Soil and Its Ecosystem
- Plants take up water and nutrients from the soil through the root system (from upper layers of soil)
- Plants that live in soil that is nutrient-poor use carnivoriy to get mineral nutrients
- (ex/Genlisea uses underground leaves to capture soil organisms)
- Physical properties of soil
- Texture (tough, pores, air, etc.)
- Composition (what is it made of?)
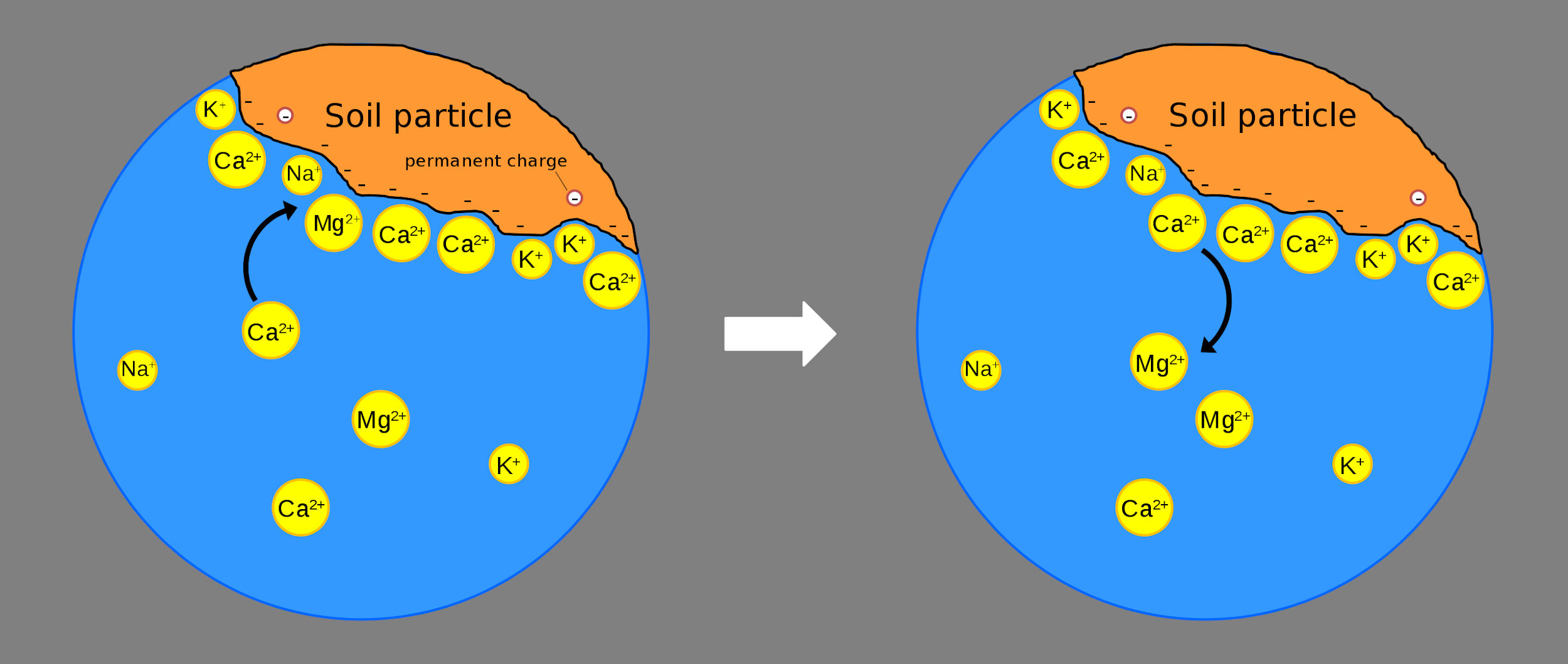
- ==Cation exchange==: cations are displaced from soil particles by other cations, particularly H+
- Displaced cations enter soil solution, taken up by roots
- Negative ions do not bind with soil particles & can be lost from soil
- Affected by pH
- Cations are more available in acidic soil (low pH)
- Hydroxil (OH-)
- More hydroxil= more acidic
- Less hydroxil= less acidic
- More OH-= less H+
- More H+= less OH-
- Soil pH<5→ toxic aluminum ions become more soluble
- Stunts root growth & prevents calcium uptake
- ==Fertilization==: addition of mineral nutrients to the soil
- Combats reduction in yields experienced when the same crops are grown in the same locations over many seasons
- Soil management
- Replaces nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
- American Dust Bowl of 1930s caused by soil mismanagement
- Formed a lot of dust in the Midwest
- Loose soil & dust
- Soil mismanagement→ 30% less food production
- ==Sustainable agriculture==: use farming methods that are conservation-minded, environmentally safe, & profitable
- ==Irrigation==: BAD; drain on water resources because water is brought to an area where it isn’t usually available
- Result in depleting of aquifers→ land subsidence (sinking of land)
- Lead to salinization
- ==Salinization==: concentration of salts in soil as water evaporates
- Reduces water potential of soil solution and diminishes water uptake
- Excess minerals are leached from the soil & causes algal blooms
- Algal blooms block the sun for plants→ plants die→ increase in bacteria
- \
