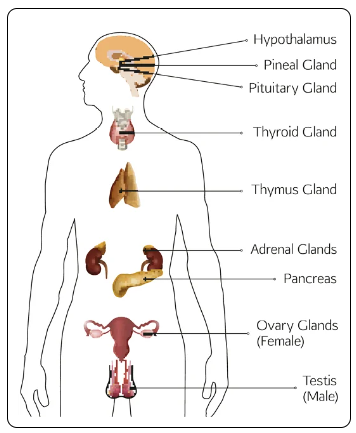
Endocrine & Lymphatic System
Endocrine System - the body's "chemical messenger"
Complex Network of glands that produce and secrete hormones that regulate a variety of bodily functions
Ex. Metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, and mood
Ductless and secrete hormones directly into the blood stream
Exocrine glands have ducts
Glands secrete hormones that affect tissues other than themselves
Works together with the nervous system to form a system of internal communication for the body
Lymphatic System - unsung hero in immunity
Vast network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials.
Primarily responsible for transporting lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body.
Endocrine System Suffixes:
Adren/o, adrenal/o | Adrenal gland, epinephrine |
Adrenoccortic/o | Afrenal cortex |
Crin/o | Secrete |
Dips/o | Thirst |
Endocrin/o | Endocrine glands or system |
Gluc/o, glyc/o | Glucose, sugar |
Hormon/o | Hormone |
Hypophys/o | Pituitary gland, hypophysis |
Insul/o | Pancreatic islets |
Pancreat/o | Pancreas |
Parathyr/o, parathyroid/o | Parathyroid gland |
Pituitar | Pituitary gland, hypophysis |
Thyr/o, thryoid/o | Thyroid gland |
Toxic/o | Poinson |
-tropic | Act upon |
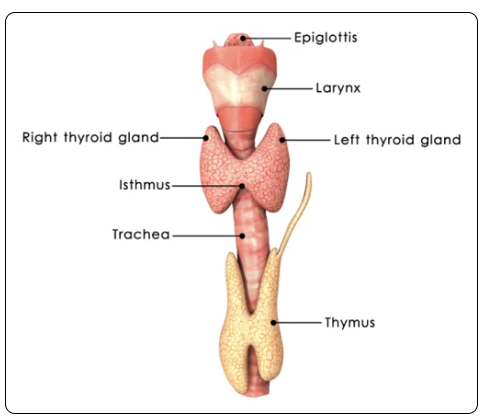
Thyroid Gland:
Located just below the thyroid cartilage (or Adam's Apple), anteriorly in the neck
Regulates metabolism and serum calcium levels through the secretion of thyroid hormone and calcitonin, and determines sensitivity of the body to other hormones
Butterfly shaped gland with 2 lobes connected by an isthmus over the trachea
Common procedures:
Lobectomies - excisions of all (total) or a portion (partial) of one lobe of the thyroid
Isthmusectomies - excision of the isthmus (body of the butterfly) of the thyroid
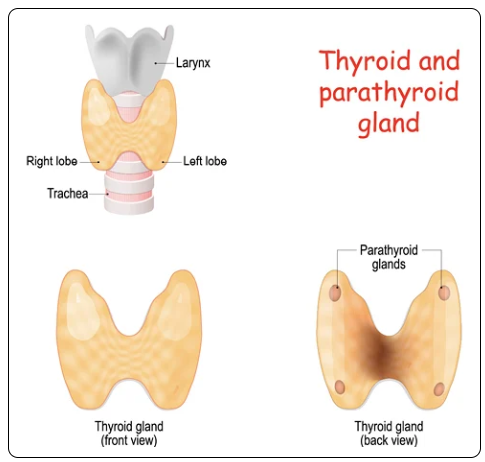
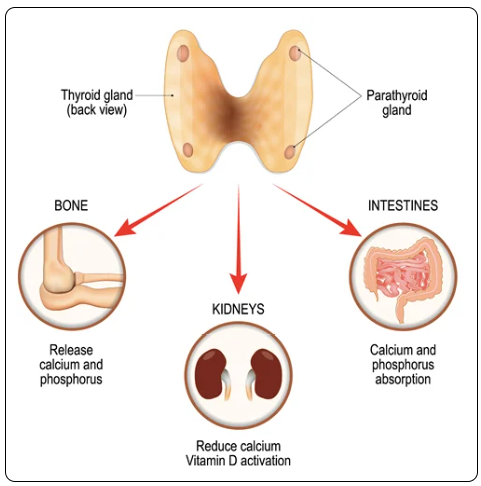
Parathyroid Gland:
4 parathyroid glands
Found on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
Regulate the body's phosphorus metabolism and calcium level for proper functioning of the nervous and muscular systems
Common procedure:
Parathyroidectomy - Excision of the parathyroid gland(s)
Thymus:
2 lobes
Located behind the sternum in front of the heart
Produces T-lymphocytes (T cells)
Produces and secretes hormones to control immune function
Prominent during infancy and childhood and usually shrinks after puberty
By adulthood, replaced by fat but continues to produce T cells
Common Procedure:
Thymectomy (partial or total) - excision of the thymus
Transcervical (via the neck)
Transthoracic (via the chest)
Sternal Split (via the chest)
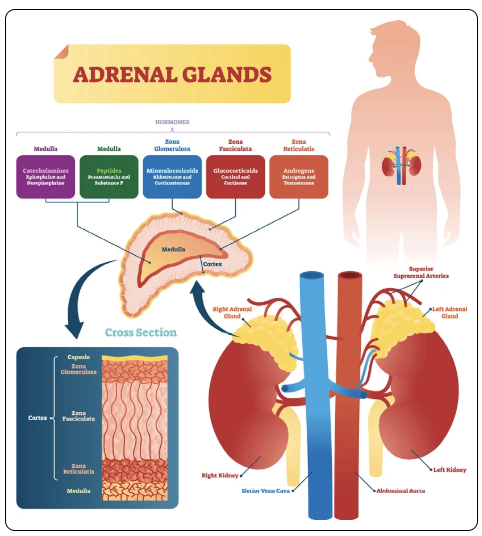
Adrenal Glands (Suprarenal):
Sit directly atop the kidneys - one per side
Adrenal means 'near the kidneys'
2 structural parts:
Medulla - the inner portion
Secretes adrenaline, epinephrine, norepinephrine
Cortex - the outer portion.
Secretes several steroids (cortisol, glucocorticoids, mineral corticoids, adrenal estrogens, androgens, etc)
Further divided into 3 distinct zones
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Fasciculata
Zona Reticularis
Common Procedure:
Adrenalectomy - excision of the adrenal glands (partial or complete, open or laparoscopic)
Pancreas:
15cm long, lies near the bottom of the stomach
Divided into head, body, & tail
Dual-function gland performing both endocrine and exocrine (digestive) functions
Islets of Langerhans (islet cells) produce the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood glucose levels (endocrine function)
Digestive organ
Secretes digestive enzymes flowing through the pancreatic duct to the small intestine (exocrine function)
Common Procedures:
Biopsies - check for malignant growths and areas of tissues that are determined to be concerning:
by excision - removing the concerning area
By ablation - either electricity or radiofrequency waves are used to destroy the tissue
Pancreatectomy - total removal or partial removal of the pancreas
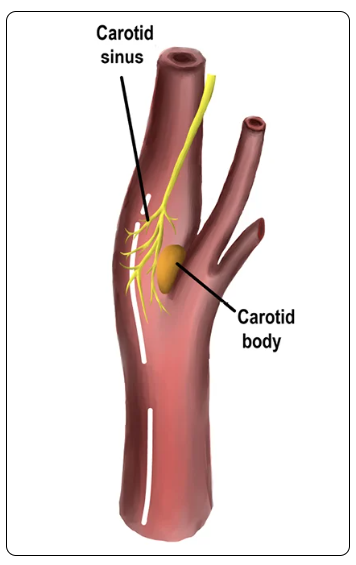
Carotid Body:
Serves primarily as an oxygen sensor helping to regulate breathing and blood pressure
Located in the neck, at the division (bifurcation) of the common carotid artery into the internal and external carotid arteries
Not a true endocrine structure
Made of both glandular and non-glandular cells
Common Procedure:
Excision can be performed on the carotid body if a tumor is present and can't be treated in other ways; either by removing the tumor, or removing the carotid body with the tumor
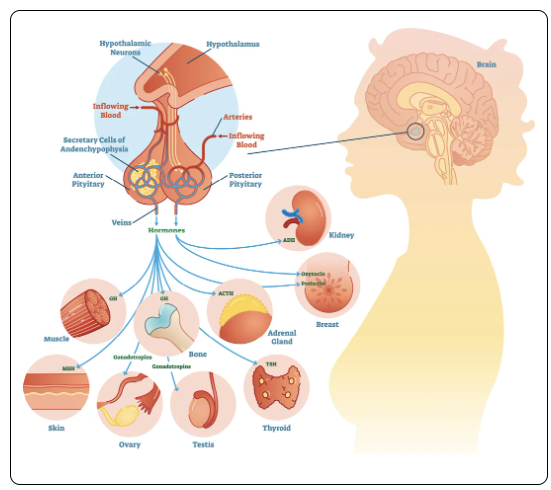
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri):
Located under the hypothalamus of the brain, which controls it
Size of a pea
This 'master gland' regulates functions like growth, metabolism, milk production, and uterine contractions in pregnant women
2 lobes:
Anterior pituitary gland - produces
growth hormones (GH)
thyroid stimulating hormones (TSH)
Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH)
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Posterior pituitary gland - secretes
Oxytocin (OT) - responsible for uterine contractions and 'let down' reflex of milk
Vasopressin
Antidiuretic (ADH)
Common Procedure: Excisions of tumors or removal of the pituitary gland when other treatment methods have been exhausted
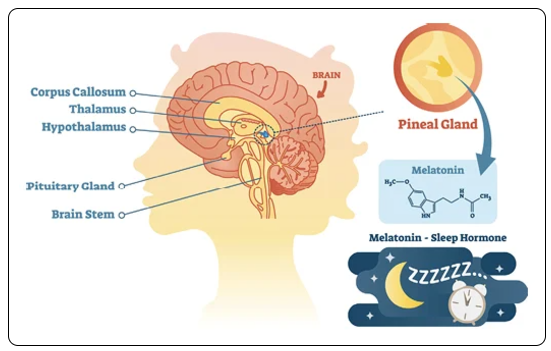
Pineal Gland (Pineal Body/Epiphysis Cerebri/Epiphysis):
Found deep within the brain, above the cerebellum, between the left and right hemispheres
Resembles a pinecone
Size of a grain of rice
Produces hormones melatonin & serotonin
Melatonin - modulates wake and sleep patterns and seasonal functions
Serotonin - Neurotransmitter & vasoconstrictor. Stimulates smooth muscle contraction and inhibits gastric secretions
Procedures: Not common since it's deep in the brain.
Pinealectomy - part or total removal due to tumor that's causing problems
Testes & Ovaries:
Secrete sex hormones as endocrine glands
Testosterone - male hormone
Estrogen - female hormone. Also produced with testosterone
Testicles are housed within abdominal cavity when boys are born and drop to scrotum at 3-6 months
Orchiopexy - if testicles don't drop, this procedure will move the undescended testicle(s) into the scrotum and fix it into the location
Procedure:
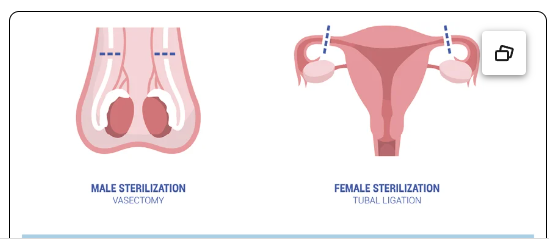
Vasectomy - surgical removal of a portion of the vas deferens tubes that carry sperm from each testicle. Intended to permanently make a male sterile
Cystectomies - surgeons will perform a laparoscopic procedure to remove cysts from one or both ovaries. Allows patient to keep ovaries to allow for continual hormone production
Oophorectomy - Unilateral or bilateral removal of the ovaries. Usually laparoscopically. Usually due to cysts or part of a hysterectomy.
Common Endocrine Conditions:
Goiters - Enlargement of the thyroid gland
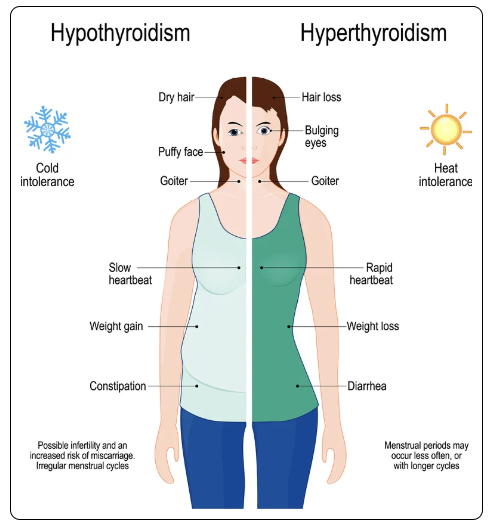
Hypothyroidism - Underactive thyroid, not producing enough hormones
Symptoms - weight gain, fatigue, hair loss, muscle cramps, depression
Hyperthyroidism - Overactive thyroid, producing too much hormone
Symptoms - weight loss, tachycardia (rapid heart rate), sweating, changes in menstrual cycle, nervousness
Thyrotoxicosis - can lead to the dysfunction of one or more organ systems
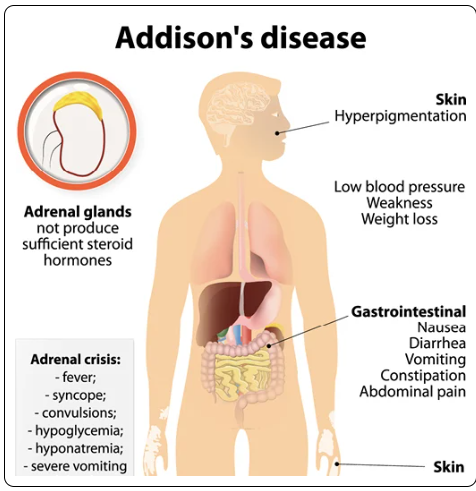
Addison's Disease - adrenal glands do not produce enough of the cortisol hormone, or sometimes aldosterone hormone.
Autoimmune diseases are related to the deficiency. Sometimes antibodies attack the body's own tissues or organs, slowly destroying them
Symptoms - chronic worsening fatigue, muscle weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss
ACTH stimulation test to diagnose
Treatment - replacing or substituting hormones
Parathyroid Disorder:
Hyperparathyroidism:
The hormonal balance is disrupted, and blood calcium rises, resulting in hypercalcemia
In 85% of people with this disorder, A benign tumor (adenoma) forms in one of the parathyroid glands, causing it to become overactive,
Other cases, excess hormone is due to enlarged parathyroid glands, a condition called hyperplasia
Surgery to remove the enlarged parathyroid gland cures about 95% of cases
Primary Hyperparathyroidism: One or more enlarged, overactive parathyroid glands secreting too much parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: a problem, such as kidney failure, makes the body resistant to the action or parathyroid hormone
Diagnosed using tests that show blood levels of calcium and parathyroid hormones are too high
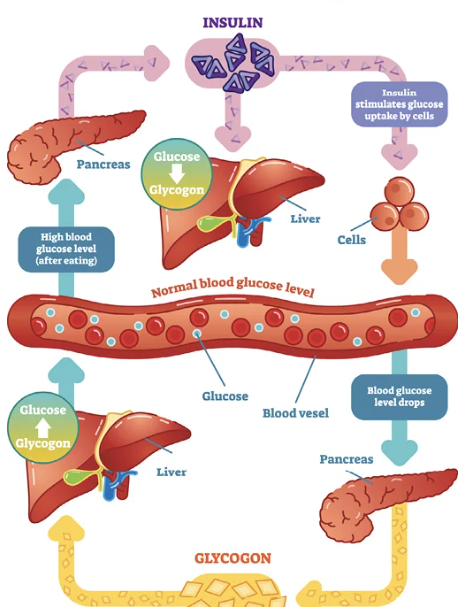
Diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus) - A group of diseases that occur when the body can't use glucose (blood sugar) normally
Glucose is the main source of energy for the body's cells. Levels of glucose in the blood are controlled by a hormone called insulin. Made by the pancreas. Insulin helps glucose enter the cells.
The inability of the body to process insulin causes glucose levels to rise in the blood.
Chronic disease that causes serious health complications including renal failure, heart disease, stroke, and blindness.
Symptoms: increased urination, extreme thirst, unexplained weight loss
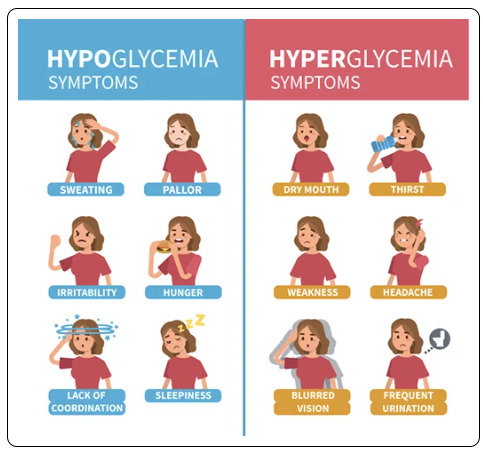
Hyperglycemia - beta cells in the pancreas do not produce enough insulin so glucose builds up in the blood
Hypoglycemia - Low glucose levels
The liver helps to manage blood-sugar levels by storing excess glucose in a form called Glycogen
Glycogenolysis - When glucose levels are low, alpha cells in the pancreas secrete the hormone glucagon, which stimulates the liver to convert glycogen back into glucose, releasing it into the blood for use by the body
Type 1 Diabetes - develops when the pancreatic beta cells no longer produce insulin
Patients must take insulin
Also referred to as juvenile diabetes, since it's most often diagnosed when the patient is in their childhood
Type 2 Diabetes - develops when the body's beta cells do not produce sufficient insulin or the beta cells have developed insulin resistance
May not have to take insulin
Secondary Diabetes - caused by another condition or event, such as cystic fibrosis, neoplasm of pancreas, drug or chemical, etc
Endocrine System Medical Terms:
Acromegaly - Overgrowth of bone and soft tissue, especially in the hands, feet, and face, caused by excess growth hormone in an adult. The name comes from acro meaning extremity and megal/o meaning abnormal enlargement
Cushing's syndrome - an excess of cortisol, caused either by an overactive adrenal gland or glucocorticoid medications; symptoms may include excess fatty tissue of the face, neck, and body; weight gain, curvature of spine; and muscle weakness
Endocrinologist - A physician who specializes in diseases of the endocrine system
Euthyroid - Normal thyroid gland activity
Glandular - pertaining to a gland
Goiter - an enlarged thyroid gland, caused by Iodine deficiency, the overproduction of thyroid hormone (TSH), or a neoplasm. A diet deficient in iodine can result in a goiter; however, this is rarely the case
Hyperkalemia - Excessive amounts of potassium in the blood
Hyperaldosteronism - Oversecretion of aldosterone by the adrenal glands; results in fluid retention and hypertension
Hyperparathyroidism - Overactive parathyroid; may result in bone deterioration, reduced renal function, kidney stones, and other difficulties
Hyperthyroidism - Excessive secretion by the thyroid gland
Hypoparathyroidism - Underactive parathyroid; may result in muscle cramps and cataracts, among other difficulties
Hypothyroidism - Underactive thyroid; too little thyroid hormone produced (the opposite of hyperthyroidism); may result in children with intellectual disability and small stature. In adults, this condition results in lower metabolism, fatigue, and fluid in the tissues (myxedema)
Insulin - Hormone secreted by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, which regulates energy and glucose metabolism. Also used in the management of diabetes.
Panhypopituitarism - Inadequate or absent production of the anterior pituitary hormones, which is caused by damage to or absence of pituitary gland. This may result in impaired sexual function, weight loss, fatigue, depression, and other symptoms.
Parathyroid - Glands located behind the thyroid gland
Prolactinoma - A benign tumor of the pituitary gland with excess production of a hormone called prolactin. In women, high blood levels of prolactin can result in infertility and changes I menstruation. In men, the most common symptom of prolactinoma is impotence.
Thyroiditis - Inflammation of the thyroid gland
Thyrotoxicosis - Condition resulting from overactivity of the thyroid gland. Symptoms include anxiety, irritability, weight loss, and sweating. The main example of thyrotoxicosis is Grave' disease
Thymitis - Inflammation of the thymus gland
Endocrine System Abbreviations:
AC | Adrenal Cortex |
ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
ADH | Antidiuretic hormone |
CAH | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
DI | Diabetes insipidus |
DKA | Diabetic ketoacidosis |
DM | Diabetes mellitus |
FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
GH | Growth hormone |
HCG | Human chorionic gonadotropin |
HGF | Human growth factor |
ICSH | Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone |
IDDM | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
IGT | Impaired glucose tolerance |
LH | Luteinizing hormone |
MEA | Multiple endocrine adenomatosis |
MEN | Multiple endocrine neoplasia |
MSH | Melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
NIDDM | Noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
OXT | Oxytocin |
PRL | Prolactin |
PTH | Parathyroid Hormone |
STH | Somatotropic hormone |
T3 | Triiodothyronine |
T4 | Thyroxine |
TFT | Thyroid function test |
TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
Lymphatic System:
Lymph/o | Lymph, lymphatic system |
Lymphaden/o | Lymph node |
Lymphangi/o | Lymphatic vessel |
Splen/o | Spleen |
Thym/o | Thymus |
Tonsil/o | Tonsil |
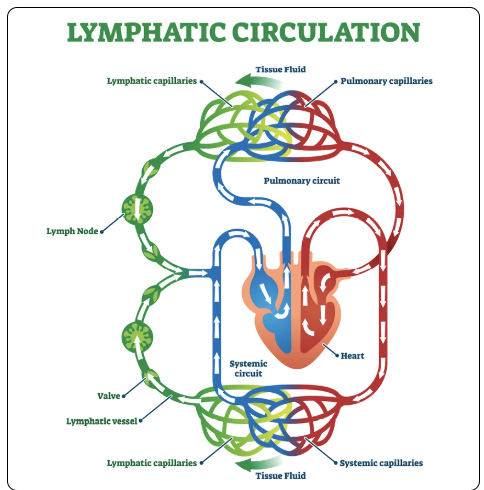
Lymphatic System - Comprised of lymph vessels and nodes. Collects excess fluid from the interstitial spaces (a potential space between tissues) and returns it to the heart.
Venous end of the lymph capillaries reabsorb fluid pushed from the arterial capillaries into the interstitial space; the lymphatic vessels pick up any excess fluid
Operates without a pump using a series of valves to ensure the fluid travels in one direction back to the heart
Lymphoid organs scattered throughout the body that house phagocytic cells and lymphocytes that are essential to the body's defense system and its resistance to disease
Lymphoid organs: spleen, thymus, tonsils, Peyer's patches of the intestine, and appendix
Lymphatic Vessels - similar in structure to blood vessels. Lymphatic capillaries are closed at one end. After the lymph fluid is picked up, it is circulated to increasingly larger lymph vessels called lymphatics. Lymphatics empty into either the right lymphatic duct or the thoracic duct, both of which are situated in the thoracic cavity.
Right Lymphatic Duct - collects from the right arm, right side of the head, and right side of the thorax.
Thoracic Duct - collects lymph from the rest of the body
Both ducts empty their contents into the subclavian veins. Right lymphatic ducts empties into the right subclavian vein and the thoracic duct empties into the left subclavian vein.
For the body to maintain an appropriate volume of circulating blood, it's necessary to put all this fluid back into the main system of circulation.
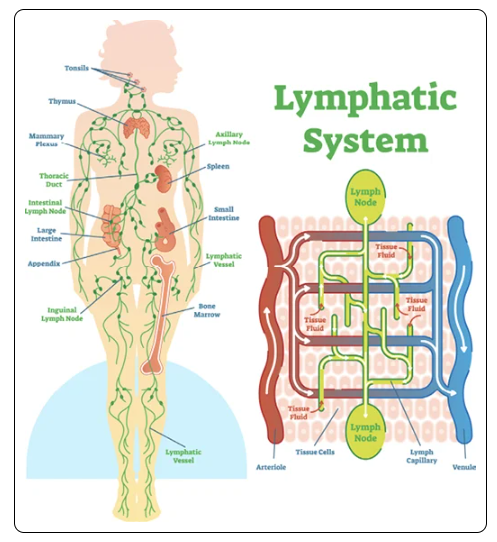
Spleen: an organ of the lymphatic system in the left upper abdomen that filters and destroys red blood cells that are no longer efficient.
Serves as a blood-forming organ early in life, later as a storage unit for extra red blood cells and platelets
Thymus: Responsible for T-lymphocyte maturation, enabling them to function against specific pathogens in the immune response
soft organ located behind the sternum and between the lungs.
2 identical lobes that lie almost on top of the heart and traces up along the trachea
Prominent in newborns and continues to increase in size during the first year. After puberty, the thymus atrophies gradually.
Tonsils: Simplest lymphoid organs. Partially encapsulated lymphoid tissue located in the throat.
Named according to their location:
Palatine tonsils
Lingual tonsils
pharyngeal tonsils (referred to as adenoids, if enlarged)
Peyer's Patches & Appendix:
Found in the lining of the intestine and help to protect against invading microorganisms
The appendix is a "finger-like" projection of tissue attached to the cecum, the first part of the large intestine
Lymphatic System Conditions:
Lymphadenitis - Inflammation and enlargement of lymph nodes, usually as a result of infection
Lymphangitis - Inflammation of lymphatic vessels as a result of bacterial infection
Lymphedema - swelling of tissues with lymph caused by obstruction or excision of lymphatic vessels
Lymphocytes - Help with immunity (T cells & B cells)
Lymphoma - Any neoplastic disease of lymphoid tissue
Thymitis - Thymus gland inflammation
Lymphatic System Medical Terms:
Appendix - Organ in the abdomen; contains lymphoid tissue that can destroy bacteria before crossing the intestinal wall during absorption
Collecting ducts - collect lymph from lymphatic vessels; connect to subclavian vein, which returns lymph to bloodstream; helps to maintain normal blood volume and pressure
Lymph - Collection of the extra fluid that drains from cells and tissues; transports infection-fighting white blood cells
Lymph Nodes - Bean-shaped glands that monitor and cleanse the lymph as it filters through them; produce and store lymphocytes and other immune system cells
Lymphatic Vessels - Network of capillaries and tubes throughout the body that transport lymph away from tissues
Peyer's patches - Small masses of lymphatic tissue in the mucous membranes that line the small intestine; monitors and destroys bacteria in the intestines
Spleen - Largest lymphatic organ, located on left side under ribs and above stomach; filters and stores blood and produces white blood cells to fight infection or disease
Thymus - Organ in the upper chest beneath the breastbone; matures a specific type of white blood cell that fights off foreign organisms
Tonsils and adenoids - lymphoid organs that trap pathogens from food that has been eaten; the body's first line of defense against foreign invaders
AIDS | Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
HD | Hodgkin's disease (Hodgkin Lymphoma) |
HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
HPV | Human papillomavirus |
HSV | Herpes simplex virus |
IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
IgD | Immunoglobulin D |
IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
MALT | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue |
NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
NKT | Natural killer T-cell |
RBC | Red blood cells |
SLNB | Sentinel lymph node biopsy |
WBC | White blood cells  |