Slides PTC & Senior Review
Chapter 1: Terminology
Section 1.04
Terminology
Property: means any matter or thing capable of private ownership
Real Property: land, improvement, mine/quarry, mineral in place, standing timber, or estate/interest
Improvement: a building, structure, fixture, or fence erected on or affixed to land;
Personal Property: property that is not real property.
Tangible personal property: means personal property that can be seen, weighed, measured, felt, or otherwise perceived by the senses, but does not include a document or other perceptible object that constitutes evidence of a valuable interest, claim, or right and has negligible or no intrinsic value.
Intangible personal property: means a claim, interest (other than an interest in tangible property), right, or other thing that has value but cannot be seen, felt, weighed, measured, or otherwise perceived by the senses
Market value: means the price at which a property would transfer for cash or its equivalent
Appraised value: means the value determined as provided by Chapter 23 of this code.
Assessed value: means, for the purposes of assessment of property for taxation, the amount determined by multiplying the appraised value by the applicable assessment ratio
Taxable value: means the amount determined by deducting from assessed value the amount of any applicable partial exemption
Partial exemption: means an exemption of part of the value of taxable property.
Taxing unit: means a county, an incorporated city or town (including a home-rule city), a school district, a special district or authority
Tax year: means the calendar year
Assessor: means the officer or employee responsible for assessing property taxes
Collector: means the officer or employee responsible for collecting property taxes for a taxing unit by whatever title he is designated
Possessory interest: means an interest that exists as a result of possession or exclusive use or a right to possession or exclusive use of a property and that is unaccompanied by ownership of a fee simple or life estate in the property. However, ‘‘possessory interest’’ does not include an interest, whether of limited or indeterminate duration, that involves a right to exhaust a portion of a real property.
Conservation and reclamation district: means a district created under Article III, Section 52
Clerical error: means an error:
(A) that is or results from a mistake or failure in writing, copying, transcribing, entering or retrieving computer data, computing, or calculating; or
(B) that prevents an appraisal roll or a tax roll from accurately reflecting a finding or determination made by the chief appraiser, the appraisal review board, or the assessor; however, ‘‘clerical error’’ does not include an error that is or results from a mistake in judgment or reasoning in the making of the finding or determination.
Comptroller: means the Comptroller of Public Accounts of the State of Texas.
Section 1.07
Delivery of Notice: 1.07(a)An official or agency required by this title to deliver a notice to a property owner may deliver the notice by regular first-class mail
Section 1.08
When a property owner is required by this title to make a payment or to file or deliver a report, application, statement, or other document or paper by a specified due date, his action is timely
Section 1.111
(a)On the written request of a property owner, an appraisal office or an assessor or collector shall deliver all notices, tax bills, and other communications relating to the owner’s property or taxes to the owner’s fiduciary.
(b)To be effective, a request made under this section must be filed with the appraisal district. A request remains in effect until revoked by a written revocation filed with the appraisal district by the owner.
Chapter 5: State Administration
Glenn Hegar (Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts)
Chapter 6: Local Appraisal
Different appraisal districts (e.g., Tarrant, Harris) operate under state guidelines.
Chapter 11: Property Tax Exemptions
Types of Exemptions:
Mandatory and Total
100% Disabled Veterans
Surviving spouses of military personnel killed in action
Mandatory but Partial
General Homestead Exemptions:
General Homestead - School District
General Homestead- FM Road or Flood Control
Over 65 - School District
Disabled Persons - School District
Disabled Veterans
Disabled Veterans with Charitable Housing
Local Option and Partial
General Homestead - Cities, Counties, School Districts, Special Districts
Cannot be less than $5,000 or more than 20% of the value
Over 65 - Cities, Counties, School districts, Special Districts
Cannot be less than $3,000 - no max limit
Exemption Limitations
Limitations on Value Increases: The Appraised Value equals the LESSER of the Market Value or 10% of Last Year’s Appraised Value
Chapter 21: Situs Rules
Situs: Refers to the location where a property is taxable.
BPP is mobile and can be in different taxing units throughout the year.
Cannot be taxed in more than one county.
Different than Interstate Allocation
Four Rules for Situs: Establishes where property is taxable.
Step 1: Location on January 1 must be established.
Step 2: Determine normal location of property.
Step 3: Identify the property's return location between usages.
Step 4: Assess owner's principal place of business.
Business Personal Property
Any property that is not real property.
Movable items of property that are not permanently affixed to, or part of the real estate
Use Items
Inventory
Supplies
Owned
Leased
Consigned
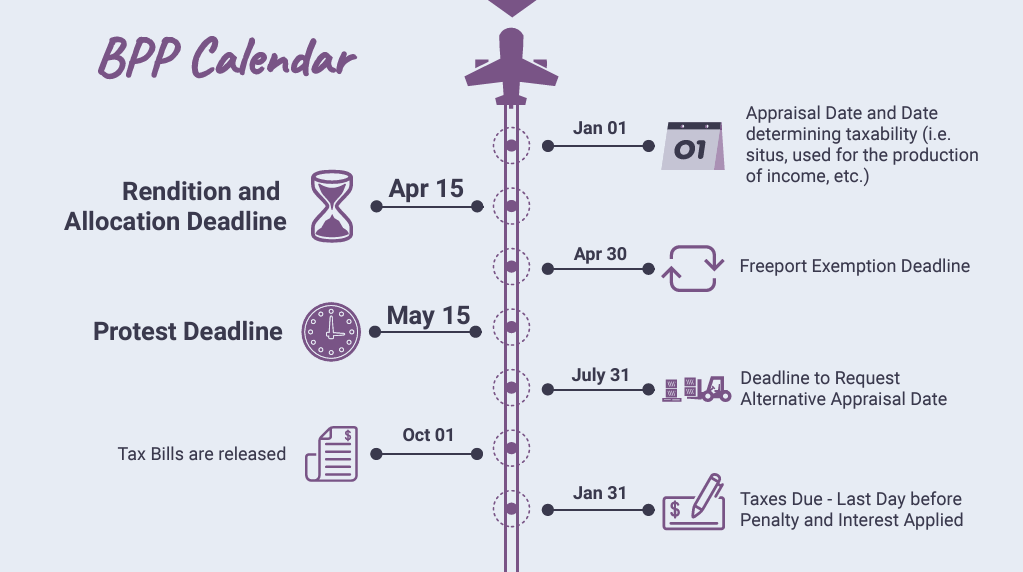
Freeport
An exemption from taxation
Only applies to Inventory
Annual application required
Must leave the state within 175 days
Application due by April 30
Aircraft parts allowed 730 days
Inventory must turn 2.09 times per year
Rendition Basics:
Filing required by April 15 annually, with extensions available. Property Owner can request a 30 Day extension.
Must include a good faith estimate of property value.
If the Market Value is less than $20,000, the rendition is limited.
If the property owner’s business is less than 50 employees, the opinion of value on the rendition can be based on Federal Income Tax returns.
Penalties for late/no filing(10%) or fraudulent filings(50%) of determined value.
Chapter 23: Appraisal Methods and Procedures
CAD must appraise same and similar kinds of property using the same and similar methods and techniques.
However, each property must be appraised based on its individual characteristics.
23.0101 Three Main Approaches: The chief appraiser shall consider all three in determining property value but, must only use the most appropriate.
Cost Approach: Estimates reproduction cost, useful for special-use properties.
Best used for Special Use Properties, Historic Properties, and New Construction
Sales Comparison Approach: Values based on sales of similar properties
Best used for residential Properties and Owner Occupied Commercial Properties
Income Approach: Based on the property's capacity to generate income
Primarily used for revenue-generating properties.
Special Appraisal
Inventory - 23.12
Dealer’s Inventory
Dealer's Motor Vehicle Inventory - 23.121
Dealer's Heavy Equipment Inventory - 23.1241
Oil & Gas Interests - 23.175
Appraisal of Wildlife Management Use - 23.521
Appraisal of Timberland - Subchapter E
Appraisal of Recreational, Park, and Scenic Land - Subchapter
Appraisal of Public Access Airport Land - Subchapter G
Appraisal of Restricted-Use Timberland - Subchapter H
Agricultural Appraisal
Texas allows for a property to be appraised based on the use of the property instead of the market value of the property when the property owner uses the property for agricultural purposes.
2 Main Types of Ag Land
Ag Use - 1-d
Requires agriculture to be the property owner's primary occupation.
Annual application required.
Requires the property owner to be an individual.
Open Space - 1-d-1
No income, occupation, or profit requirements.
Reapplication only required when ownership changes or the Chief Appraiser sends a request for application.
Allows individuals and corporations to own property.
Chapter 25 - Corrections
25.21 Omitted Property
Omitted from the "Appraisal Roll"
5 previous years for Real Property
2 previous years for Business Personal Property
25.25(b): Allows the Chief Appraiser to correct: Anything Any Year
25.25(c): Up to 5 Previous Years
Clerical Error
Multiple Appraisal
Not in the form or at the location as described on the appraisal roll
Incorrect Ownership
25.25(d): Substantial Error
Non-Homestead Properties: Must prove the property is 1/3 over-appraised
Homestead Properties: Must prove the property is 1/4 over-appraised
Cannot have finalized a 41.41 protest in the same year
10% Penalty if successful
Filing Deadline January 31 - before the delinquency date
Chapter 26: Assessment
Tax Calculation Formula
([Appraised Value - Exemptions]/100) * Tax Rate
(Taxable Value/100) * Tax Rate
Chapter 31: Collections
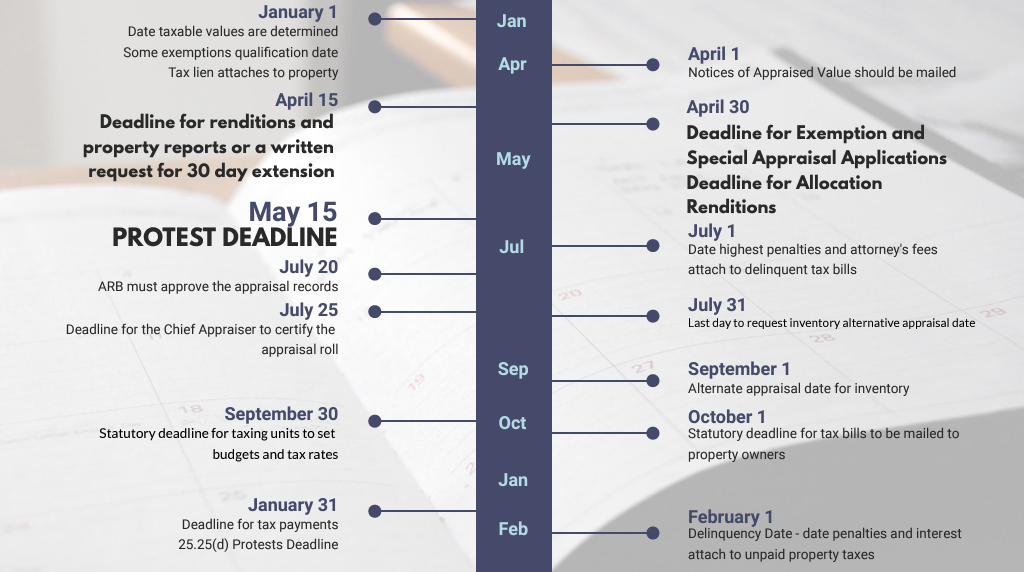
Taxes are due on January 31st
Chapter 32: Tax Liens & Personal Liability
Texas attaches a Tax Lien on every taxable property January 1 of each
year.
If taxes are not paid, taxing entities can foreclose on and sell the property on the courthouse steps in a tax auction.
Chapter 33: Delinquency
Delinquency Date Exceptions: Taxes are due before February 1
< Jan 10 = Jan 31 deadline
> Jan 10 = 1st of next month to allow 21 days
If tax bill includes previous years, then deadline = next Jan 31 that allows at least 180 days
Penalty & Interest
Month | Penalty | Interest | Total P&I |
February | 6% | 1% | 7% |
March | 7% | 2% | 9% |
April | 8% | 3% | 11% |
May | 9% | 4% | 13% |
June | 10% | 5% | 15% |
July | 12% | 6% | 18% |
August | 12% | 7% | 19% |
September | 12% | 8% | 20% |
October | 12% | 9% | 21% |
November | 12% | 10% | 22% |
December | 12% | 11% | 23% |
January | 12% | 12% | 24% |
Chapter 34: Tax Sales and Redemption
Chapter 41: Protests
What can be protested?
Section 41.03: Taxing Units / Jurisdictions (Deadline before June 1st)
Exclusion of a property
Granting of an Exemption
Determination of Special Use Appraisal
Failure to identify the taxing unit
Section 41.41: Taxpayers (Deadline on or before May 15th or 30 days after the Delivery of Notice)
Reasons
Market Value
Equal and Uniform Valuation
Inclusion of a property
Denial of an Exemption
Determination of Special Use Appraisal
Identification of a taxing unit
Determination of Ownership
Determination of a Change in Use
Any other action adversely affecting the property owner.
Section 41.411: Failure to Give Notice
A taxpayer can protest the failure of the CAD or the ARB to deliver a required notice.
Notice is considered delivered when it is deposited in the mail.
It is presumed that notice was delivered, however the presumption is rebuttable.
Filing Deadline January 31 - before the delinquency date
Section 41.43(b): Three Tests of Equity
Two Appraisal Ratio Tests
The appraisal ratio of the subject must be greater than the median of...
The appraisal ratio of a reasonable and representative sample of other properties in the appraisal district.
The appraisal ratio of a reasonable number of other properties similarly situated to, or of the same general kind or character as, the subject property.
Section 41.43(b)(3): The appraised value of the subject is greater than a…
Reasonable Number
Comparable Properties
Appropriately Adjusted
Who can file a protest?
A Property Owner
A New Property Owner
A Person claiming an interest
A Lessee
An Agent representing any of the other filers
How and where is a protest filed?
A protest must be in writing, but can be on any form.
A protest is sufficient if it:
1. Identifies the owner
2. Identifies the property
3. Gives an indication of dissatisfaction
Some CAD's and ARB's allow for electronic filing of protests.
Hearings
Scheduling Hearings
Notice of hearing must be sent 15 days prior to the date of the hearing.
Preferential scheduling before agents and other owners
Attending an ARB Hearing
By Affidavit
In Person
By Telephone
By Representative
Postponements
One-time free reschedule if not represented by an agent
Unlimited reschedule for "good cause"
Unlimited reschedule if the chief appraiser consents
If the hearing does not start within two hours of the scheduled time
Scheduled in another county and can prove the other CAD sent notice first
If the ARB reassigns a hearing to another panel without the consent of the owner/agent
CAD fails to deliver requested evidence timely
If a hearing is missed, reschedule request can be made within 4 days and granted if good cause is shown.
Evidence Inspections
If requested more than 14 days before a scheduled hearing, the CAD must deliver any evidence they intend to present at the hearing to the owner/agent.
Evidence requested timely, but not delivered timely is inadmissible in a
hearing.
However, the rule does not apply to rebuttal evidence.
Determination of Value
The burden of proof is on the CAD by a Preponderance of the Evidence
If the CAD fails to meet the Burden - the case should be determined in favor of the taxpayer!
Hearing Procedures 41.66
Three Post ARB Remedies
SOAH
District Court
Binding Arbitration
LIMITATIONS ON APPEAL: ONLY properties that are the property owner's residence homestead or that the ARB determined a value of less than $5,000,000 can be appealed through Binding Arbitration
DEADLINE: within 60 days from the receipt of the Board Order
ADVANTAGES:
relatively inexpensive
opportunity to settle
can recover filing fee if successful
relatively quick resolution
value cannot be raised
virtually no discovery
Chapter 42: Judicial Review
Value
Price = Cost = Value
4 types of Value
Market
Appraised
Assessed
Taxable
Other Types of Value
Business Value
Exchange Value
Fair Value
Insurable Value
Investment Value
Liquidation Value
Public Interest Value
Use Value
Factors of Value
Four interdependent factors of value.
Utility
Scarcity
Desire
Effective Purchasing Power
All four factors must be present for a property to have value.
Bundle of Rights
SLUGER
Sell
Lease
Use
Give Away
Enter/Exit
Refuse to do anything
Government Restrictions on the Bundle of Rights
Leased Fee(Landlord): The Landlord receives the money (rent) and holds the Leased Fee Estate.
Leasehold(Tenant):The tenant holds the property (in exchange for rent) and therefore has the Leasehold Estate.
The Leasehold Estate:
-Estate for Years
-Estate for a Period of Time
-Estate at Will
-Estate at Sufferance
Subject Analysis
Identify the Land
Site Analysis: land should always be analyzed as if vacant
Highest and Best Use
Physically Possible
Legally Permissible
Financially Feasible
Maximally Productive
The Cost Approach:
Land + RCNLD(Reconstruction Cost New Less Depreciation) = Total Cost Value
Depreciation
Physical Deterioration
wear and tear
can be curable or
incurable
Functional Obsolescence
flaw in materials, design, or structure
can be curable or incurable
Economic Depreciation / External Obsolescence
negative external influences
typically incurable
Age/Life Comparisons:
How does the age of the property compare to the life of the property?
Actual Age vs. Effective Age
Economic Life vs. Useful Life
Remaining Economic Life vs. Remaining Useful Life
The Sales Approach
Determine Elements of Comparison
Size
Condition
Amenities
Views
Time of Sale
Legal Restrictions
Determine Appropriate Adjustments
The Income Approach
Basic Assumptions:
A dollar in the future is worth less than a dollar today
Value depends directly on income
Value varies with the number of income-generating periods
Value varies with risk
Positives:
Income potential is primary
Enough data to lead to credible results
Negatives
Income estimates are weak
Data does not lead to a cap rate
Owner-Occupied properties are predominant
Other considerations besides income are prevalent
Rental Income:
Rent
Market Rent
Contract Rent
Excess Rent Effective Rent
Deficit Rent
Percentage Rent
Overage Rent
Potential Gross Income
Vacancy and Collection Loss
Stabilization
Other Income/Secondary Income
Effective Gross Income
Expenses
Allowable vs. Not Allowable
Fixed vs. Variable
Net Operating Income (NOI)
Effective Gross Income - Operating Expenses = NOI
Direct Capitalization Formula
Potential Gross Income(PGI)
-Vacancy and Collection Loss(V&C)
+ Secondary Income(SI)
=Effective Gross Income(EGI)
-Operating Expenses(OE)
=Net Operating Income(NOI)
/CAP Rate
=Value
PTC Requirements
Who does NOT have to register?
POA
Attorney
Lessee
Employee
Public Employee
Broker/RE Salesperson
CPA
Person Assisting
RE Appraiser
Preliminary Requirements:
Completed Application
HS Diploma
18+
Passed Test
Paid Fees
Completed 40 classroom hours
Prohibited Acts
A Senior Property Tax Consultant may not supervise more than 10 property tax consultants unless each additional consultant has more than six months of experience
Cannot file a protest without the approval of the property owner
May not falsify a document
May not file a protest on a single-family home without authorization from the property owner or another person authorized to sign on behalf of the property owner
May not solicit by assuring a specific outcome
May not maintain a website that appears to be a government website
Must identify the company of the consultant prominently on the homepage of the consultant’s website
May not destroy, erase, or remove client records for at least 3 years following the date of the last action taken or service performed on behalf of the client.
TDLR Code of Ethics
Shall not plan, scheme, or arrange the evasion of the rules
Shall not lend their registration to another person
Shall use reasonable care in the supervision of other persons
Shall not engage in any activity that constitutes dishonesty, fraud, or gross incompetence
Shall promptly report any known violation
Shall cooperate fully with an investigation
Shall not offer anything of value with the intent of influencing a public
employee
Shall not contract or accept compensation for services not performed
Shall not knowingly engage in false advertising
Shall not knowingly furnish inaccurate, deceitful, or misleading information
Shall not reveal confidential information
Shall not state or imply representation of a person or firm that is not in fact someone represented
Shall not solicit or advertise the promise of a specific out come
*without prior analysis
Phases of the Property Tax Calendar
Appraisal
Equalization
Assessment
Collections