Science 9- Unit 5
Science notation
Used when writing very large or very small numbers
Distance of the sun to the earth= 150,000,000, or 1.5 × 10^8km (1.5 representing the 15, and 10^8 representing the number of times the decimal moved to the right when writing it in regular form)
When adding or subtracting numbers, their exponents must be the same, and the answer will also have the same exponent
When multiplying or dividing numbers , they don’t have to have the same exponent
Ex: What is the total mass of the earth and moon?
597×10^22 - 7.3×10^22 = 589.7 × 10^22= 5.897 × 10^22
Ex: How far is mercury from the sun?
35,980,000 / 92,960,000= 0.4 au
Celestial events and objects
A celestial object is any object in outer space. Stars, Our sun, Planets, and Moons are all Celestial objects!
Stars- Are supersized space bodies with large nuclear fusion. Vary in size
Celestial events are any observable occurrence or phenomenon involving celestial bodies. Solar and Lunar eclipses, meteor showers, Aurora Borealis, and comets are all Celestial events
Planets- are large celestial bodies that orbit a star. First 4 in our solar system are terrestrial planets (made out of rock) and the other 4 are gas giants (made out of gas)
Moon- orbits a planet
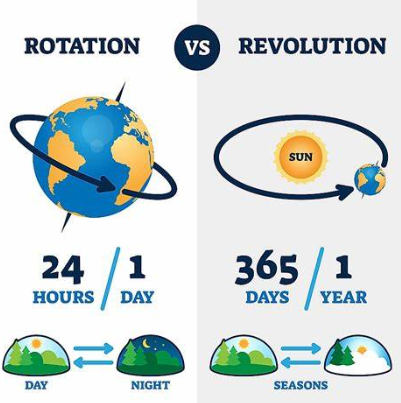
Prograde rotation- Counter Clockwise. 6 planets in the solar system do this
Retrograde Rotation- Clockwise. Venus and Uranus do this
The Greeks
The Greeks were the first to explain how the universe worked in a logical systematic manner
Aristotle had thought that earth was the center of the universe.
Copernicus then invented the telescope, since Aristotle did not have access to this technology yet
Our longest day of the year is June 21st, when we get 24 hours of sun. The shortest day of the year is December 21st, when we get 0 hours of sun
The tilt of Earth gives us our 4 seasons. The rotation of earth gives us our day and our night. For earth to make 1 whole rotation around the sun, it takes 365.25 days.
Discovery through technology
Sundial- Measure the passage of time based on the suns position
Merkhet- Charts astronomical positions and predict the movement of stars
Quadrant- Measures the stars height above the horizon. Most are made for people who live near the equator
Astrolabe- used to make accurate charts of a stars positions
Cross Staff- Measures angles between the moon and any given star
Early telescopes- allowed astronomers to discover details about earths closest planetary neighbors and relative size and distance
Optical/Radio Telescopes + Space bases telescopes- Operating from earth, satellites, travels across space an takes pictures and send it to earth
An astronomical unit (AU) is a standard unit of measurement used in astronomy to describe distances within our solar system.
The sun and stars
The sun releases light which is the source of life for everything on earth. Light has many different wavelengths such as Gamma, X-ray, Ultra Violet, Visible, Infrared, Microwave, and Radio.
As the wavelength of light increases, the frequency and energy decrease.
Spectroscopes( a device that creates a detailed spectrum of light) tell us what a star is made of and how fast it is moving towards (blue wave lengths) or away from us (red wavelengths)

The sun has a very high gravitational force, so the particles in the sun will collide together, resulting in the nucelli fusing. This process is called fusion

The cooler regions on the outside of the sun are called sunspots
A solar flare is when large quantities of charged particles can erupt in the sunspots
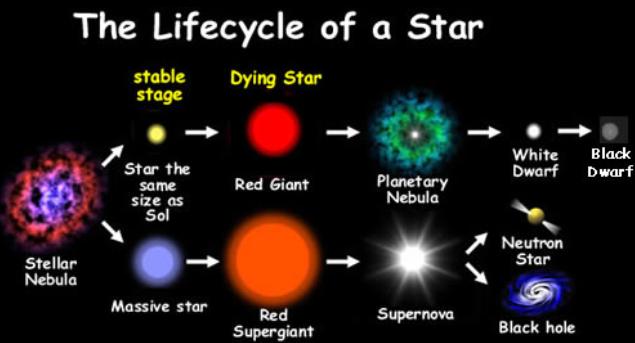
Areas of Gas and dust are called molecular clouds. Protostar begins to rotate and collect more interstellar matter
10mil and 8 hydrogen is changed to helium
A stars mass is either low or heavy.
A star spends most of its time being called sequence hydrostatic, and they remain in this state until the fuel is balanced
As the nuclear fuel of a star begins to run out, so does the energy required to keep the gases together, and the star expands dramatically. A sun like star becomes a red giant, and a massive star becomes a super nova
Our sun will expand to the orbit of mars using fuel at an even grater rate, but this will not happen for at least another 5 billion years
Sky coordinates
Orion- Light from Betelgeuse. It is 4.0 zillion km away from us
The location of celestial bodies in the sky is determined by their altitude and azimuth
Altitude is the measured angle above the horizon in degrees. Azimuth is the measurement of its angle clockwise from north in degrees
These coordinates are based on the assumption that earth is fixed in space
Planets
Mercury: Closest to the Sun, smallest planet, extreme temperature changes, no atmosphere.
Venus: Similar size to Earth, thick toxic atmosphere, hottest planet due to greenhouse gases.
Earth: Only planet known to support life, has water in all three states, diverse ecosystems.
Mars: Known as the Red Planet, has the largest volcano and canyon, potential for past life.
Jupiter: Largest planet, gas giant, famous for its Great Red Spot, has many moons.
Saturn: Known for its stunning rings, gas giant, has numerous moons including Titan.
Uranus: Ice giant, rotates on its side, has a faint ring system, coldest planetary atmosphere.
Neptune: Farthest from the Sun, strong winds, deep blue color, has a storm system similar to Jupiter's.
Telescopes
Telescopes are instruments that gather and magnify light to observe distant objects. They come in three main types:
Refracting Telescopes: Use lenses to bend light.(magnifies object with lens)
Reflecting Telescopes: Use mirrors to reflect light. (magnifies object with concave mirror)
Combination Telescopes: Composed of a lens and an objective mirror
Magnification- Objective focal length/ Eye Piece Focal length
We can increase the strength of a telescope by improving its resolving power
The 1st telescope was made in 1608
Galileo Galilei
Who: Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist, and mathematician.
Contribution: Improved the design of the telescope and made significant astronomical observations.
Discoveries:
Moons of Jupiter
Phases of Venus
Sunspots
Detailed observations of the Moon's surface
Johannes Kelper
Newtons law- Larger mass= Larger Force
Made a mathematical formula to explain the planets motion of orbit around the sun, and found out that planets travel in elliptical orbits, not perfect circles
Triangulation
Modern day telescopes also allow us to determine a more accurate measure pf distance between 2 objects
This is accomplished through a process known as triangulation
To use the triangulation method you need to know the length of 1 side of the triangle (the base line) and the measure of the angles created when an imaginary line is drawn from either side of the baseline to the same point on the distant object.
Technologies for living in space
Temperatures can range from 270 degrees Celsius, to 120 degrees Celsius
Drop in pressure on the body causes heartbeat to increase.
No oxygen in outer space. You need an oxygen tank.
You need to clean carbon dioxide From the environment using scrubbers.
No water in space. You need to conserve and recycle.
It can be very psychologically difficult for people to live in a small confined area for up to two years.
Gravity- Is the force of attraction between masses.
Microgravity- whenever an object is in freefall.
Bones expand and become brittle.
Muscles weaken.
Heart works less hard to pump blood to the rest of the body.
The space suit
Each suit is custom made for the astronaut and must be able to provide everything.
In outer space, You must recycle wastewater to produce drinking water.
Recycled water is used to produce oxygen, remove carbon dioxide from the air, filter microorganisms and dust from the air. and keeping the air pressure, temperature and humidity stable.
Dangers in space
Strapping a human to hundreds of tons of highly explosive fuel.
Floating debris and meliorates in space.
Cosmic radiation from the Milky Way and other galaxies.
Definitions
Geocentric= Earth model, earth is in the middle
Heliocentric= sun Center.
Copernicus= created by Galileo. He used A telescope to prove this to earth
Galileo didn't invent the telescope, but he was the first to view a star in 1608.
he observed The phases of Venus, and found out that they are similar to the phases of the Moon.
He observed moons on Jupiter, which inferred that not every object orbited Earth.
The first man on the moon was in 1969