Digestive System - Detail
Basic
Function
cells need nutrients from our food
processes include digestion and absorption
gets rid of solid waste
mainly one tube from mouth to anus called gastrointestinal tract (GI-Tract)
Organs
mouth
stomach
smal/large intestine
liver
gall bladder
pancreas
rectum and anus
Definition of Digestion
The process of breaking down food into nutrients and moving it into blood
Mechanical Digestion
Large chunks of Food are broken down into small pieces. Starts with the mouth and physical processes, such as chewing.
Chemical Digestion
Large food molecules are broken down into small nutrient molecules using enzymes. Strats with the mouth and goes basically to the end. Examples include saliva digesting carbohydrates for the brain.
Definition of Absorption
process that allows substances to enter the blood system
blood absorbs nutrients for growth or even re-making cells
some substances are not able to be processed so they leave the body as solid waste (called elimination)
Organs
Muscle Movement
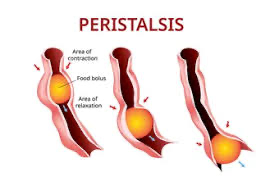
muscles contract or tighten to push the food through the system, wave like
movement called peristalsis - involuntary process which is the reason why food can go through our system
liver, gall bladder, and pancreas are the organs which no food passes through as they store or secrete enzymes which help break down the food chemically
Mouth
seeing or smelling can cause the release of saliva in the mouth
once you start eating saliva were and therefore helps break and swallow food
digestive enzymes (including amylase) start breaking down starches into sugars
tongue mixes food with saliva and enzymes
teeth break down food mechanically by chewing it into smaller bits before your tongue helps swallow the food
Oesophagus
uses peristalsis to move down food its self as it is just a long tube with muscles from mouth to stomach
at the bottom there is a muscle that fully closes the path after the food has entered the stomach
Stomach
is an organ which is sack like and uses its muscles to move the food its storing so that enzymes such as pepsin can reach every bit of food
pepsin helps digest proteins
water, salts and simple sugars can also be absorbed
food stays and gets stored in the stomach until the small intestines are ready to receive it (average 3h)
fluids mainly are hydrochloric acid
muscles surrounds the insides of the stomach to protect other tissue from burning - can also re grow
Small Intestines
juices from the liver/gall bladder and pancreas make the food “non acidic” in the first part called the duodenum
from the stomach to the large intestine
around 7 meters long in a average adult
enzymes cut down last piece of nutrients
later section is full of villi which are like the inner wall
villi are like the doors for the nutrients to enter the bloodstream
millions of trillions of villi in the small intestine creating a way larger surface area so that nutrients have a way higher chance of entering the circulatory system
villi make the surface area around 1000 times larger
Large Intestine
wide tube that connects the small untestine with the anus
around 1.5 meters long in a normal adult
the waste eneetrs still in a liquid dtate before the fluids get absorbed and drained leaving a solid which then gets passes and released through the anus and rectum, which then gets called a bowl movement
Digestive Enzymes
enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions
break larger food molecules in simpler ones
released/secreted by organs in the digestive system
types include protease that digest proteins and nucleases that digest nucleic acidic
Examples
amylase
produced in the mouth
breaks down large starch mollecould into simple sugars
Pepsin
produced in the stomach
breaks down proteins into amino acids
Pancreatic lipase
produced in the pancreas
digests lips and fats
Deoxyribonuclease and Ribonuclease
produced in the pancreas
break down bonds in nucleic acids like DNA and RNA
trypsin
produced in the pancrease
breaks down protein in the small intestines
Bile
Bile salts are acids that break down fats and lipids
bile acids are made in the liver and get stoard in the call bladdr
when eating, bile gets released/secreated into the small intestine