The Cultural Landscape (An Introduction To AP HUG) Chapter 1 Quick Notes
| ==Main Ideas/Topic Question== | Simpler Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Important Vocab | ||
| %%Important Phrases/words%% |
==Introduction To Human Geography==
==Introduction To maps==
Reference maps - Informational maps that show boundaries & place names
Often display Physical and Man-made features.
- (E.g. Subway maps, Fire evac. maps, world maps, etc.)
Thematic Maps - Shows us the quantitative data (Data that is shown by numbers)
- To know what it is about we’ll have to read the title!
==/What are the 5 ways to Geospatial Data?==
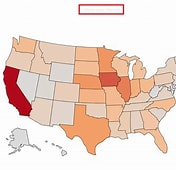
Choropleth - Maps using colors/shading to show quantity. data (Darker=more)
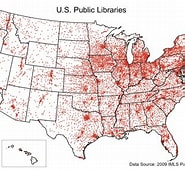
Dot - Dots that represent a value in its approximate location (Bigger dot =more)
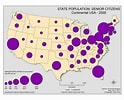
Graduated Symbol - Feature symbols proportional to the size of the actual data (If the Data is big then the symbol will also be big)
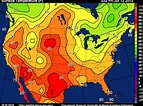
Isoline - Maps Connect areas of equal value w/ lines (E.g. Weather maps)
Cartograms - Distort the appearance of places on a map to represent their values
\