Chapter 11 - Communication
- @@Communication@@: transfer and understanding of meaning.
Functions of communication
- Communication serves four major functions within a group or organization:
- Control
- Motivation
- Emotional expression
- Information
The communication process
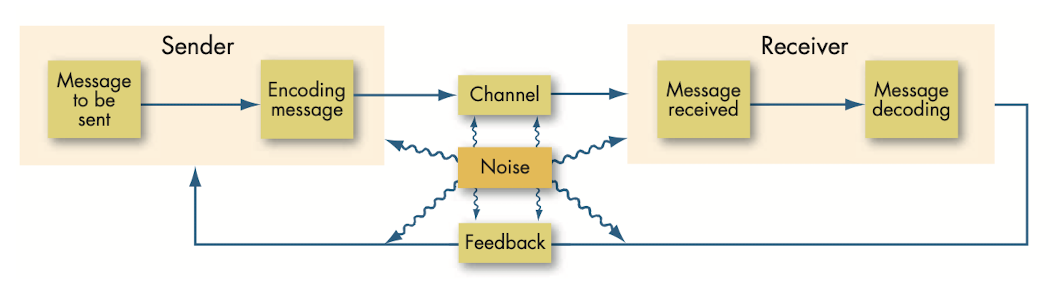
- @@Communication process@@: steps between a source and a receiver that result in the transfer and understanding of meaning.
- @@Formal channels@@: communication channels established by an organization to transmit messages related to the professional activities of members.
- @@Informal channels@@: communication channels that are created spontaneously and that emerge as responses to individual choices.
Direction of communication
@@Downward communication@@: communication that flows from one level of a group/organization to a lower level.
@@Upward communication@@ flows to a higher level in the group/organization. It’s used to provide feedback to higher-ups, inform them of progress towards goals, and relay current problems.
@@Lateral communication@@: when communication takes place among members of the same work group, members of work groups at the same level, managers at the same level, or any other horizontally equivalent personnel.
Organizational communication
- @@Grapevine@@: organization’s informal communication network.
Modes of communication
- @@Oral communication@@: primary means of conveying messages.
- Forms
- Speeches
- Formal one-on-one
- Group discussions
- Informal rumor mill or grapevine
- Advantages
- Speed
- Feedback
- Disadvantage
- The more people a message must pass through, the greater the potential distortion.
- @@Written communication@@
- Forms
- Letters
- Instant messaging
- Organizational periodicals
- Any other method that conveys written words or symbols
- @@Non-verbal communication@@
- Forms
- Body movements
- Intonations or emphasis we give to words
- Facial expressions
- Physical distance between the sender and receiver
Choice of communication channel
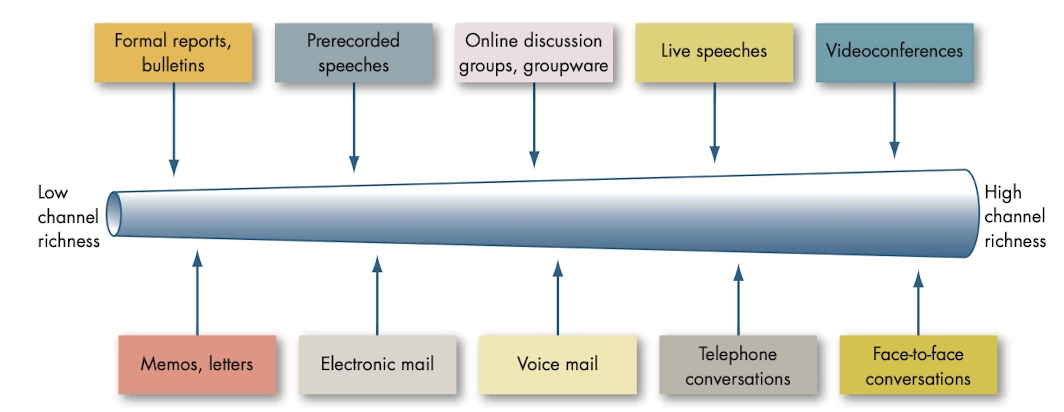
@@Channel richness@@: amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode.
Persuasive communication
- @@Automatic processing@@: relatively superficial consideration of evidence and information making use of heuristics.
- @@Controlled processing@@: detailed consideration of evidence and information relying on facts, figures and logic.
Barriers to effective communication
- @@Filtering@@: sender’s manipulation of information so that it will be seen more favorably by the receiver.
- Selective perception
- @@Information overload@@: condition in which information inflow exceeds an individual’s processing capacity.
- Emotions
- Language
- Silence
- @@Communication apprehension@@: undue tension and anxiety about oral communication, written communication or both.
- Lying
Cross-cultural communication
- Cultural barriers
- Barriers caused by semantics
- Barriers caused by word connotations
- Barriers caused by tone differences
- Differences in tolerance for conflict and methods for resolving conflicts
- Cultural context
- @@High-context cultures@@: cultures that rely heavily on nonverbal and subtle situational cues in communication.
- @@Low-context cultures@@: cultures that rely heavily on words to convey meaning in communication.