topic 1 The subject, objectives and cintent of gentics, and its history and development
Genetics - the science of heredity and variability of living organisms
From the Greek word genesis- origin
Key words = heredity (наследственность) and variability (изменчивость)
Genetics is divided into two parts
Фундаментальная fundamental
Прикладная applied
Фундаментальная генетика
Studies the general patterns( общие закономерности) of inheritance ( наследования) of traits in laboratory or model species: prokaryotes (eg e.coli ( кишечной палочки)) , mold, yeast and fungi, mice.
These sections are included in this category
Classical/formal genetics
Cytogenetics
Molecular genetics
Genetics of mutagenesis (including radiation chemical genetics)
Evolutionary genetics
Population genetics
Genetics of individual development
Genetics of behaviour
Ecological genetics
Mathematical genetics
Cosmic genetics (studies the effect on an organism of cosmic factors eg cosmic radiation or prolonged weightlessness)
классическая (формальная) генетика,
цитогенетика,
молекулярная генетика,
генетика мутагенеза (в т. ч, радиационная и химическая генетика),
эволюционная генетика,
генетика популяций,
генетика индивидуального развития,
генетика поведения,
экологическая генетика,
математическая генетика.
космическая генетика (изучает действие на организм космических факторов: космических излучений, длительной невесомости и др.).
Прикладная генетика
Develops recommendations for the application of genetic knowledge in breeding, genetic engineering and other branches of biotechnology, in the field of nature conservation.
The ideas and methods of genetics find application in all areas of human activity related to living organisms
They are important for solving the problems of medicine, agriculture and the microbiological industry
Genetic engineering (генетическая инженерия)
It’s a branch of molecular genetics associated with the purposeful creation in vitro of new combinations of genetic material capable of multiplying in a host cell and synthesizing end products of metabolism
Частная генетика (private genetics)
Genetics of plants растений :wild and cultivated. About 150 species in total
Animal genetics животных: wild and domestic animals . About 20 species in total
Genetics of microorganisms микроорганизмов eg viruses prokaryotes. Dozens of species
Наследственность (heredity)
The ability способность of all organisms to preserve сохранить and transmit передавать structural and functional features from their ancestors предков to their offspring потомству
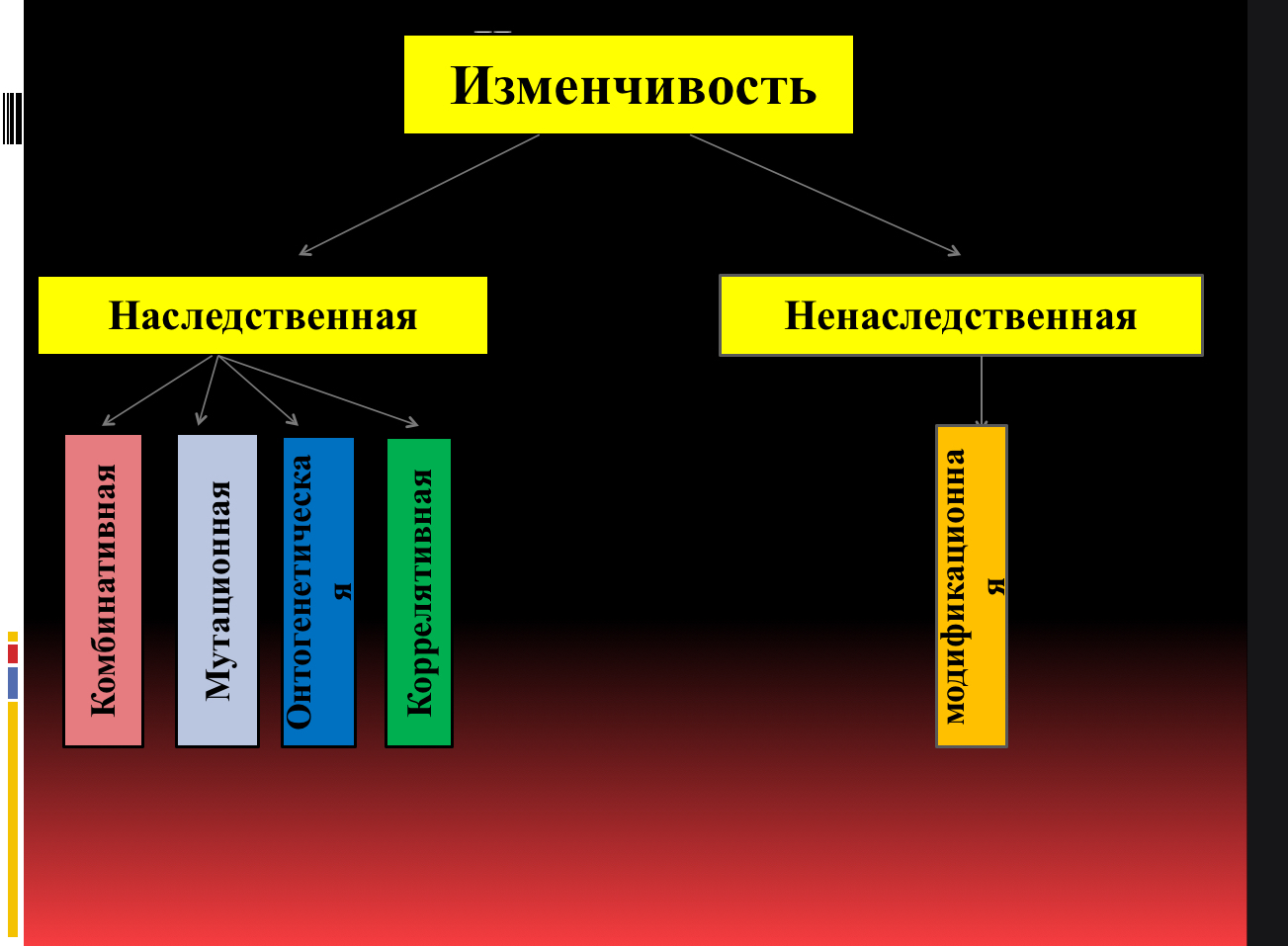
Изменчивость (variability)
The ability способность of an organism to change under the influence действием of hereditary наследственных and non hereditary не наследственных factors
Наследование (inheritance)
The process of transferring передачи traits признаков and properties свойств from parents to descendants потомкам
Наследуемость (heritability)
The proportion or fraction доля of generic variability генетической изменчивости in the total phenotypic variability фенотипической изменчивости of a trait признака in a particular конкретной population of animals or plants
 Knowt
Knowt