Chapter 5 Sterioisomerism
Constitutional Isomers: Same molecular formula but different constitution order of connectivity of atoms
Stereoisomers: Same molecular formula and constitution but different spatial arrangements of atoms
Cis (same) 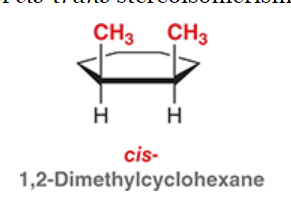 Trans (different)
Trans (different) 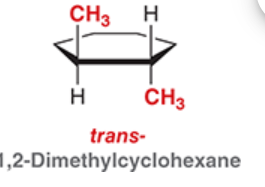
A cis stereoisomer has groups all on the same side
A trans stereoisomer has groups all on different sides
Chemists use cis-trans terminology to describe disubstituted (has two substituent atoms/groups) alkenes, even when the two substituents (connected to the π bond) are different from each other
Chirality and Introduction to Stereoisomerism
Superimposable- mirror image is identical to the actual object.
Nonsuperimposable- the object and its mirror image are now different
Diasterisomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images
The most common source of molecular chirality is the presence of a Carbon atom bearing 4 different groups
Is this a superimposing or nonsuperimposable image 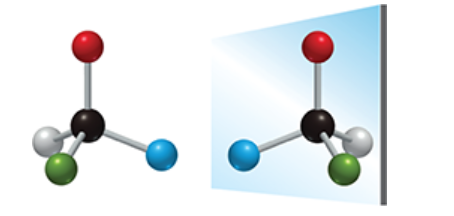 nonsuperimposable
nonsuperimposable
Chirality describes nonsuperimposable images in their mirror’s reflection
achiral- can superimpose in their mirror image
A chiral center- is a tetraheadral carbon holding four different groups
Locate the chiral center 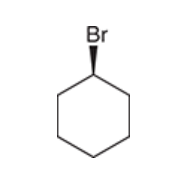 There is not chiral center here because it is symmetrical and the clockwise path and the counterclock wise path are intentical
There is not chiral center here because it is symmetrical and the clockwise path and the counterclock wise path are intentical
Locate Chiral center 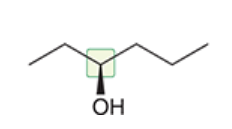 There is a tetrahedreal with OH-C-C-H
There is a tetrahedreal with OH-C-C-H
Spot the Chiral centers
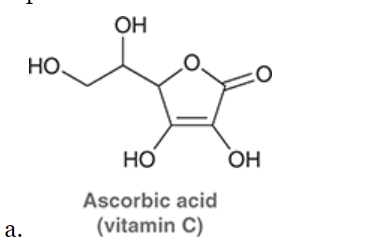 The Answer
The Answer 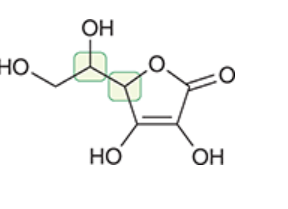 Located Chiral centers
Located Chiral centers
Testing for Chiralilty include:
Plane of symmetry (mirror plane) If plane can bisect molecule and it is same with its two halves it is achiral
Without internal plane is chiral
look for chiral centers
- if one it is chiral
- if more than one may or may not be chiral
- if none may or may not be chiral but probably not
- \
Look for mirror plane
- Then draw image to test if superimposable
When a compound is nonsuperimposable, chiral mirror images of each other it is an Enantiomers
Compounds and its Enantiomers 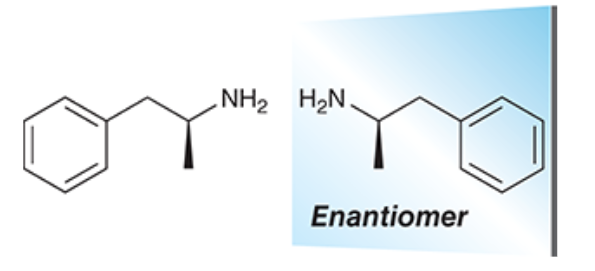
Cahn Ingold Prelog
Order the four groups by atomic weight/number (#1 highest atomic weight)
Rotate so lowest atomic weight is pointing away
Point arc from highest priority to next highest priority
If turns counterclock wise <-- to c. center= @@R@@
- if turns counterclockwise -→ to c.center=^^S^^