World History Final Study Guide
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on June 28, 1919, that officially ended World War I between Germany and the Allied Powers. The treaty imposed heavy penalties on Germany, including the loss of territory, military restrictions, and reparations payments. The treaty also established the League of Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future wars. The harsh terms of the treaty are often cited as a contributing factor to the rise of Nazi Germany and the outbreak of World War II.
- War guilt clause was clause 231
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, between the new Bolshevik government of Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire) that ended Russia's participation in World War I. The treaty was highly unfavorable to Russia, as it ceded large territories to the Central Powers and required Russia to pay large reparations. The treaty was later nullified by the Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I.
Aftermath of WW1
The aftermath of World War I saw the collapse of empires, the rise of new nations, and the beginning of the Cold War. The Treaty of Versailles, which ended the war, imposed heavy penalties on Germany and set the stage for the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party. The war also led to the creation of the League of Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future wars. The war had a profound impact on the world, leading to changes in political, economic, and social structures that continue to shape the world today.
- Antisemitism
Holocaust and Hitler
The Holocaust was a genocide that occurred during World War II, in which Nazi Germany, aided by its collaborators, systematically murdered approximately six million European Jews, as well as other targeted groups, including Romani people, homosexuals, disabled individuals, and political dissidents. The Holocaust was orchestrated by Adolf Hitler, who rose to power in Germany in 1933 and implemented policies aimed at purging the country of Jews and other "undesirables." Hitler's ideology of racial purity and his belief in the superiority of the Aryan race led to the implementation of policies such as the Nuremberg Laws, which stripped Jews of their citizenship and rights, and the establishment of concentration camps, where millions were imprisoned and killed. The Holocaust remains one of the most horrific events in human history and serves as a reminder of the dangers of hatred, prejudice, and discrimination.
Women’s liberation movement
The women's liberation movement, also known as the feminist movement, was a social and political movement that aimed to achieve gender equality and women's rights. It emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and gained momentum in the 1960s and 1970s. The movement focused on issues such as reproductive rights, equal pay, and ending gender discrimination in the workplace and society as a whole. It led to significant changes in laws and social norms, including the legalization of abortion and the passage of anti-discrimination laws. The movement continues to evolve and address new challenges faced by women today.
1918 influenza’s and responses of nations
The 1918 influenza pandemic was a global outbreak of the H1N1 virus that infected an estimated 500 million people worldwide and caused the deaths of 50 million people. Nations responded to the pandemic in various ways, with some implementing strict measures such as quarantine and isolation, while others downplayed the severity of the outbreak. The pandemic had a significant impact on society, including on healthcare systems, economies, and political structures. It also led to advancements in medical research and public health measures. Spread by soldiers. Lost generation.
Great depression cause and effects across countries
The Great Depression was a worldwide economic downturn that lasted from 1929 to the late 1930s. It was caused by a combination of factors, including the stock market crash of 1929, overproduction, and a decline in international trade. The effects of the Great Depression were felt across the globe, with many countries experiencing high unemployment rates, bank failures, and a decrease in industrial production. The depression had a profound impact on the political and social landscape of many countries, leading to the rise of authoritarian regimes and the adoption of new economic policies. Despite the severity of the depression, it ultimately paved the way for new economic theories and policies that helped to prevent future economic crises. USA, Germany, and GB hit the worst. Germany hit bad because reperations. USA got out by new deal. Japan got out becasue gov could controll industry.
Impact of WW1 across countries
World War I had a significant impact on countries around the world. In Europe, the war led to the collapse of empires and the redrawing of national borders. It also resulted in the deaths of millions of people and left many more injured or traumatized. The war had a profound impact on the economy, with many countries experiencing inflation and debt. In the United States, the war helped to establish the country as a global superpower and led to significant social and cultural changes. In Africa and Asia, the war had a mixed impact, with some countries experiencing economic growth and others suffering from increased exploitation and oppression. Overall, World War I had a lasting impact on the political, economic, and social landscape of countries around the world.
Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian independence activist who is known for his nonviolent civil disobedience. He was born in 1869 in Porbandar, India and studied law in London. Gandhi became a leader in the Indian National Congress and advocated for Indian independence from British rule. He is known for his philosophy of Satyagraha, which means "truth force" or "soul force," and his use of nonviolent resistance to achieve political and social change. Gandhi was assassinated in 1948 by a Hindu nationalist who opposed his vision of a united India. He is remembered as a symbol of peace, nonviolence, and social justice.
- Indian Independence
- Mohandas Gandhi- “Great Soul”
- Protests about British laws in India
- Nonviolence- civil disobedience
- Still imprisoned
- Government of India Act
- British passed to extend Indian role in government
- Indian National Congress
- Reforms then full independence
- CIVIL DISOBEDIENCE
Events leading to WW2
The events leading up to World War II were complex and multifaceted. Some of the key factors included the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh penalties on Germany after World War I; the rise of fascist regimes in Italy, Germany, and Japan; the failure of appeasement policies by Western powers; and the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany in 1939, which sparked the war. Other factors included the failure of the League of Nations to prevent aggression, the Great Depression, and the failure of collective security efforts. After WW1 started by Woodrow Wilson. Ultimately, a combination of these factors led to the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
Holocaust
The Holocaust was a genocide during World War II in which Nazi Germany, aided by its collaborators, systematically murdered approximately six million European Jews, as well as other targeted groups such as Romani people, homosexuals, disabled individuals, and political dissidents. The Holocaust is widely regarded as one of the most heinous crimes against humanity in modern history and serves as a reminder of the dangers of prejudice, discrimination, and hatred.
Nazis and Soviets in WW2
During World War II, the Nazis and Soviets were bitter enemies. The two sides fought on the Eastern Front, with the Nazis invading the Soviet Union in 1941. The war on the Eastern Front was brutal, with millions of casualties on both sides. The Soviets eventually emerged victorious, but at a great cost. The war had a profound impact on both countries, shaping their politics and societies for decades to come.
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of political and military tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasting from the end of World War II in 1945 until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The two superpowers engaged in a global struggle for influence and power, with each side seeking to spread its ideology and gain allies around the world. The Cold War was characterized by a nuclear arms race, proxy wars, espionage, and propaganda. Despite the absence of direct military conflict between the US and the USSR, the Cold War had a profound impact on global politics and international relations.
China- Communist won civil war
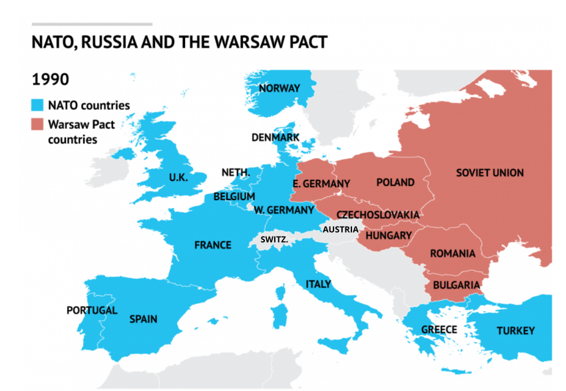
NATO- military alliance
Here are the countries that were part of NATO as of 2021:
- France
- Italy
- United Kingdom
- United States
Warsaw Pact- reaction to NATO
- Soviet union
- Satellite states of SU
Arms Race
The term "arms race" refers to the competition between nations to develop and acquire weapons and military technology. This race has been a major feature of international relations since the early 20th century, with countries seeking to gain an advantage over their rivals. The arms race has led to the development of increasingly sophisticated and destructive weapons, including nuclear weapons, and has contributed to tensions and conflicts between nations. Efforts to control the arms race have included arms control agreements and disarmament initiatives, but progress has been slow and uneven. The arms race remains a significant challenge for global security and stability.
- Building up armies and stores of weapons to keep up with an enemy
- US v Soviet Union
- Deterrence, fear, devastation,prevention
- Sputnik 1- “Missile gap”
Policy of Containment
The policy of containment was a United States foreign policy during the Cold War that aimed to prevent the spread of communism. It was first articulated by diplomat George F. Kennan in 1947 and was implemented by the Truman administration. The policy involved providing economic and military aid to countries threatened by communism, as well as using diplomatic and military means to prevent the spread of communism. The policy was successful in preventing the spread of communism in Europe, but was less successful in other parts of the world, such as Vietnam. Overall, the policy of containment was a key strategy in the United States' efforts to contain the Soviet Union and prevent the spread of communism during the Cold War.
- A plan to keep something, such as communism,within its existing geographical boundaries and to prevent further aggressive moves
Berlin Airlift
The Berlin Airlift was a massive humanitarian effort undertaken by the United States, Great Britain, and other Western powers to supply the city of Berlin with food, fuel, and other necessities during a Soviet blockade in 1948-1949. The airlift involved thousands of flights and millions of tons of supplies, and was a major victory for the West in the early stages of the Cold War. The airlift ended in September 1949, when the Soviets lifted the blockade.
- Soviet Union- Blocked West Berlin
- Berlin Airlift (solution)
- British and American planes
- Russia lifted blockade
- West- Federal Republic of Germany- Bonn
- East- German Democratic Republic- East Berlin
China’s and Soviets 5 year plan
The Five-Year Plans were a series of social and economic development initiatives launched by the Communist Party of China and the Soviet Union. The plans aimed to rapidly industrialize and modernize their respective countries, with a focus on heavy industry and infrastructure development. The first Five-Year Plan in China was launched in 1953, while the Soviet Union began its first plan in 1928. Both plans were characterized by centralized planning, state ownership of industry, and a focus on collective agriculture. While the plans achieved some success in terms of industrial growth, they also had negative consequences such as environmental degradation and social inequality. Not sucessful. Stalin and Mao did them.
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a political and military standoff between the United States and the Soviet Union in October 1962 over the installation of Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba. The crisis is widely regarded as the moment in which the Cold War came closest to escalating into a full-scale nuclear war. The crisis was resolved when the Soviet Union agreed to remove the missiles in exchange for a US pledge not to invade Cuba and to remove US missiles from Turkey. The crisis had a lasting impact on US-Soviet relations and the global balance of power.
- Fidel Castro overthrew Batista and set up Soviet supported regime
- Bay of Pigs- Kennedy Failed
- Khrushchev wanted to put missiles in Cuba because US had missiles in Turkey
- Blockade- Peace
- Hotline- Moscow to DC
Mao Zedong’s Cultural Revoultion
Mao Zedong's Cultural Revolution was a political movement launched in China in 1966. The movement aimed to purge capitalist and traditional elements from Chinese society and promote Maoist ideology. It was characterized by mass mobilization, violence, and political persecution. The Red Guards, a group of young people, were the main agents of the movement. They attacked and humiliated intellectuals, artists, and other perceived enemies of the revolution. The Cultural Revolution caused widespread social and economic disruption and led to the deaths of millions of people. It ended in 1976 with Mao's death and the arrest of the Gang of Four, a group of Mao's closest associates who had led the movement. The Cultural Revolution remains a controversial and divisive period in Chinese history.
Permanent Revolution - In China during the 1950’s, a group of collective farms, which contained more than 30,000 people who lived and worked together.An atmosphere of constant revolutionary fervor favored by Mao Zedong to enable China to overcome the past and achieve the final stage of communism
- Nationalist Chiang Kai-shek v Communist Mao Zedong
- Peoples Liberation Army –Communist- took Beijing and Shanghai
- Chiang Kai-shek fled to Taiwan
- New China under Mao Zedong
- Socialist society
- All private farmland-collectivized
- Industry and commerce-nationalized
- Great Leap Forward
- Collective farms became communes
- Attempt for final stage of communism
- Failed- Return to collectivefarms and private plots
Chinese Communism
Chinese Communism refers to the political ideology and system that has been in place in China since the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949. It is based on the principles of Marxism-Leninism and Mao Zedong Thought, and emphasizes the importance of collective ownership of the means of production, the elimination of social classes, and the establishment of a classless society. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) is the ruling party in China and has maintained its grip on power through a combination of political repression, economic development, and nationalist propaganda. Despite significant economic growth in recent decades, the CCP has faced criticism for its human rights record, censorship, and lack of political freedom.
Fall of the Soviet Union
The fall of the Soviet Union was a complex event that occurred over several years, beginning with the policies of Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev in the mid-1980s. Gorbachev's reforms, including glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring), aimed to modernize the Soviet economy and political system, but ultimately led to the unraveling of the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union faced economic and political challenges, including a growing independence movement in the republics, which ultimately led to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The fall of the Soviet Union had significant global implications, including the end of the Cold War and the emergence of the United States as the world's sole superpower.
- Soviet Union falling- Gorbachev
- Perestroika- restructuring economic policy
- Glasnost- open discussion political policy
- New Parliament- Congress of People’s Deputies
- New President- Gorbachev
- Ended Cold War
- Intermediate-Range INF Treaty
- Stopped aiding Communist Governments
OPEC and Middle East Post WW1
After World War I, the Middle East became a crucial region for oil production and transportation. In 1960, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was formed by five Middle Eastern countries and Venezuela to coordinate oil production and pricing. OPEC's power grew in the 1970s when they imposed an oil embargo on countries that supported Israel in the Yom Kippur War. This led to a global oil crisis and increased OPEC's influence in the oil market. However, OPEC's power has since declined due to increased competition from non-OPEC countries and the rise of renewable energy sources.
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a conflict that lasted from 1955 to 1975, fought between the communist government of North Vietnam and the government of South Vietnam, which was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war was marked by guerrilla warfare, heavy casualties, and controversy over the U.S. involvement. The conflict ended with the fall of Saigon to North Vietnamese forces in 1975, leading to the unification of North and South Vietnam under communist rule. The war had a profound impact on American society and politics, leading to widespread protests and a loss of faith in government institutions.
- Ho Chi Minh- Elected Comm Party leader against French Colonialism- seized Vietnam
- Geneva Peace Accords- temporarypartition- Comm & Anti-CommGlobalization
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world's economies, societies, and cultures. It has been driven by advancements in technology, transportation, and communication, and has led to increased trade, investment, and migration across borders. While globalization has brought many benefits, such as increased economic growth and cultural exchange, it has also led to challenges such as income inequality, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization. The future of globalization is uncertain, as some countries are turning towards protectionism and nationalism, while others continue to embrace globalization and its potential benefits.
Creation of Israel
The creation of Israel in 1948 was the result of a long-standing Zionist movement to establish a Jewish homeland in Palestine. After World War I, the League of Nations granted Britain a mandate to govern Palestine, but tensions between Jews and Arabs escalated. In 1947, the United Nations voted to partition Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, but the Arab states rejected the plan. In May 1948, Israel declared its independence, leading to a war with neighboring Arab countries. Israel emerged victorious and expanded its territory, displacing hundreds of thousands of Palestinians in the process. The creation of Israel remains a controversial issue, with ongoing conflict between Israelis and Palestinians over land and political rights.
- 1947, Israel declares independence
- 1947 Israel defends itself against an attack by all of its Arab neighbors. Takes control of land from Syria.
- 1949 formal recognition of state
- 1967- aka Six Day War. Israel suspects a surprise attack and so takes control of West Bank, Golan Heights, Gaza, and Sinai Peninsula.
- 1979- Israel gives back Sinai Peninsula to Egypt in exchange for peace.
Muslim Brotherhood
The Muslim Brotherhood is a Sunni Islamist organization founded in Egypt in 1928. It seeks to establish Islamic law and promote Islamic values. The group has been involved in political and social activities in many countries, including Egypt, Syria, and Jordan. It has been accused of supporting terrorism and has been banned in some countries. The group has also been involved in providing social services and has gained support from some segments of the population.
- Mandate
- Rome Berlin access - vs GB and allies
- Krystalnacht
- Stalin Soviet WW2, pact with Hitler and Hitler went against
- Berlin airlift
- Glasnost
- Peristroka
- France had vietnam colonies - HO chi min was leader vietnam
- Japan wanted vietnam
- Globolization
- Little red book