Cellular Respiration Study Guide
Fermentation
Glucose
Glucose is good for storage but not as good as fuel
Glucose must be converted to ATP
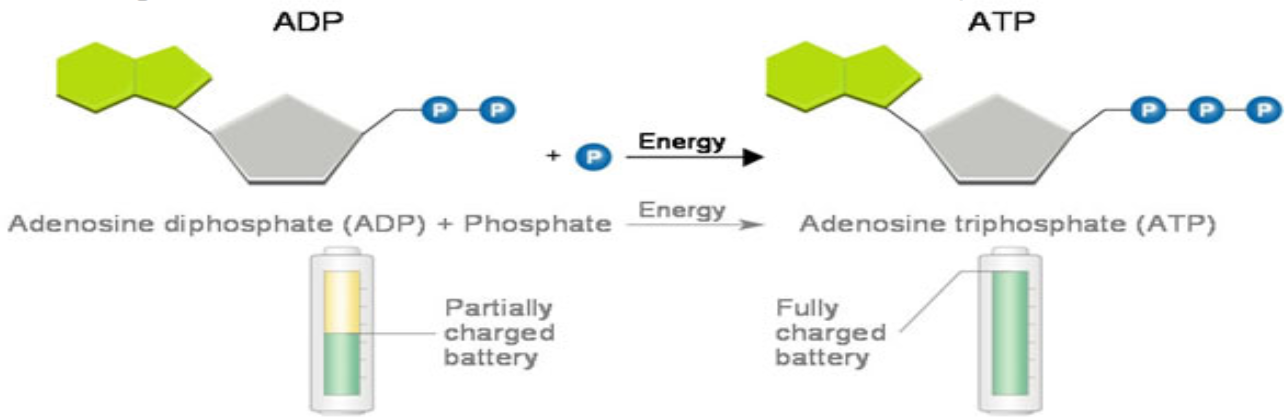
ATP
ATP stands for Adenosine triphosphate
2 Ways to Convert Glucose to ATP
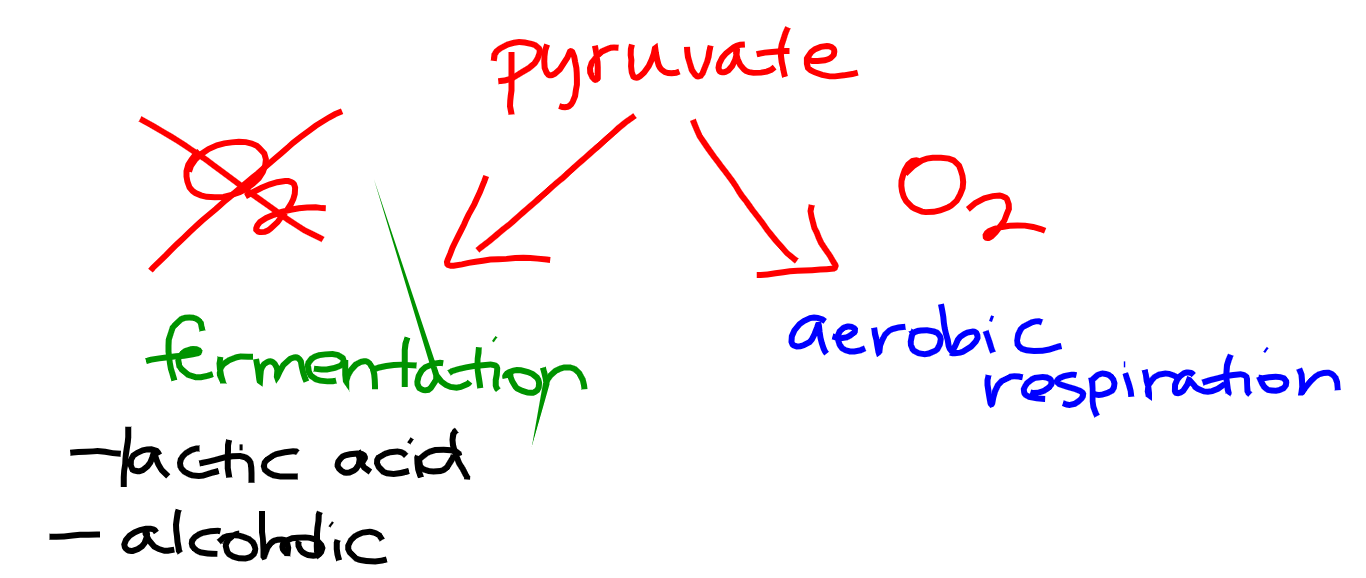
Fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
Does not require oxygen
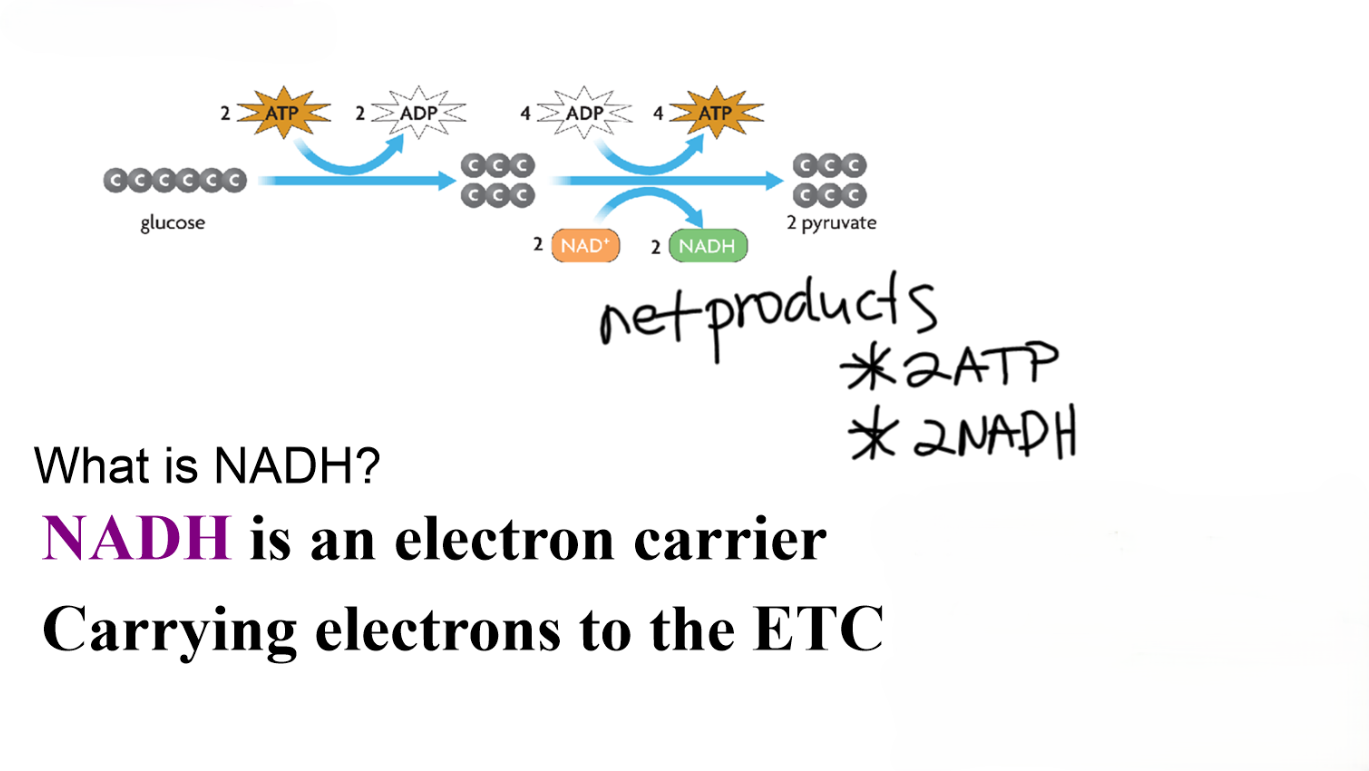
Makes 2 ATP
Aerobic Respiration
Requires oxygen
Makes 36 ATP
We do/prefer aerobic respiration but can also do anaerobic respiration
So, now that glucose has entered the cell…
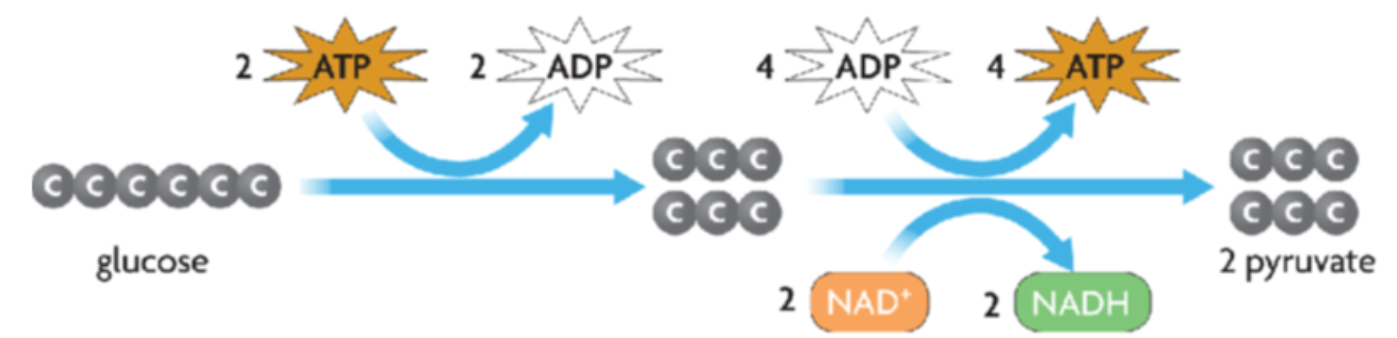
Both types of respiration, aerobic and anaerobic, begin with Glycolysis in the cytoplasm of the cell
Glucose is “lysed” (split) in Glycolysis
What happens to pyruvate will depend on the presence of oxygen
Bacteria
How do bacteria benefit from living in our intestines?
They get food and a warm environment
How do we benefit from having bacteria in our intestines?
We get short-chain fatty acids, which we can digest
Mutualism - A win/win relationship
Types of Fermentation
Lactic Acid
Glycolysis produces 2 lactic acid
The purpose is to generate a small amount of ATP without oxygen
Alcoholic
Glycolysis produces 2 alcohol (ethanol) and 2 carbon dioxide
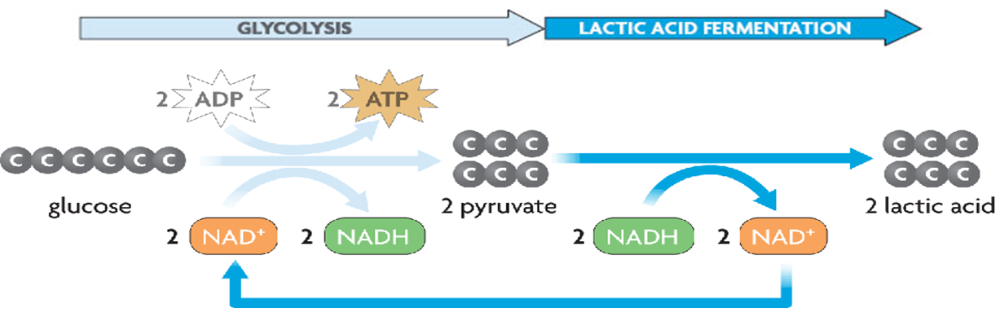
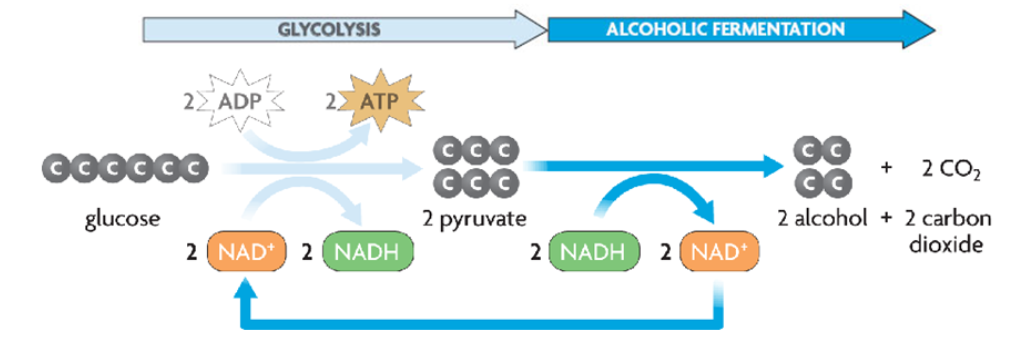
Fermentation Process
Recycles NAD+ back to glycolysis
ATP can be continually generated even in the absence of oxygen
The purpose of Fermentation is to allow glycolysis to continue
Only 2 ATP is generated for every glucose molecule
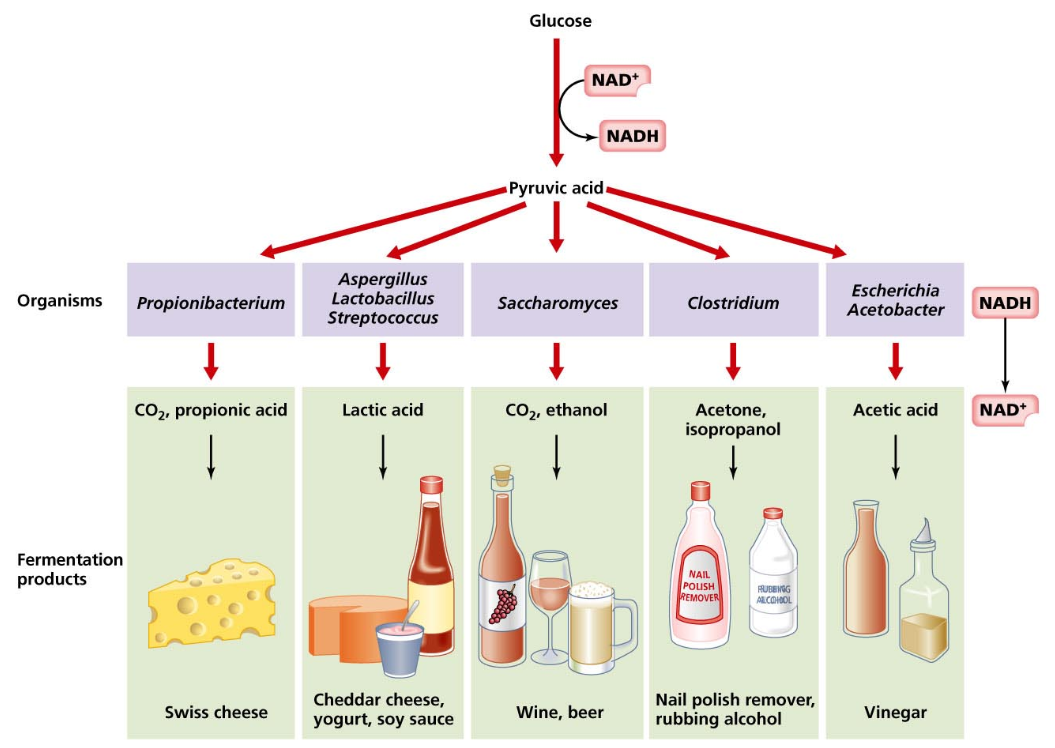
Fermentation product depends on…
Type of microorganism
Type of fermentation
Source of glucose
We can measure CO2 to determine the rate of fermentation
Aerobic Respiration
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ => 6H₂O + 6CO₂ + 36 ATP
Cellular Respiration is a biochemical pathway
Series of chemical reactions in which the products of one reaction are consumed in the next
Sugar doesn’t combine with oxygen
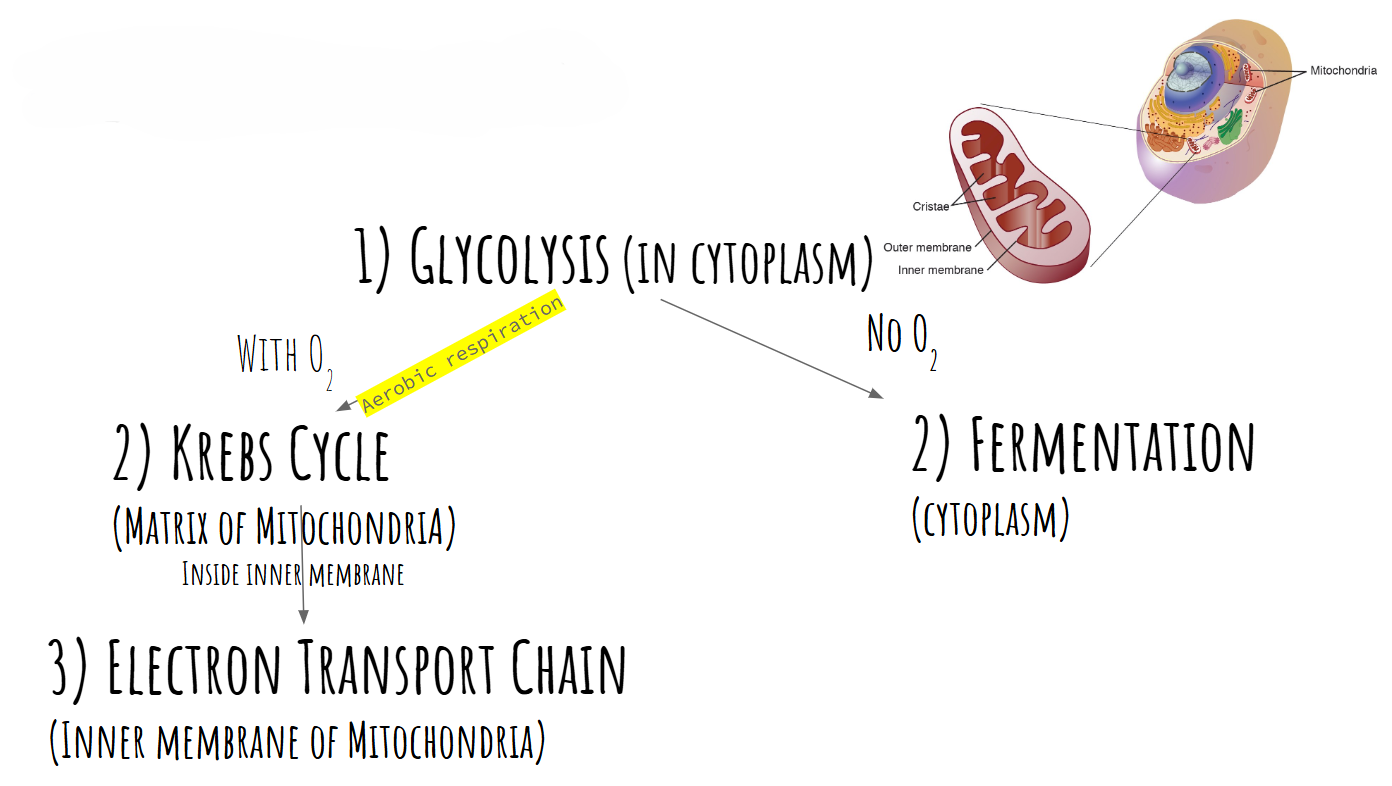
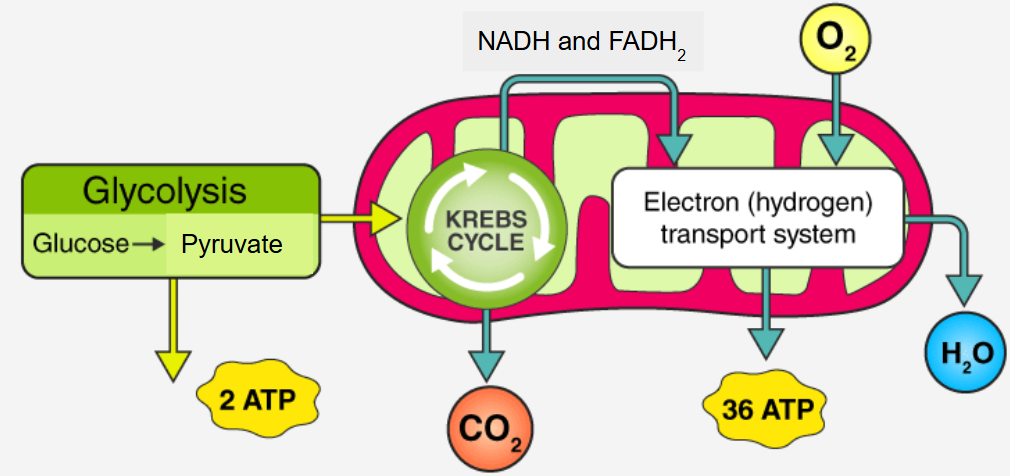
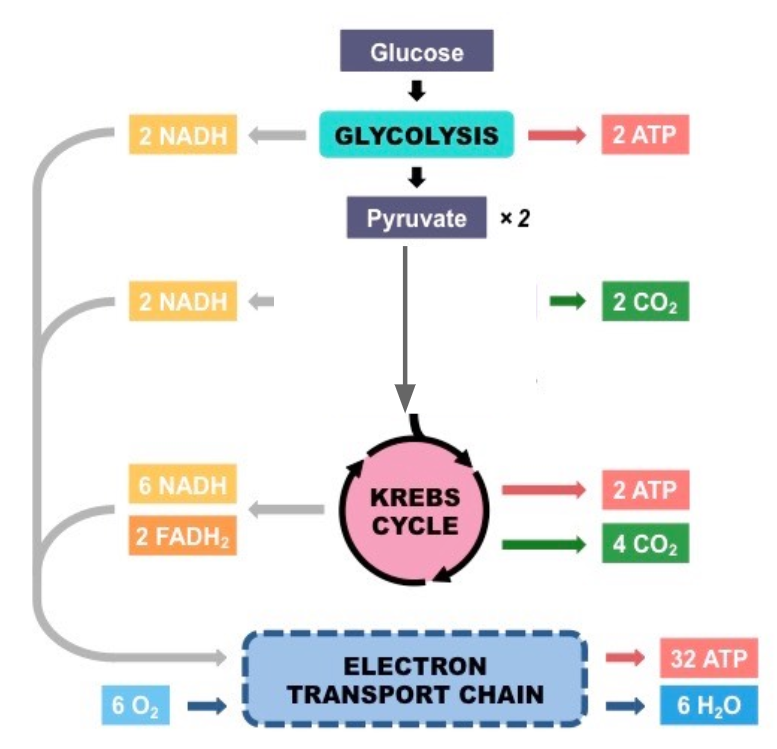
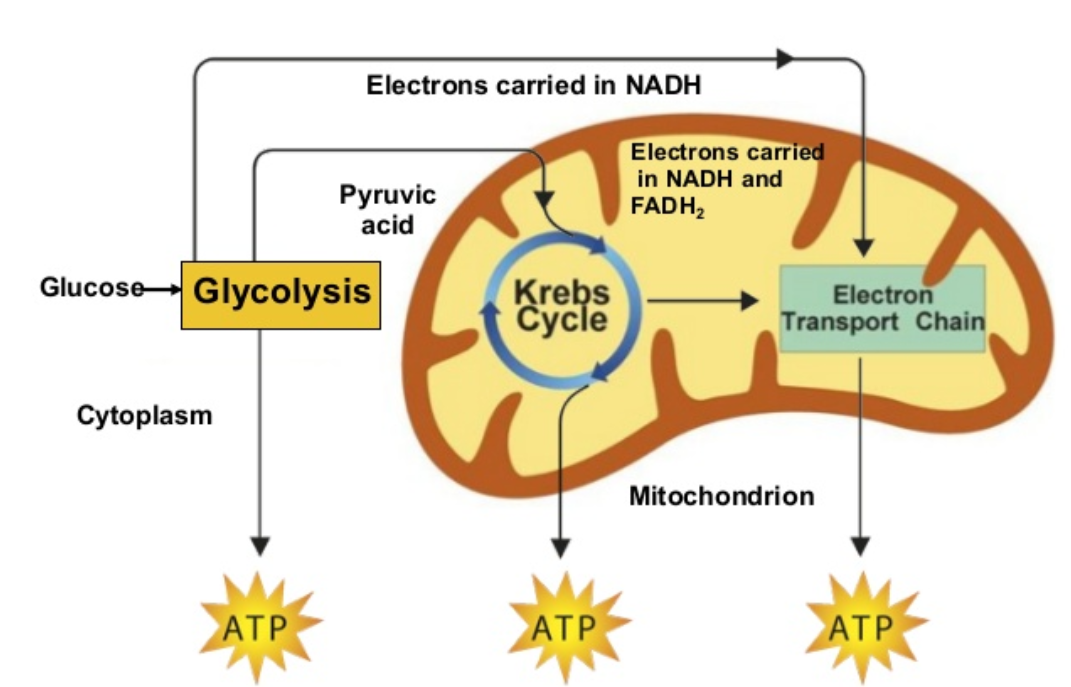
Steps in Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis (occurs in the cytoplasm) - splits glucose into 2 3-C molecules of pyruvate
Krebs Cycle (occurs in the mitochondrial matrix)
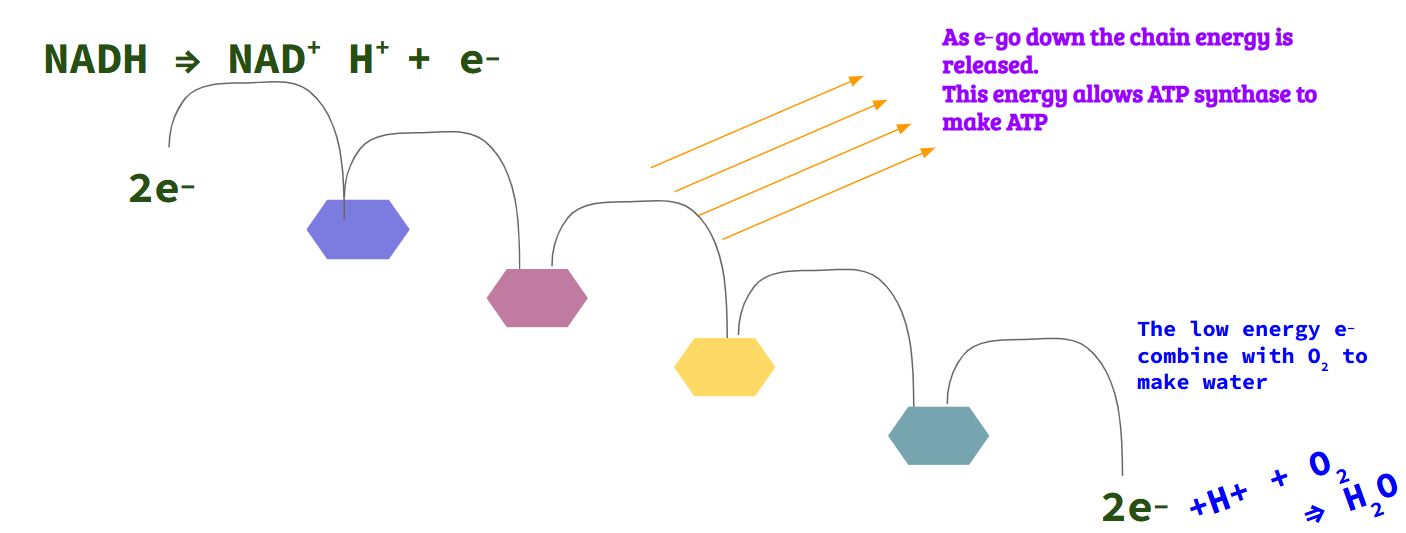
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) uses electrons from NADH and FADH2 molecules to make ATP using the enzyme (ATP synthase)
Krebs Cycle
The function of the Krebs cycle is to add electrons to the electron carriers NAD+ and FAD+
Pyruvate is used in the Krebs cycle
More NADH and FADH2 => More ETC => More ATP
NADH and FADH2 go to the ETC
NADH, FADH2, ATP, and CO2 are made in the Krebs cycle
Electron Transport Chain
NADH supplies the electrons to the ETC
The ETC is a series of proteins that “pass” the electrons down the chain
Overview of Cellular Respiration