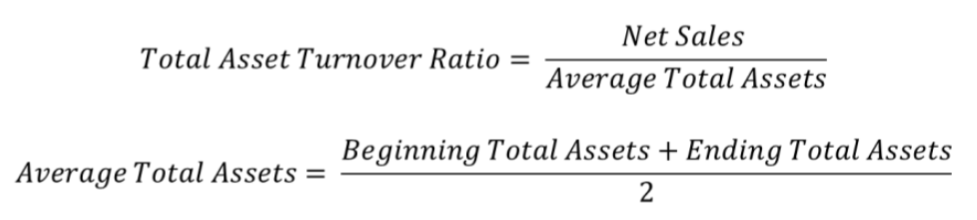Adjustments, Financial Statements, & the Quality of Earnings
Creation of Financial Statements:
During the Accounting Period:
Analyze business transactions
Record transactions using journal entries
Aggregate journal entries
End of the Accounting Period:
Prepare the (unadjusted) trial balance
Make adjusting entries (record & post)
Prepare financial statements
Close temporary accounts
“Regular” Journal Entry:
Recorded in the normal course of daily business transactions
May or may not involve cash (ie selling goods to customers for cash, buying inventory on account)
May or may not involve recording Revenue or Expenses
Adjusted Journal Entry (AJEs):
Recorded at the end of the accounting period
Never involves cash
Always involves Revenue or Expenses
Necessary because:
Timing differences between Revenues being earned vs receipt of cash
Timing differences between Expenses being incurred vs exchange of cash
Expenses that are difficult or inefficient to recognize on a daily basis (ie depreciation expense)
Types of Adjusting Entries:
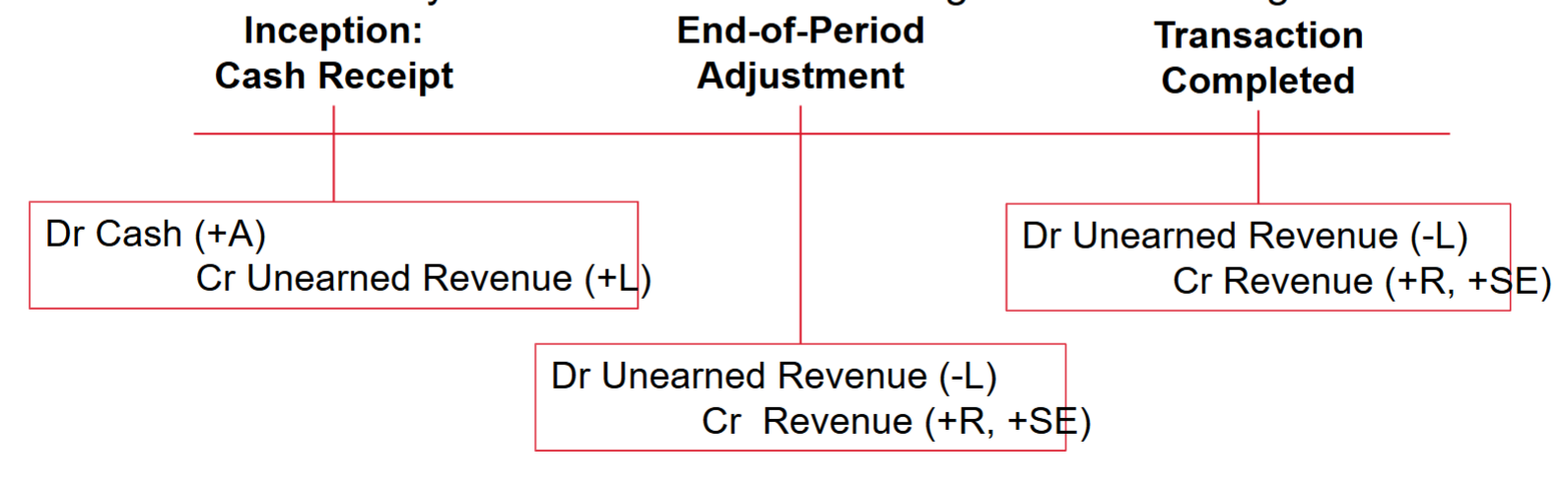
Deferred Revenue:
Revenue after cash
Inception: A liability (ie promise from future services) was recorded at the time cash was received
Adjustment: Liability is reduced to recognize revenue earned
Conclusion: Liability is eliminated & remaining revenue is recognized
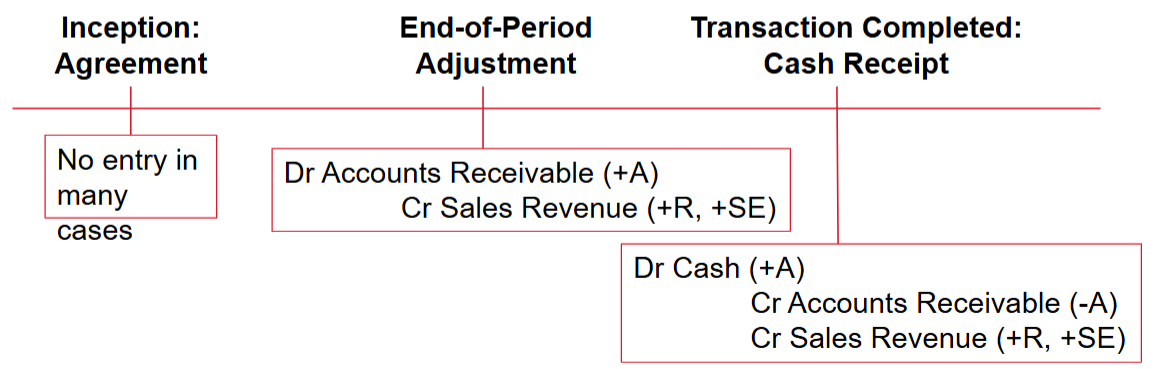
Accrued Revenue:
Revenue before cash
Inception: Reaches an agreement for future services; no transaction in most cases
Adjustment: Revenue earned for services performed; receivable is increased
Conclusion: Cash receipt recorded, receivable eliminated, & remaining revenue recognized (if any)
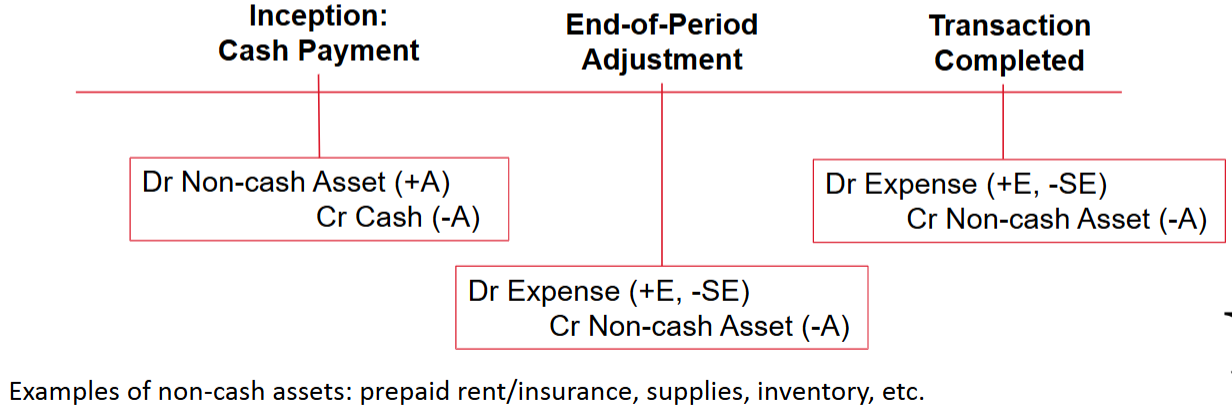
Deferred Expense:
Expenses after cash
Inception: An asset was acquired at the time cash was paid
Adjustment: Asset is used; asset balance reduced to recognize expense incurred
Conclusion: Asset is eliminated & remaining expense is recognized
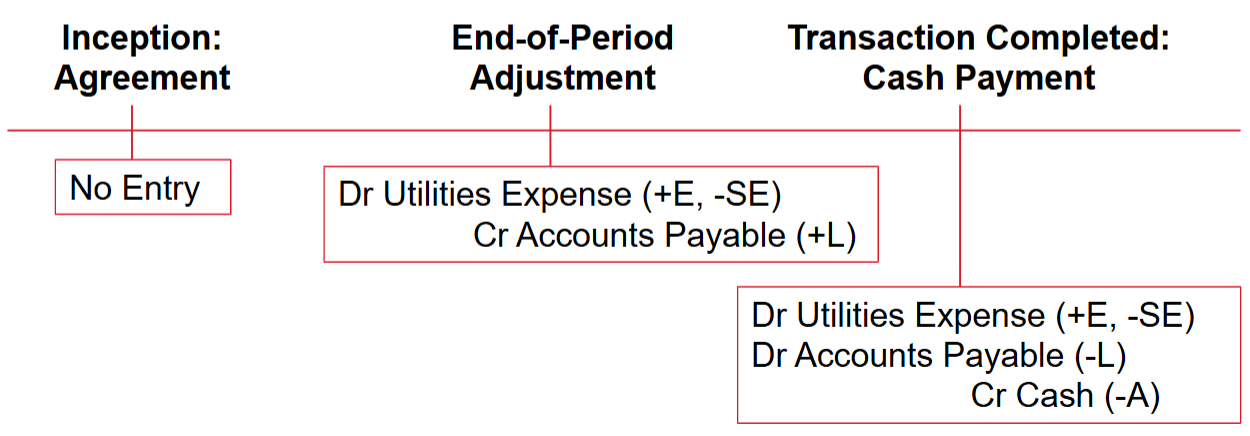
Accrued Expense:
Expenses before cash
Inception: Reaches an agreement for future services; no transaction
Adjustment: Expense incurred for services received; payable is increased
Conclusion: Cash payment made, payable eliminated, remaining expense recognized (if any)
Closing the Books:
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s resources & sources at a given date
These balances carry forward from period to period
Balance sheet accounts are permanent accounts
The income statement provides a report of performance over a period
These account balances need to be reset at zero each period so current period income is not included in future income
Income statement accounts are temporary accounts
Total Asset Turnover Ratio: