Unit 5.2 Language Translators
Aims
Know what is meant by the term translator and the different types of translators available.
Know the difference between an interpreter and a compiler, including the benefits and drawbacks of each.
Know what is meant by the term Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and typical features they contain to help programmers write programming code.
EXAM - KNOW HOW COMPILER & INTERPRETER WORKS INCLUDING PRO’S & CON’S
Language Translators
High level programming languages/Assembly code need to be converted into low-level machine code (binary instructions that the CPU can process)
3 Different translators:
Assembler - Software that translates assembly to machine code (not expected to know how this works)
Interpreter - High to Low Level (1terpreter)
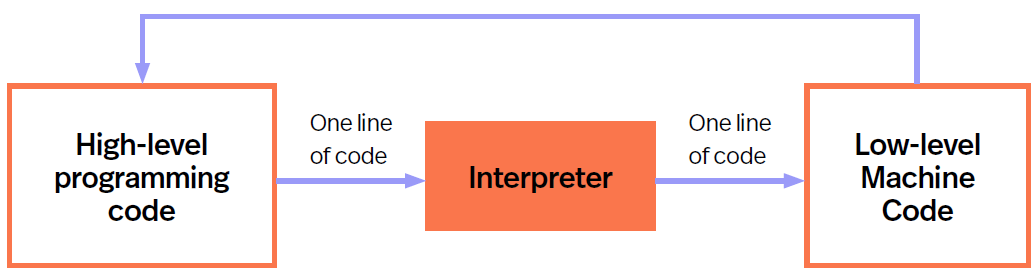
Translates code one line at a time and executes immediately
Doesn’t produce object code or executable file - object code is sequence of instructions written in computer language.
Pro’s | Con’s |
Runs until first error then stops | Runs slowly as code is translated one at a time |
Easier to debug as individual lines are tested | Interpreter needed each time program is run |
Compiler - High to Low Level

Translates all programming code simultaneously
Does produce object code and single executable file. (then machine code)
Pro’s | Con’s |
Runs program faster (once compiled) as code already translated | Difficult to debug and test individual lines of code |
Only needed once for initial translation | Code wont run if there is an error. |
Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
Programmers need place to write programming code, so language rules can be utilized programmers use IDE’s (instead of word processors etc.)
IDE’s understand language used and have tools to assist programmers to write and debug code.
Features - BASVAPE (see end)
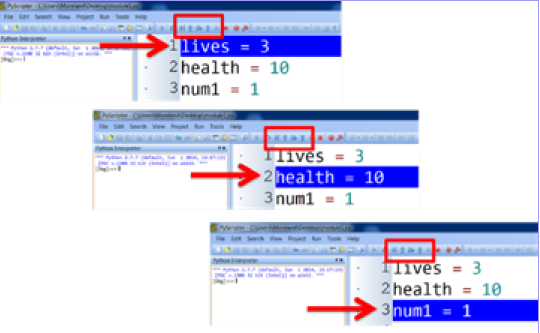
Single Stepping
Codes often run all at once - this allows code to be run one at a time for checking, to slow execution speeds of code to find errors
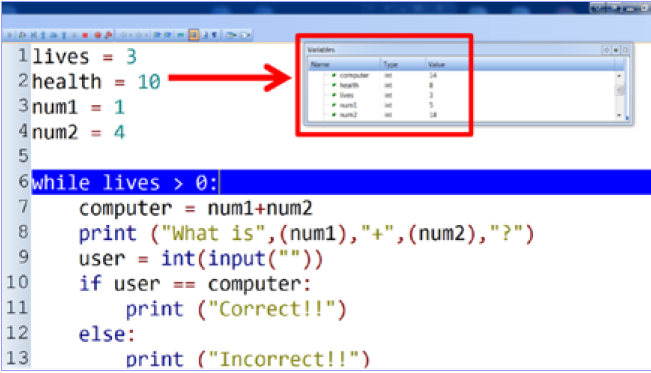
Variable Watch Window
Allows display of variables (often in separate window), to see value of all variables whilst code is running instead of keeping track yourself.
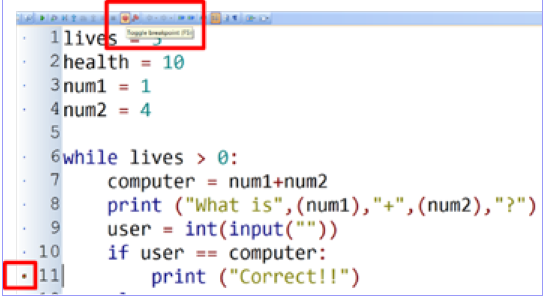
Breakpoints
Allows code to be stopped at particular points, point is set, the code runs and pauses when point is reached, allows you to check the value of variables to check for errors.
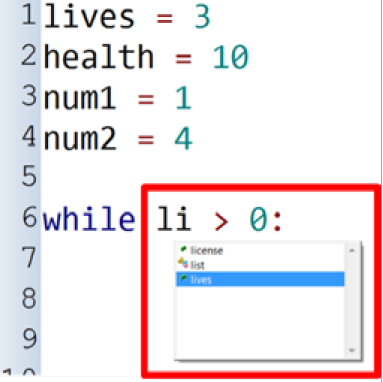
Auto Complete
IDES often attempt to complete statements
e.g. type in name of built-in function like print/input it displays a drop down list.
Start to enter variable name it displays list of variables already defined in program for you to select.
Helps to reduce spelling mistakes and code errors.
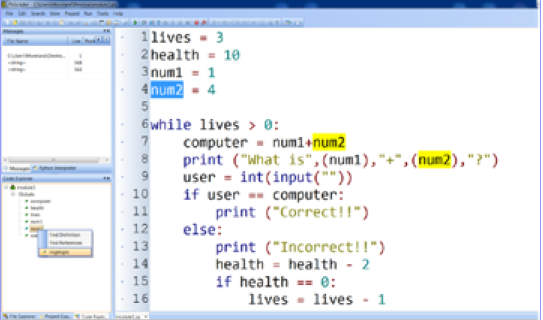
Pretty Printing
IDE colour codes different parts of statements for distinguishing quickly, e.g. Display built in functions in purple or Display IF, ELIF, ELSE statements in orange
Python highlights syntax errors red (Print instead of print) so helps with code checking.
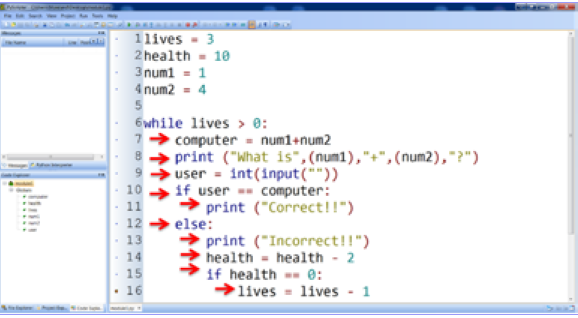
Auto Indent
Indenting code is important to group statements to a condition
In some languages if indents are done incorrectly it stops the code from working, auto indents does it automatically.
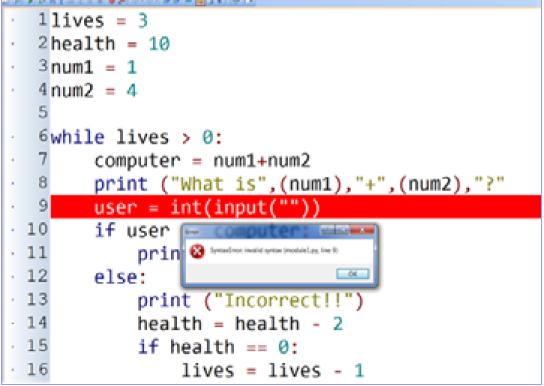
Error Diagnostics
Locates and reports errors and sometimes gives error details (either pinpoint or rough idea of where error is)
BASVAPE
Break Points
Auto Indent
Single Stepping
Variable Watch Window
AutoComplete
Pretty Printing
Error Diagnostics