protonated vs
Here are the "templates" exam questions like to use, with the correct answers:
Q: When a strong acid is added to a buffered solution, the…
Acid form of the buffer deprotonates. ❌
Acid form of the buffer becomes protonated. ❌
Basic form of the buffer deprotonates. ❌
Basic form of the buffer becomes protonated. ✅
Q: When a strong base is added to a buffered solution, the…
Acid form of the buffer becomes deprotonated. ✅
Acid form of the buffer becomes protonated. ❌
Basic form of the buffer becomes deprotonated. ❌
Basic form of the buffer becomes protonated. ❌
Q: A buffer resists changes in pH because…
Its conjugate acid–base pair neutralizes added strong acids or bases. ✅
It prevents H⁺ ions from entering solution. ❌
It reacts only with weak acids and bases. ❌
Q: In an acetic acid/acetate buffer, if HCl is added…
Acetate (CH₃COO⁻) is protonated to form acetic acid. ✅
Q: In an acetic acid/acetate buffer, if NaOH is added…
Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) is deprotonated to form acetate. ✅
At what stage of the biological organization does the property of life emerge?
Atoms
Molecules
Cells
Organs
Organisms
When glucose is dissolved in water, it means that…
Each atom of a glucose molecule is separated from each other by water molecules.
Each molecule of glucose is separated from each other by water molecules.
Each glucose molecule is covalently bound to a hydration shell of water molecules.
Each glucose atom is covalently bound to a hydration shell of water molecules.
what does a covalent bond look like in a protein???
Which of the following is NOT a weak interaction?
Ionic interactions
Hydrogen bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Polar covalent bonds.
Solution A is pH 6. Solution B is pH 9. Which of the following statements is true about these two solutions? (short answer - enter letter only)
A has 3x the hydrogen ion concentration than B
B has 3x the hydrogen ion concentration than A
B has 100x the hydrogen ion concentration than A
A has 100x the hydrogen ion concentration than B
B has 1000x the hydrogen ion concentration than A
A has 1000x the hydrogen ion concentration than B
What type of lipid contains several rings?
Triglyceride
Phospholipid
Sterol
What functional group does every fatty acid have?
Phosphate group
Amino group
Carbonyl group
Carboxyl group
Dehydration reactions lead to the _______________ of polymers, and hydrolysis reactions lead to the _______________ of polymers.
Production; production
Breakdown; breakdown
Production; breakdown
Break down; production
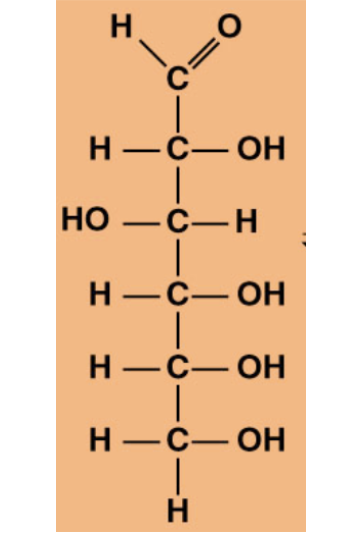
Which carbon in the molecule above is always involved in going from the chain form to the ring form? (start counting from the top)
1
2
3
4
5
The oxygen connected to which carbon in the molecule above will be part of the ring when it is converted from the chain form to the 6-membered ring form?
1
3
4
5
6
Which carbon is considered the anomeric carbon when the molecule above is in its ring form?
1
2
4
5
6
Which carbon is considered the anomeric carbon when the molecule above is in its ring form?
1
2
4
5
6
The atoms connected to which carbon determines whether the monosaccharide is in its alpha- or beta-anomer?
1
2
4
5
6
What type of starch is most similar to glycogen?
Amylose
amylopectin
What is the monomer of glycogen?
amino acids
glycerol
glucose
Fructose
anomer
The carbons of the pentose sugar of a nucleotide are numbers 1’ to 5’. Which carbon is bound to phosphate groups?
1’
2’
3’
4’
5’
Which two carbons are involved in the formation of the covalent bond between adjacent nucleotides in a strand of DNA?
1’ and 2’
1’ and 3’
4’ and 5’
3’ and 5’
2’ and 3’