Enzymes
What are Enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that can @@catalyze chemical reactions.@@ Enzyme kinetics looks into how @@enzymes bind substrates and turn them into products.@@
Enzymes Structure
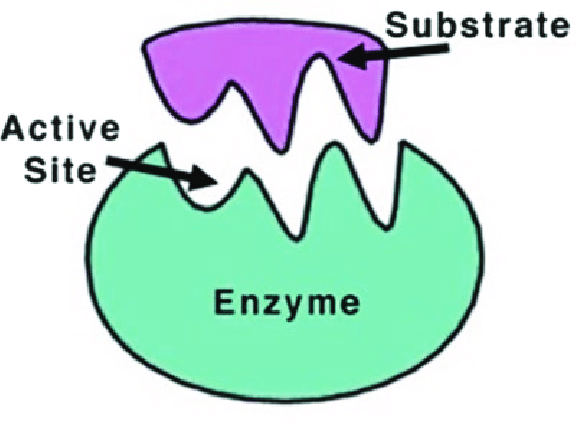
Enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. This sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is called the primary structure. This, in turn, determines the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme, including the shape of the active site.
Enzymes Functions
Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They are essential for respiration, digestion of food, and muscle and nerve function, among thousands of other roles.
The difference between the active site and allosteric sites on enzymes
The allosteric site and active site are two different regions in the enzyme structure.
\n An allosteric site is a region of an enzyme that allows==activator or inhibitor molecules== to bind to the enzyme and either activate or inhibit enzyme activity.
\n The active site is a region of an enzyme where%%substrate molecules%% bind and catalyze the reaction resulting in the production of particular products.
Mechanism Enzyme Functioning
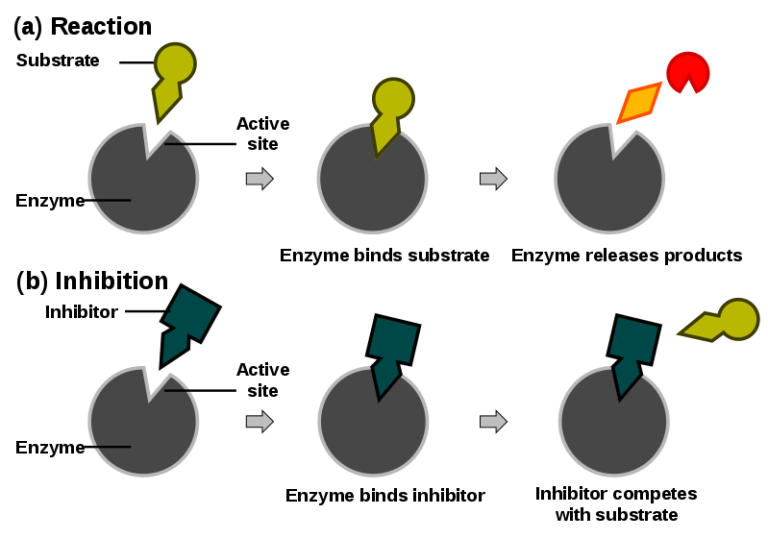
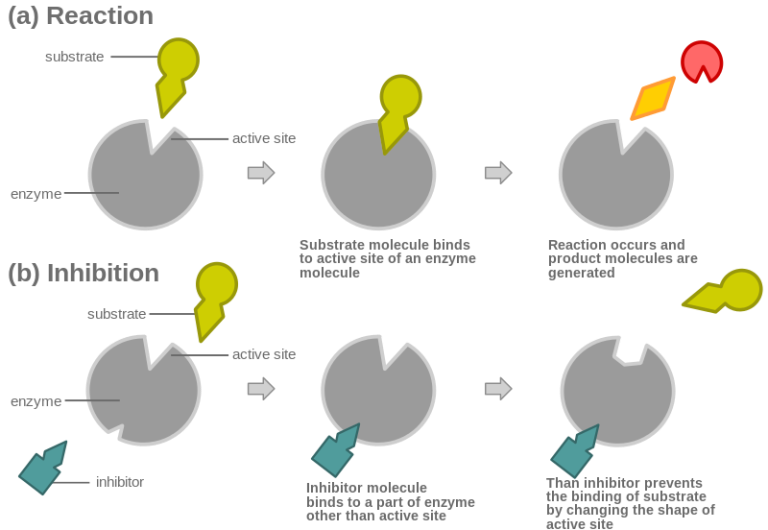
An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site, catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed, and then allows the products to dissociate (separate from the enzyme surface). The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzyme-substrate complex.
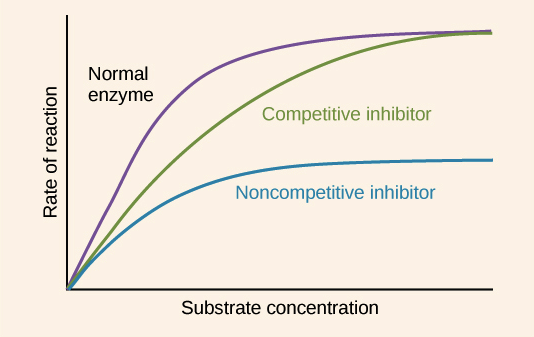
Difference between competitive and noncompetitive inhibition:
Competitive inhibition: Competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition in which an inhibitor binds to the active sites of an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding to the enzyme.
Non-Competitive Inhibition: Noncompetitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition in which an inhibitor reduces the activity of an enzyme.
Competitive Inhabitor Figure:
Noncompetitive Inhibitor Figure:
Predict and explain the impact of [substrate], [enzyme], [product], temperature, pH, etc on enzyme function
@@Substrate:@@ Higher the concentration, the faster the rate until enzyme saturation occurs
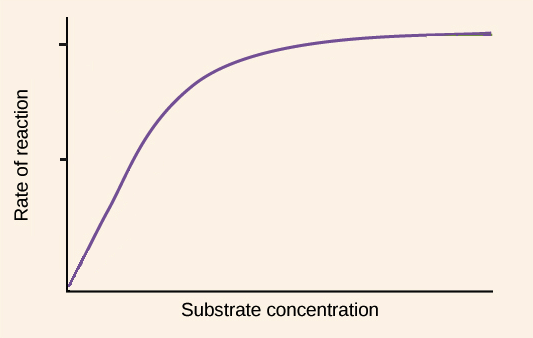
\n ^^Product:^^ Remember metabolic reactions are reversible so a high concentration of product can favor the reverse reaction
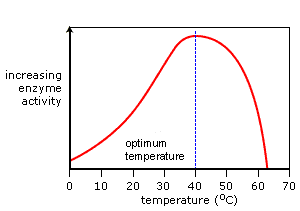
%%Temperature:%% pH and other environmental conditions that affect protein folding
\n Enzyme: Higher the concentration, the faster the rate until the substrate limits the reaction
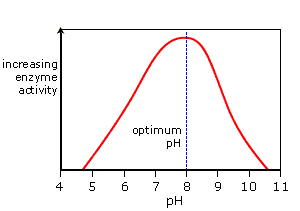
==pH:== Enzyme activity is at its maximum value at the optimum pH. As the pH value is increased above or decreased below the optimum pH the enzyme activity decreases.