker for 24hrs or so. Next you take them out, dry them and measure the masses again. If they have drawn out water then the masses have decreased but if they have drawn in water then the masses have increased. Now plot a few graphs and measure the percentage change in mass. The Dependant variable is the mass of the chip and the independent variable is the concentration of the sugar solution. The controlled variable can be the time or temperature. Errors that could arise are the chips not being dried properly or the water evaporating.
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Communicable diseases are diseases that can be easily spread. It can happen in both plants and animals.
A pathogen is a microorganism that can enter the body and cause disease. Examples are viruses, bacteria, fungi and protists.
Bacteria are very small living cells that reproduce rapidly inside your body. They make you feel ill by producing toxins that damage your cells and tissues.
Viruses are not cells and much smaller. Like bacteria, they reproduce rapidly inside your cells however they live inside your cells and replicate using the cells machinery to form many copies of themselves. The cell will eventually then burst releasing all new viruses.
Fungi come in different shapes. Some are single celled and some are made out of a body called hyphae. These hyphae can grow and penetrate human skin and the surface of plants causing diseases. They can also produce spores that can spread to other plants and animals.
Pathogens can be spread in 3 ways:
By water - picked up when bathing or drinking dirty water
Direct contact - touching contaminated surfaces like skin
RESPIRATION
Respiration involves many reactions. These are important due to respration transferring all the energy a cell needs to do just about everything, this energy is used in all living processes.
Its the process of transferring energy from the breakdown of glucose which goes on in every cell in your body continuosly.
Respiration is the process of transferring energy from glucose which goes on in every cell .
Its exothermic meaning energy is transferred to the environment.
Examples of how organisms use the energy transferred by respiration :
To build up larger molecules into smaller ones (protein into amino acids )
In animals it allows muscles to contract so they can move about
In mammals and birds it keeps body temperatures steady in colder surroundings
Aerobic respiration needs plenty of oxygen. Its respiration using oxygen and the most effiecient way of transferring energy from glucose.
It happens all the time in plants and animals and mostly happens in mitochondria.
Glucose + oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water
C6H1206 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20
Anaerobic respiration is used if there is not enough oxygen. It happens when you start doing vigorous exercise and your body cant supply enough oxygen to your muscles.
Its the incompleted breakdown of glucose making lactic acid.
GLUCOSE → LACTIC ACID
DIFFERENCES :
aerobic energy transfers lots more energy than anaerobic. Anaerobic doesnt transfer as much due to glucose not being fully oxidised.
Anaerobic is only useful in emergencies
CONTROLLING BODY TEMPERATURES
Body temperatures must be kept constant at 37 degrees which is the optimum body temperature for enzymes in the body. The body must balance the amount of energy gained or lost to keep this core body temperature stable.
Thermoregulation is the control of internal of internal body temperatures.
To achieve stable temperatures, there is a thermoregulatory centre in the brain, which acts as a thermostat containing receptors that are sensitive to the temperature of blood flowing to the brain. It also receives impulses from temp receptors in the skin giving info about skin temperatures.
When the body warms up, Temperature receptors detect that body temperatures are too high. This causes the thermoregulatory centre to act as a coordination centre receiving info from the temperature receptors and trigger the effectors automatically. Effectors, such as sweat glands produce a response and counteract the change.
When the body cools down, Temperature receptors detect that body temperatures are too low. This causes the thermoregulatory centre to act as a coordination centre receiving info from the temp receptors which trigger the effectors automatically.
When your too hot sweat is produced by sweat glands and evaporates the skin. Meaning energy is transferred to the environment. Blood vessels supplying the skin dilate so that blood flows to the surface of the skin causing energy to transfer to the environment.
When your too cold hair stands up to trap insulating layer of air. No sweat is produced. The blood vessels suppling the skin capillaries constrict to close off the blood supply.
Filtration is when the kidney makes urine by taking waste products out of the blood. Substances are filtered out of the blood as they pass through the kidney.
Selective reabsorbtion is when useful substances like glucose, ions and the right amount of water are absorbed back into the blood.
The substances that remove from the body in urine include:
Urea- proteins cant be stored by the body. So any excess amino acids is converted into fats and carbohydrates which is stored. This takes place in the liver and involves a process called deamination. Ammonia is converted as waste in this process. Ammonia is toxic and is converted into Urea and stored in the liver. Urea is then transproted to the kidneys where its filtered out of the blood and excreted out through urine.
Ions - Ions such as sodium is taken into the body in food, and then absorbed into the blood. If the ion content of the body is wrong, this could upset the balance between ions and water, meaning too much or too little water is drawn into cells by osmosis. Some ions are lost in sweat however this amount is not regulated, so the right balance of ions in the body must be maintained by the kidneys.The right amount of ions is reabsorbed into the blood after filtration and the rest is removed through urine.
Water - The body has to constantly balance the water coming against the water going out. We lose water from the sweat in skin or lungs when breathing out.
The concentration of urine is controlled by ADH which is released into the blood stream by the pituitary gland. The brain monitors the water content in the blood and instructs the Pituitary gland to release ADH based on how much is needed.
If water content increases then the receptors in the brain detect that water content is too high. The Coordination centre in the brain release the information and coordinates a response. The pituatry gland then releases less ADH so less water content is reabsorbed by the kidney tubules.
If the water content is too low then the receptors in the brain detect that water content is too low. The coordination centre in the brain releases the information and organises a response. The Pituatry gland then releases more ADH so more water is reabsorbed by kidney tubules.
KIDNEY FAILURE
Kidneys remove waste substances from the blood.
If kidneys dont work properly then waste substances build up in the blood, and your body loses the ability to control the amount of ions and water in the body, resulting in death.
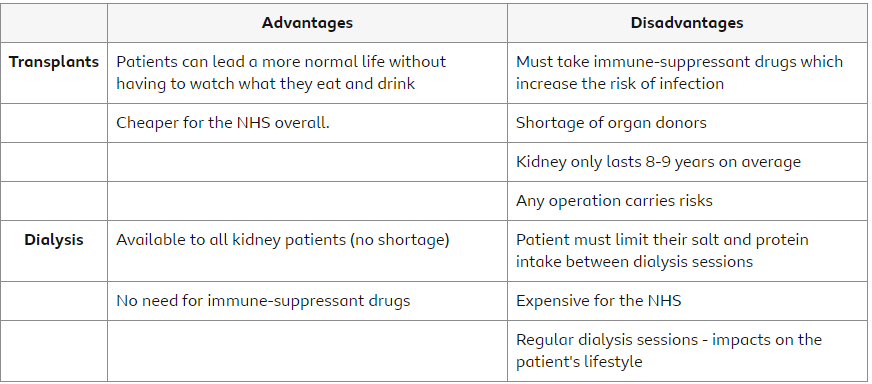
People with kidney failure can have Dialysis treatment. This is where machines do the job of kidneys or can have kidney transplants.
Dialysis is the medical treatment where blood is removed from the body and filtered out before being returned.
Dialysis has to be done regularly to keep the concentration of dissolved susbtances at normal levels and remove waste substances.
In a dialysis machine, a persons blood flows through a partially permeable membrane surrounded by a dialysis fluid. Its permeable to things like ions and waste substances but not bigger molecules like proteins.
The dialysis fluid has the same concentration of dissolved ions and glucose as healthy blood, meaning useful dissolved ions and glucose wont be lost from the blood during dialysis. Only waste substances (urea) and excess ions and water diffuse across the barrier.
Disadvantages :
expensive
only works for a limited amount of time
patient must follow a very rigid diet to avoid any complications
Patient must have blood flowing through them for several hours per week
Unpleasant experience causing problems like blood clots and infections
Kidney transplants involve implanting a kidney from a organ donor into a patients body that doesn’t have a kidney.
The donor kidney cells have protein antigens on their surface which are specific to each of us and allow our body to identify our own cells to those of potential pathogens.
Differences of antigens of the kidney cells and those recieiving the transplant are that the immune system would quickly form antibodies to kill the kidney cells antigens which would result in the kidney being destroyed which can be harmful to the patient. This is called organ rejection.
A precaution against rejection is Immune suppressant drugs. This is where transplant patients are given drugs for the rest of their lives. They suppress the immune system greatly reducing the immune response against the donor kidney. However they also suppress the immune response against pathogens which can cause infections.
Culturing Microorganisms
Bacteria is grown on a culture medium containing all of the nutrients they need to grow. The Culture medium can be a nutrient broth solution or a solid agar jelly. Bacteria grown on agar plates can create visible colonies on the surface of the jelly or create an even covering of bacteria.
To make an Agar plate, hot agar jelly is poured into a petri dish. Once the jelly is cooled and set, inoculating loops can be used to transfer microorganisms to the culture medium. Or a sterile dropping pipette can be used to create an even covering of Bacteria. The Microorganisms then multiply.
In labs at school cultures of microorganisms are not allowed to exceed 25 degrees othweise pathogens may enter. However, in industrial condtions they are to help bacteria grow faster.
RP - INVESTIGATING THE EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS O BACTERIAL GROWTH
place paper discs soaked in different types of antibiotics that has an even covering of bacteria.
The Antibiotics should then diffuse into agar jelly. The AB resistant bacteria will contue to grow on the Agar around the paper discs but the non resistant strains will die.
Next you should make sure you use a control. This is a paper disc that has not been soaked in the antibiotic. Instead soak it in sterile water.
Now leave for 48hrs at 25 degrees.
ways to avoid contamination :
Sterilise the petri dish and culture medium to stop any unwanted microorganisms that may be lurking on them getting in.
Sterilise the inoculating loop by passing it through a hot flame
Lightly tape the lid of the petri dish on to stop microorganisms getting in
The petri dish must be upside down to stop drops of condensation falling onto the agar surface.
The Heart
The Double Circulatory system is two circuits joined together.
In the first one, the right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to take in oxygen. The blood then returns to the Heart.
In the second one, the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood around all the other organs of the body. The blood then gives up its oxygen at the body cells and the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart to be pumped out to the lungs again.
The heart is a pumping organ that keeps blood flowing around the body.
The heart has valves stopping blood flowing backwards
First, blood flows into the two atria from the pulmonary vein and the vena cava. The atria then contract forcing the blood into the ventricles. The ventricles then contract forcing the blood into the pulmonary artery and the aorta and out of the heart. The blood now flows to the organs through the arteries and return throught the heart. The atria then fill again and the cycle repeats.
Coronary arteries branch off the aorta and surround the heart making sure it gets it gets all oxygenated supply it needs.
Pacemakers are a group of cells in the right atrium wall that control your resting heart rate. They produce electric impulses which spread to muscle cells causing them to contract.