Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Objectives:
Know the parts of the cell cycle: Interphase, M phase, Cytokinesis
Understand mechanisms of cell division: reproduction, growth, repair, or replacement of cells
Know the cell cycle processes of Interphase at G1, G2, G0, and S phases
Identify the names of the phases of mitosis and the characteristics of each phase
Know the types of chromosomes present in each phase of the cell cycle
General terms:
Chromosomes: condensed DNA (DNA + protein )
pre interphase: 46 chromosomes (single chromatids)
Post interphase: 46 chromosomes (replicated chromatids attached)
2N = 4 → two sets of chromosomes, total number chromosome is 4
Centromere:
hold together sister chromatids
Centriole:
organelles involved in the creation of spindle fibers
Spindle Fibers:
protein structure aiding division
Cell cycle:
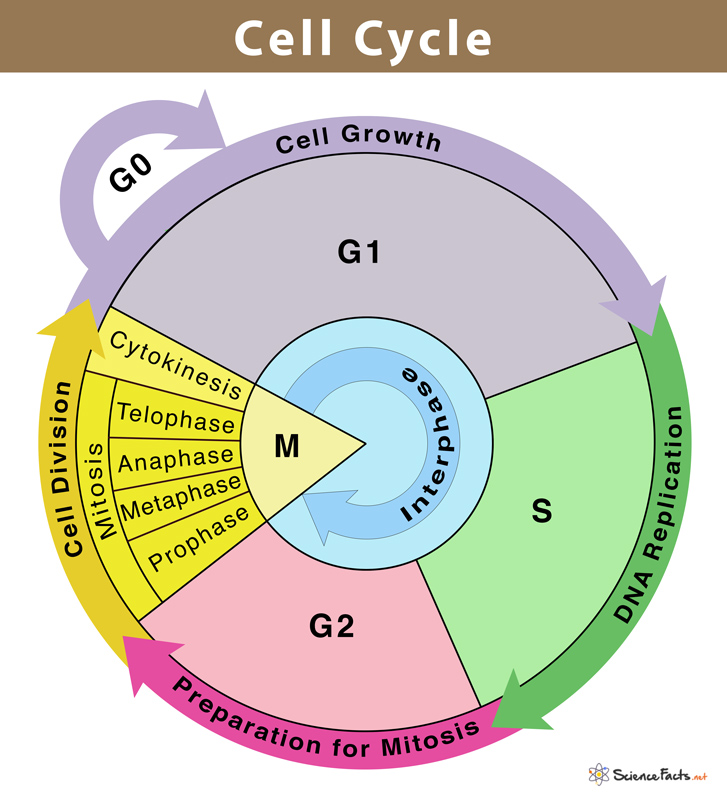
interphase:
the cell grows, makes copies of its DNA
the longest phase of the cell cycle
preparation for division occurs in 3 steps:
G1 phase: cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes molecular building steps *checkpoint, check if cell is large enough
S phase: cell synthesizes a complete copy of DNA in its nucleus and duplicates centrisomes
G2 phase: cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, begins to reorganize in preparation of mitosis *checkpoint, successful DNA replication (no errors)
chromatin
Mitosis: cell divides its copied DNA and cytoplasm to make 2 new cells
purpose: assexual repreduction, make cells, replace cells
prophase: chromatin condenses into replicated chromosomes, spindle fibers (made of tubulin, move chromatids) begin to assemble from the centrioles, nuclear envelope begins to break down (longest phase of mitosis)
replicated chromosomes
prometaphase: the nuclear membrane is completely broken down and spindle fibers (already attached to the k___ on centrioles) attach to the replicated chromosomes.
replicated chromosomes
metaphase: the genetic material in the nucleus becomes aligned along the equatorial plane of the cell (middle). The chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers. *checkpoint, ensure spindle fibers attached
replicated chromosomes
anaphase: the replicated chromosomes are separated —> two identical daughter chromatids. The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers (GTP necessary to separate the chromatids)
sister chromatids
telophase: condensed chromosomes begin to decondense, cell is cleaved into two new daughter cells and daughter nuclei form at each pole. A new nuclear envelope begins to form around each set of separated chromatids.
chromatids and then chromatin (towards end when cytokinesis begins)
Cytokinesis: final stage of the cell cycle
cytoplasms of the two cells split to form two identical cells
the sister chromatids are now chromatin and the two cells will return to interphase
Cytokinesis plant v. animal:
Plant division starts at the center of the cell and moves towards the cell wall
Animal division starts at the edges of the cell at the plasma membrane and moves towards the center
plants create Create vesicles that fuse → cell plate
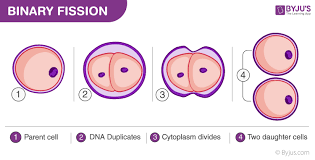
Mitosis vs. Binary fission:
binary fission is type of cell division (mostly in prokaryotes and bacteria)
Cancer and Cell cycle:
 Knowt
Knowt