Topic_1_slides__cognition__motivation_and_emotion
Cognitive Psychology Methods
Methods Overview
Cognitive psychology traditionally relies on experiments and quantitative methods.
Increased use of self-report questionnaires and factor analysis.
Challenges from reliance on introspective data over direct behavior observation.
Considerations in Research
Importance of good experimental design; no one-size-fits-all approach.
Relevance of both qualitative and quantitative methods based on research questions.
Acknowledgment of inherent limitations in study designs.
Latent Constructs
Definition
Latent constructs are theoretical; cannot be directly observed or measured.
Examples include depression, motivation, and intelligence.
Case Study: Depression
Definition: Depression reflects persistent sadness and loss of interest with physical symptoms.
Diagnosis requires symptoms to persist for at least two weeks.
Limitations of Self-Report Questionnaires
Key Challenges
Social Desirability: Tendency to answer in ways viewed favorably by others.
Personality Differences: Self-perception can distort accurate reporting.
Response Styles: Biases in answering scales can affect results.
Self-Reflection: Difficulty in recognizing and reporting true behaviors.
Points of Reference: Responses can be skewed based on comparisons with others.
Operationalization and Hypothesis
Operationalization
Defined as the process of making a research question measurable (e.g., measuring conscientiousness).
Hypothesis Formation
A hypothesis provides an expected relationship between variables, structured as "If-Then" statements.
Criteria for a good hypothesis: specific, measurable, testable, free of ambiguity.
Variables in Research
Independent vs. Dependent Variables
Independent Variables: Predictors/causal factors (e.g., conscientiousness).
Dependent Variables: Outcomes affected by independent variables (e.g., grades in school).
Emotions and Cognition
Key Theories
Three concepts: the trilogy of the mind (Hilgard, 1980)
Cognition
Emotion
Motivation
Affective Terminology (Forgas, 1995)
Affect: General term encompassing emotions and moods.
Emotion: Intense response to a stimulus .
Mood: Generalized, longer-lasting emotional state.
Basic Emotions (Paul Ekman)
Seven Basic Emotions categorized as fundamental elements of human experience: anger, contempt, disgust, enjoyment, fear, sadness, surprise.
Theoretical Perspectives on Emotion
Evolutionary Perspective
Ekman assumes that basic emotions have evolved to deal with fundamental life tasks. This implies that emotional responses are universally shared within our species rather than being learned from culture or environment
Constructed Emotion Theory (Lisa Feldman Barrett)
Suggests that emotions emerge from cognitive appraisals of sensations in real-time, challenging the assumption of biologically fixed emotions.
Arousal and Performance
Arousal Theory
Wundt Curve, relationship between arousal and activity enjoyment:
Low arousal: boredom (activity too simple and familiar),
Medium arousal: enjoyable (activity simple but novel/complex but familiar),
High arousal: overwhelming and frustrating (activity new and complex).
Yerkes-Dodson Law. relationship between arousal and performance:
Low arousal: performance unlikely to be good,
Medium arousal: optimal performance,
High arousal: anxiety or panic, performance is likely to suffer.
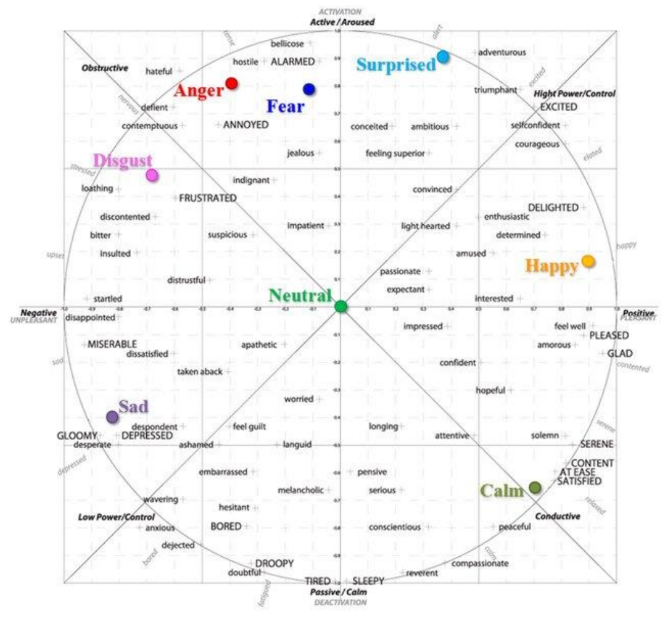
Valence and Arousal (Russel, 1980)
Valence refers to how positivie/negative an emotional experience is
Arousal describes the level of activation that is experienced
Two-Factor Theory (Schachter-Singer Theory)
Two key elements to every emotion; physical arousal and a cognitive label
Experiment:
Injecting participents with adrenaline and placing them in a room with happy or angry people
Participants in the happy room felt excitement as side effect and vice versa
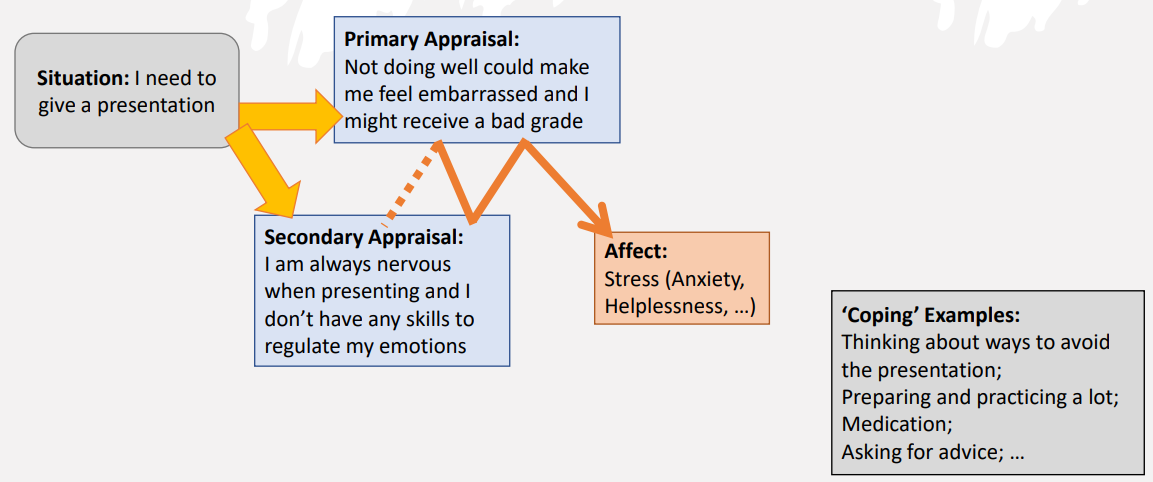
Cognitive Appraisal Theory (Lazarus, 1991)
Cognitive appraisal is subjective affect and how we cognitively interpret and evaluate the things that are happening to us.
Attribution is what we think we know about the world and how it works
Appraisals are the implications of this ‘knowledge’ for one’s personal well-being
Primary appraisal: the motivational relevance of what is happening
Secondary appraisal: evaluative judgements whether any actions can be taken to improve the person-environment relationship
Four assumptions about the theory:
Primary and Secondary Appraisals are mediators of the emotional reaction
They influence each other but have no temporal order
Appraisal (of relevance and available strategies) and coping behaviour interact
The relationship between appraisal and chosen coping strategies are context
specific
Affect-Infusion Model (Forgas, 1995)
Affect infusion is the process whereby affectively loaded information exerts and influence on and becomes incorporated into the judgementel process
Broaden-and-Build Theory of Positive Emotions (Fredrickson,2004)
Positive emotions such as joy, interest, contentment and love broaden our thought-action repertoire
Negative emotions tend to narrow our mindsets, as does exerting self-control
Positive emotions promote novel and creative actions, strategies, ideas and social bonds, which builds personal physical, intellectual, social & psychological resources
Memory and Mood
Mood-Congruent vs. Mood-Dependent Memory
Mood-Congruent Memory: Recalling information consistent with current mood.
Mood-Dependent Memory: Recall improves when the mood during learning matches the mood during retrieval.
Implications for Design in Psychology
Emotionally Impactful Design (Denisova et al., 2021)
Exploration of emotional experiences in game design indicates that gameplay can stimulate complex emotional responses. Design considerations include:
Emotional experiences should be intertwined with gameplay, emphasizing the importance of player feedback in early design phases.
Game mechanics and narrative techniques can be utilized to elicit specific emotional responses, enhancing engagement and immersion.
Designers should consider the emotional arcs of gameplay to provide players with not only challenges but also moments of relief, joy, or tension, which contribute to a rich emotional experience.
Understanding cognitive and emotional responses can help in designing interfaces and interactions that resonate with players on a deeper level, ultimately contributing to the game's success and player satisfaction.