Unit 3 Managing human population
3.1 Human population dynamics & structure
Calculations
Population density: total population/land area
# of ppl per km²
Low density: low marriage (low birth rate), fewer jobs in rural areas (causes urbanisation), lack of available healthcare
Intrinsic growth rate: dN/N0
dN = (births + immigration) - (deaths + emigration)
N0 = original population
Doubling time: period of time required for a population to double in size
Rule of 70: 70/percent
Factors that influence population density & distribution:
Environmental: natural resources, geographic & climatic factors
Large, flat lowland plains are easier to access + better for food production than mountainous areas
Areas w/ few extreme weather events are more appealing
Areas w/ fertile soil like river deltas tend to have higher populations than areas with high rainfall (leached soil) & cold areas with permafrost
A secure water supply
Areas w/ a wealth of natural resources
Economic:
Agriculture is a primary industry & is manufactured by a secondary industry
These increase job opportunities & standard of living, causing population growth
Areas w/ good transport links are often more densely populated due to trade links
Political:
Government policies have an impact on population density
Can encourage/discourage investment in an area
War is a ‘push’ factor & causes out migration + decrease in food production
Factors affecting changes to a population:
Population change: # of people b/t the start and end of a given time period
Birth rate: # of live births per thousand ppl in a population per year
High birth rate = increased population & vice-versa
High infant mortality rate in LICs → high birth rates
Due to: spread of disease & lack of both medical care + access to clean water
Death rate: # of deaths per thousand ppl in a population per year
Influenced by: climate, medical facilities, living standards, & social conflict + crime rates
Life expectancy increases due to: increased standards of living, access to both clean water & nutrition, & education improvements
Overall population change: annual population change of an area
(birth rate - death rate) + net migration
Population Differences in HICs & LICs
Stage 1 pyramid (pre-industrial): high birth & death rate w/stable population
Rarely found & low life expectancy
Stage 2 pyramid (transitional): declining death rate (due to medicine, better nutrition, & clean water)
Stage 3 pyramid (industrial): birth rate declines from stage 2, death is still declining/low
Less population growth than stage 2; birth rates can typically be controlled by contraceptives
Avg. life expectancy increases & mortality rates stabilize
Stage 4 pyramid (late-industrial): low birth & death rates
Population size fluctuates due to economic conditions; slow growth
Stage 5 pyramid (post-industrial): birth rate is lower than death rate
Older population reaches full life expectancy
Analyzing a population pyramid:
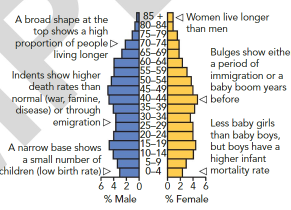
Dependency ratio: relationship b/t a country’s working & non-working populations
Dependent: ages 0 to 14 (young)& 65+ (old)
Independent: age 15-64
Total dependency ratio: [young population (0 to 14) + old population (65+)] × 100 / population aged 15 to 64
Expressed as # of dependents per hundred ppl in the workforce
Considered high when it’s above 62%
Decreases due to: young population reaching working age, anti-natalist policy, immigration of working age ppl, & lower birth rate
3.2 Impacts of human population change
Ageing populations: population w/ a high percentage of older people
Occur when birth rates decline & life expectancy increases — typically stage 5
Average age is increasing due to: better nutrition, sanitation, standard of living, & care
Impacts of an ageing population:
Shrinking workforce impact economy
Pensions may be insufficient to care for older populations - higher spending
Health care systems have more pressure since older ppl need more care
Increased retirement age, so gov’ts can collect extra taxes
3.3 Managing human population change
Global organizations
The Club of Rome: aims to alert the world about consequences of a rapidly growing population → focused on sustainable economic growth + limited population growth
UN Agenda 21: plan of action to limit human impact on the environment
Both are concerned w/ issues related to human population growth
Government policies:
Pro-natalist: encourage ppl to have children & increase birth rates
Shrinking populations pressure a country’s workforce + financial stability
Monetary incentives, childcare assistance, free schooling, & monthly grants
Anti-natalist: discourage ppl from having children & decrease birth rates
Increasing populations that cause declining mortality rates & high rates of poverty
e.g) China’s One Child Policy
Other policies include:
encouraging marriage later in life
increasing access to contraceptives & family planning
improving education + employment opportunities for women
making abortions legal + safe
Limitations as a population stabilizes: an ageing population + declining workforce