UNIT 4 Grade 8
Unit 4.1
Objective
Explain what a network is
Remember vocabs
Explain PAN, LAN, WAN
Understand core knowledge
Vocabulary
high bandwidth: high amount of data being transmitted
network switch: connect devices together on a network to form a wired network
data: raw facts and figures
servers: computers on a network that offers service to other devices
file server: offer devices a place to store and access file
computer network: a system that connects 2 or more computing devices for sending and recieving, sharing information (include PAN, LAN, WAN, MAN)
PAN (Personal area network): types of network where devices communicated over an small area
weak, slow connection, limited range of communication, convenient & flexible, cost effective
LAN (Local area network): type of network where devices communicate over a small geographical area
Have access within range (can only in access in the geographical area), for specific locations
Fast & reliable, easy to set up & manage
limited geographical coverage, high cost, limited mobility for wired device
WAN (Wide area network): type of network where devices communicate over larger geographical area
enables communication in vast distances, provide access to remote recources and services, realtime collaboration in different locations
higher cost of installation and maintenance, lower data transfer rate, need specialized language
wearable techonology: devices that could easily be worn on our body
Unit 4.2
Objective
Explain what a network topology is
Remember vocabs
Understand core knowledge
Vocabulary
Network topology: a diagram that shows how device in a network are connected to one another and shows the network hardware (structure)
Bus topology: all the devices are joined to one cable (bus), terminator at the end of cable to absorb signals and stop them from being reflected down the bus
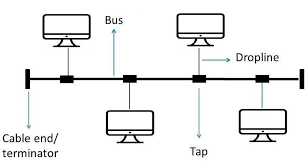
Easy to install, cheap
If the main cable fails/damage => whole networks stop working
Larger network => data likely to be collided
Devices on the network are visible to each other => security risk
Ring topology: each device is connected to 2 other devices forming a ring for the data to be passed around, data is travelled in 1 direction
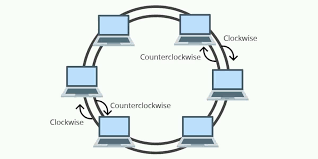
Data does not collide, flows 1 way, can be transferred quickly
If the main cable is broken then the network in devices stop
Star topology: every device on the network has its own connection to the switch, main switch sends data packets to the destination device only
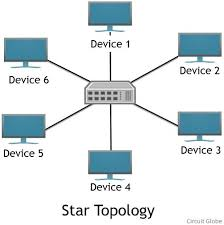
Each device is connected seperately. dependable to other devices (will continue to work if a device or cable fails)
Network performance is good - direct destination, easy to add new devices
Expensive to install, if main switch is broken than other devices can’t be connected
Mesh topology: network structure where computers and devices are interconnected
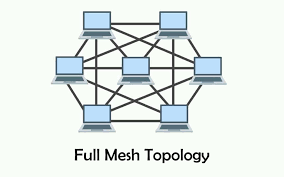
Network can be expanded without disruption
redundant paths between devices, requires more cable => expensive, complicated implementation
Network architecture: How a network is designed
Node: single device in a network
Network hardware: dependable, fast hardware related for the use of networks (routers, NIC, wireless access point, network switch)
Router: connects diferent networks (provides access to the internet), connect LAN to the internet, router find the fastest route to send data
Network interface card (NIC): connects a computer to a computer network, has pre-programmed MAC address
Wireless access point (WAP): allows devices to connect to a network using Wifi
MAC address: number programmed into NIC and identify devices on a network
Unit 4.3
Objective
Explain what a network is
Remember vocabs
Understand core knowledge
Vocabulary
Network switch: main device that allows devices to join together to form a network
Router: connect several LAN to form a WAN
Network interface card (NIC): allows any device that want to connect a network, contains MAC address
MAC Address: able to indentify you on a network
Wireless Access Point (WAP): network device that allows wireless devices to connect to the network using wifi
Ethernet cable: designed to work with ethernet parts on a NIC, helps for higher speeding
Server: basically computers that have anything: when you send someting you have to go to the server
File sever: offers a device a place to store and access files
Print server: take printing jobs: order to print
Mail server: store email messages to log in, send and recieve messages
Web server: provide internet accesibility to files and transmit files over the www.
Firewall: a security software that acts as a barrier to unauthorised access network traffic, check for security risks.
Pictures


Sub unit
Objective
Explain what a protocol is
Remember vocabs
Understand core knowledge
Vocabulary
Protocol: an agreed set of rules that computers follow to communicate to each other over a network
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP): routes data between devices and ensures it reaches intended destination
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): Transfers website content (“hypertext”), these are set of rules for communicating with web servers => no S so websites that doesn’t have this isn’t secure
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS): Transfers website content (“hypertext”), these are set of rules for communicating with web servers with added encryption to improve security => websites that have this is secure
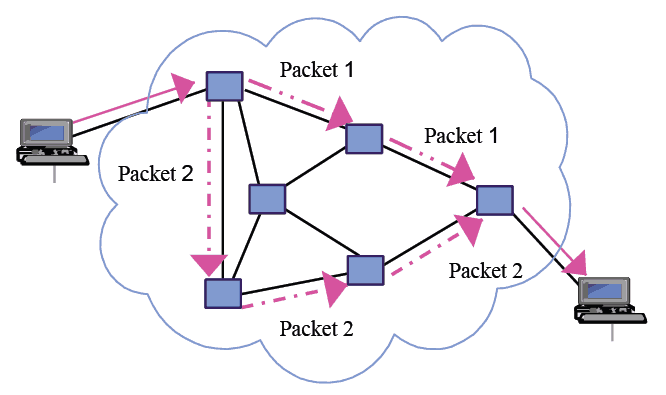
Data packet: small unit of data that is packaged to be sent across the network
IP address: unique number assigned to a computer on a network
Sender IP address: need to include this on the network to know where to forward the packet to
Recipient (Receiver) IP address: in case of a dropped packet, reciever address can request the package to be sent again
Packet number: needs to be included so the receiving (receipient) device can reassemble the packets in the correct order, helps receiving device know which packet is missing
Packet switching: the process of splitting data in smaller units
Pictures
Scalable considerations
Vocabulary
Electrical spikes/power surges: more voltage comes though the electrical wire to an device
Faulty wiring or lightning strikes often cause binary bits to be flip between 0 and 1 => error in data transmission
Interference: occurs when many electrical devices are used in a small area
Electrical & radio waves disrupt each other’s signals => errors in binary data, devices to disconnect from the network
Security breaches: unauthorized access to computer data, caused by malware or hackers
Hardware failure: a switch or other hardware fails => errors in dservers
Keeping it all secure
Vocabulary
dataset: collection of data (stored in a table)
Firewall: examines the incoming and outgoing of a network traffic to see if it violate rules or suspicious activity is blocked
User access control: network manager allowing some users such as administator to access the datasets
Password policies: creating strong passwords by following the policies given. Such as:
Have at least 8 characters
Password must contain letters, numbers, or symbols
Brute-force attack: an unauthorised access to the computer system by using a large dictionary to try multiple password combinations
Two-factor authentication: requiring two types of method in signing in, often by password and email verification/code from a 2nd device
Biometric security: uses people’s physical appearance to sign in (Ex. facial recognition, fingerprints)
Encryption: convert (information or data) into a cipher or code, especially to prevent unauthorized access. Uses secure protocols like (HTTP or HTTPS
Plaintext: data that has not been encrypted, can be intercepted
INTERFACES
command line interface
natural & speech recognition
graphical user interface: icons, menus, pointers basically graphics