Chapter 5: Equilibrium; where supply and demand meet
Equilibrium
- buyers and sellers are reversed. When prices rise sellers are happy and buyers are not. So where are both sellers and buyers happy?
Equilibrium: when the price has moved to a level where quantity supplied meets quantity demanded.
Equilibrium Price: the price at which equilibrium occurs. sometimes call “market-clearing”
Equilibrium quantity: when the quantity supplied and quantity demanded are at equilibrium.
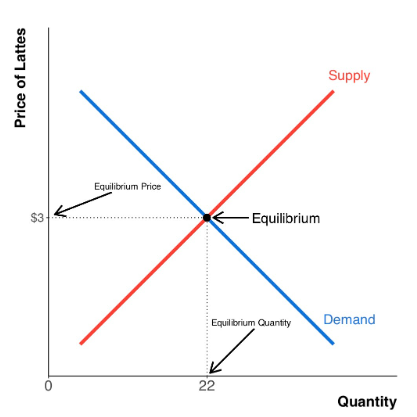
- graphs make it easier to see.
- $3 is the equilibrium price.
- You can see it on tables as well when the price is the same for both the quantity demanded and supplied.
- When the price is too high above the equilibrium this creates a surplus. It occurs when the quantity supplied is greater than what is demanded. aka, surplus happens when the market has excess supply.
- A shortage occurs when the price is too low and quantity demand is higher than what is supplied.
- to fix shortage the price must be raised and to fix surplus, the price must be lowered.
Three steps to examining a change in Equilibrium
- Determine if the event(s) shifts the supply curve, demand curve, or both simultaneously
- Dertrime which direction the curve(s) shifts.
- Draw out the shift(s) on the supply and demand model to see how the events change the equilibrium price and quantity
A shift in Demand
- Suppose new research shows that lattes prevent diabetes. what would happen?
- the study will impact the demand curve by influencing consumer preferences. It does not affect the supply curve because it does not directly impact businesses that sell lattes.
- If people discover that lattes prevent diabetes, they will want to drink more, therefore the demand curve shifts right.
- At the original price, there is one more demand which causes a shortage making businesses raise prices. So the equilibrium price and quantity are increased by the study.
The quantity supplied has changed but the supply curve has not. Be wary of that.
Imagine the economy has gone into a recession and people’s incomes are dropping. Assuming that lattes are normal goods how will the recession impact the economy?
- The recession will impact the demand curve now that people have less money. The supply curve is untouched as the recession does not directly impact businesses that sell lattes.
- Because the recession makes people want to buy fewer lattes the demand curve will shift left.
- At the original price there is now less demand for lattes so having a surplus, businesses will need to lower their prices.
In general, when the demand for a good rises, the equilibrium price and quantity will rise. But when the demand falls the equilibrium price and quantity also fall.
A Shift in Supply
- suppose a tsunami ruins much of the coffee bean crops and pushes the price up for coffee beams. How will that affect the market?
- The rise in coffee beans (an input to lattes) will impact the supply curve. The higher the cost of coffee beans the fewer lattes businesses want to sell. The demand curve is unaffected.
- Higher coffee bean prices will cause the supply curve to shift left since it reduces how much businesses want to sell at once.
- At the original price, there is now a lower supply of lattes, and this shortage will induce businesses to increase prices. So the rise in coffee bean prices raises the price of lattes and lowers the quantity sold.
- suppose a new cafe opens and starts selling lattes.
- new cafes opening will impact the supply curve. The demand curve will not be impacted.
- More cafes selling lattes will cause the supply curve to shift right as it increases how many lattes can be sold at every price.
- At the original price, there is now a higher supply of lattes, and this surplus will encourage businesses to decrease prices to maintain equilibrium.
- in general, when the supply of a good falls, the equilibrium price will increase and the quantity will decrease.
A Shift in Both Demand and Supply
- Assume the health study and tsunami happen at the same time.
- Both events will cause both curves to shift. The health study moves the demand curve, and the tsunami the supply.
- The demand curve shifts right and the supply shifts left.
- In every scenario the equilibrium price increase. Where the demand rises considerably and supply decreases a little bit, the equilibrium quantity increases. When supply decreased dramatically while demand increases a little but the equilibrium quantity decreases.