Ch.6 Variable Interest Entities, Intra-Entity Debt, Consolidated Cash Flows, and Other Issues (copy)
TEXTBOOK
Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities
Firms began establishing separate business structures to help finance their operations at favorable rates. Will be commonly referred to as Variable Interest Entities (VIEs) in textbook.
What’s a VIE?
Forms: Trust, partnership, joint venture, corporation
sometimes has neither independent management nor employees
Often created to:
accomplish a well-defined and limited business activity
to provide low-cost financing
A business can establish a VIE to purchase & finance an asset acquisition and then the VIE then leases the assets back to the business enterprise that established the VIE.
VIE is often available for a lower interest rate (saving business money)
VIE typically operates with a very limited set of assets (oftentimes just one asset)
isolating an asset in VIE, the asset’s risk is isolated from business’ overall risk which then protects VIE creditors by the specific collateral in the assets
Governing documents can strictly limit the actions of VIE which also protects lenders in the VIE
Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities
In the past, VIEs were not consolidated with those of the firm that controlled the entity. Nowadays, the FASB has created rules that keep firms from leaving VIEs out of their financial statements.
Variable interest often serve as the vehicle for a controlling financial interest, even in the absence of any equity investment whatsoever.
Business enterprises must determine of they have a controlling financial interest in any affiliated entity by applying the Variable Interest Model.
Using this model helps clarify who is the primary beneficiary
if yes, they are required to include assets, liabilities, and result of the activities of the VIE in its consolidated statements
If affiliated entity is NOT a VIE, then they must use Voting interest model to determine if financial control exists.
Identification of a Variable Interest Entity
An entity qualifies as a VIE if either of these exist:
If equity risk is less than 10% (essentially means that their equity at risk cannot be financed on their own without additional financial support)
The equity investors in the VIE lack any of these characteristics:
(does not have) the power though voting rights/similar rights to direct activities of an entity that would impact the economic performance
(does not have) the obligation to absorb losses
(does not have) the right to expected returns of the entity
Initial Measurement Issues
Remember the acquisition method requires allocation of the acquired business fair value based on underlying fair value of its assets and liabilities,
The same goes for VIEs.
If VIEs exceed fair value of its net assets, goodwill is recognized
If VIEs are less than the fair value of its net assets, a gain on bargain purchase is recognized.
Consolidation of a Primary Beneficiary and VIE Illustrated
Example:
Jan. 1, 2024 Vicente gets $2,200,000 loan from Payton as Vicente had previously been unable to secure the financing needed to continue its operations. Loan due on Jan. 1, 2029
Part of the loan contract:
5% ann. interest rate on the 2,200,000 loan
Payton has decision-making power over Vicente’s operating & financing activities
Payton gets management fee equal to 10% of Vicente’s sales.
@ end of 5 yrs, Payton can:
acquire ownership of Vicente for $500,000
or extend original contract for 5 more yrs.
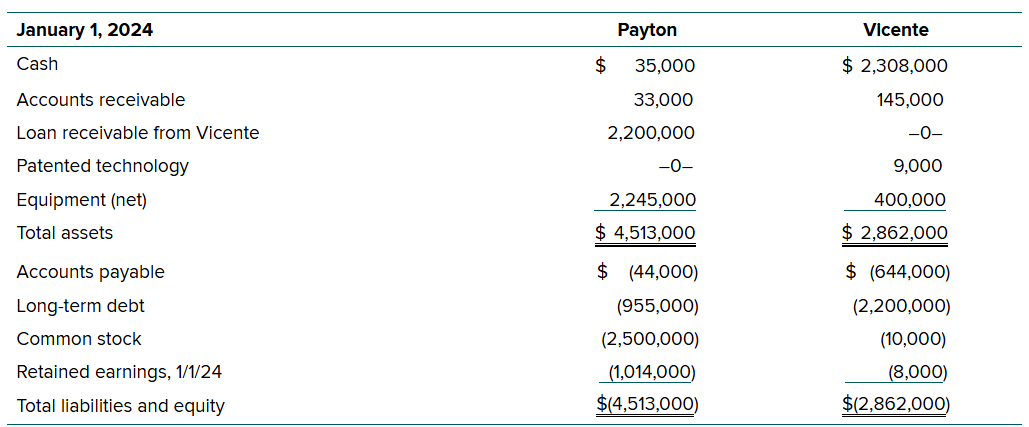
Jan. 1, 2024 Payton estimated FV of Vicente stock to be $143,000 even though the book value (assets - liabilities) of Vicente was $18,000
$18,000 comes from:
total assets - total liabilities
$2,862,000 - accts payable - long-term debt
$2,862,000 - 644,000 - 2,200,000
= $18,000 BV of Vicente
Difference of these two amounts ($143,000 - $18,000) is $125,000. In this scenario, it is attributed entirely to a patented technology with a 10 yr estimated remaining life. (Think of a patented technology like a computer program or machine or device in which the company uses to better their performance—like a new POS system or a computer program or a printing machine)
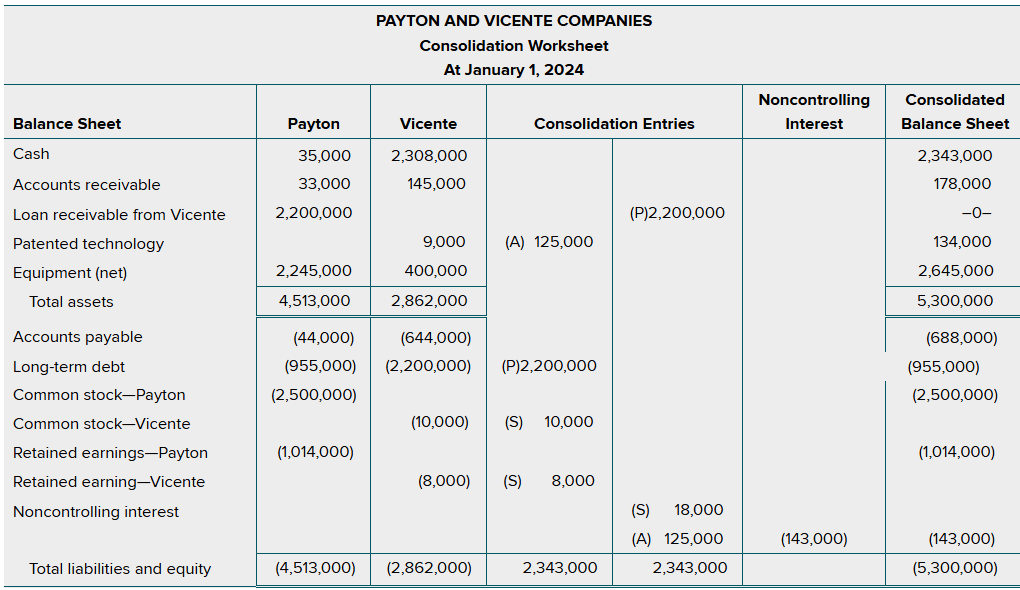
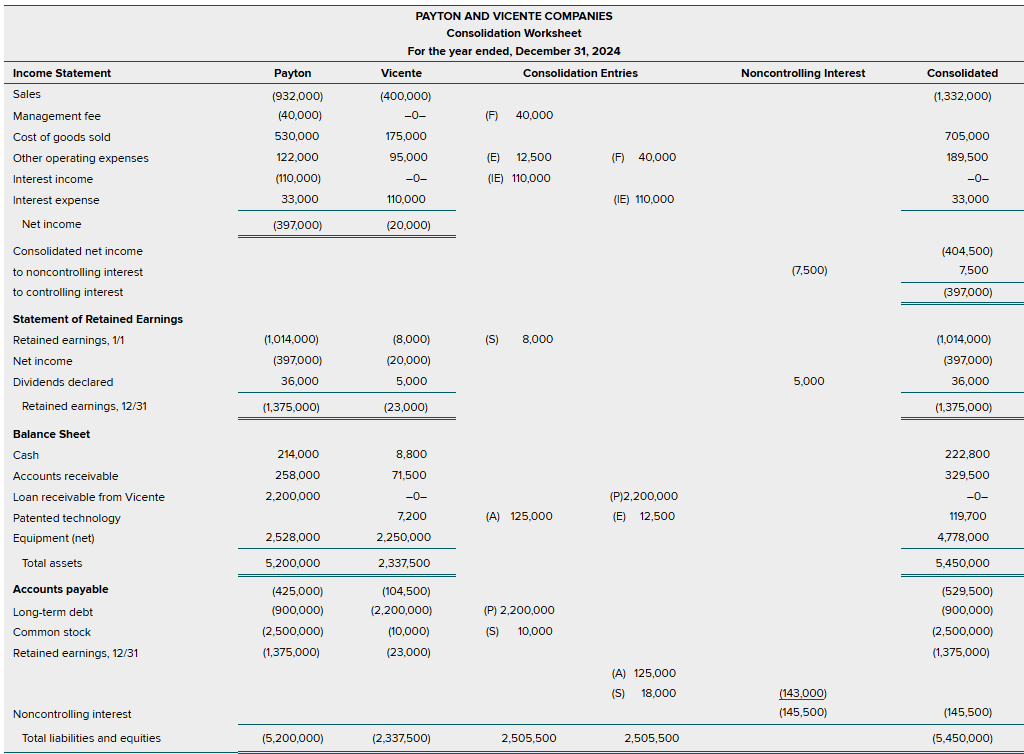
Before creating a full consolidated statement, we will take the given information and create a number of additional consolidating entries to avoid errors and double counts.
There are 6 consolidation entries:
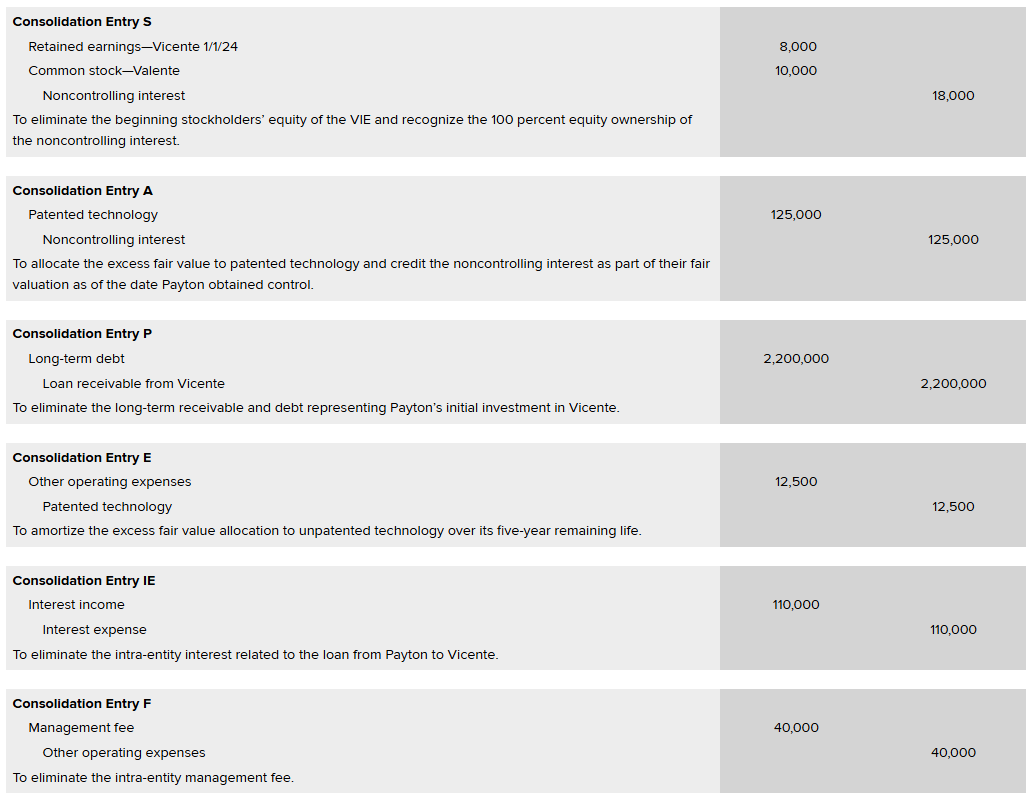
Entry S — which eliminates the VIE’s owners’ equity account balances and recognizes the 100% equity ownership as a noncontrolling interest.
Entry P — which eliminates the intra-entity Long-Term Debt and Loan Receivable from Vicente
Entry A — Which allocates the excess fair value over book value to the Patented Technology with a corresponding increase in the noncontrolling interest.
Note: The noncontrolling interest appears in the consolidated balance sheet at its acquisition-fair fair value (in this case is $143,000)/
Entry E (expenses)
Entry IE (interest expenses)
Entry F (management fees — are a common arrangement between VIEs and their primary beneficiaries)
Comparisons with International Accounting Standards
Controlling a financial interest is the critical concept in assessing whether an entity should be consolidated by a reporting enterprise
IFRS — employs a single consolidation model for all entities regardless of whether control is evidenced by voting interests or variable interests,
U.S. GAAP — employs separate models for assessing control for variable interest entities & voting interest entities.
The IASB IFRS 10 and IFRS 12 cover situations where financial control exists either through majority voting share or through other means. The standards define control to cover all possible ways in which one can exercise power over another.
Power over an investee — does the reporting entity have current ability to direct activities that significantly affect another entity’s returns?
Exposure to / rights to, variable returns from involvement with another entity.
Linkage between power and returns — does investor have ability to affect its returns through its power?
⬇
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Think of control in IFRS 10 and IFRS 12 like being the captain of a ship. You need the power to steer (direct activities), a stake in the ship's profits (variable returns), and the ability to use your control to influence those profits. Even with less than 50% ownership, you can still be the captain if you meet these criteria.
Control in business can be likened to a chess game where a player with fewer pieces can still win by strategically positioning them. Even with less than 50% ownership, a company can control another by directing key activities. IFRS 12 enhances transparency, helping investors understand control dynamics and associated risks, much like a detailed game analysis.
Intra-Entity Debt Transactions
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Think of intra-entity debt transactions like a family lending money to each other. When consolidating finances, these internal loans are erased to present the family as one unit. Gains from these loans are deferred until the money is spent outside the family. This ensures a true financial picture, treating the family as a single economic entity.
Acquisition of Affiliate’s Debt from an Outside Party
A subsidiary may have issued bonds that continue to be traded in the open market. When a parent purchases all/some of these outstanding subsidiary bonds, the entity is essentially reacquiring its own bonds (when looking at it from a consolidated viewpoint).
Though the individual companies continue to carry both the debt and the investment on their individual records, (from a consolidation viewpoint) this liability is retired as of the reacquisition date.
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
When a parent company buys its subsidiary's bonds from the market, it’s like a family repurchasing its own IOU. Individually, they still show the bonds and interest, but consolidated, the debt is considered retired. Think of it as balancing family finances: internal debts cancel out, simplifying the overall financial picture.
When a parent company buys a subsidiary's bonds from the market, it’s like a family buying back its IOU. Individually, the parent records it as an investment and the subsidiary as a liability. But in consolidation, it’s as if the debt is retired, needing adjustments to reflect that the debt is no longer owed externally.
Accounting for Intra-Entity Debt Transactions—Individual Financial Records
4 accounting problems emerge in consolidating intra-entity debt transactions:
Intra-entity investments in debt securities must be eliminated (in consolidation despite their differing balances).
Intra-entity interest revenue/expense must be removed (although these balances also fail to agree in amount).
The amortization process for discounts and premiums causes continual changes (in each of the preceding accounts).
The business combination must recognize the gain or loss on the effective retirement of the debt, (even though it is not recognized within the financial records of either company).
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Consolidating intra-entity debt transactions is like merging two family budgets. You must ignore loans between family members, even if amounts differ. Interest earned or owed between them also vanishes. Continual changes from discount/premium amortization complicate things. Finally, any gain or loss from settling this debt must be recognized, impacting the overall financial picture.
Effects on Consolidation Process
Consolidation procedures convert information generated by the individual accounting systems to the perspective of a single economic entity.
A worksheet is required to eliminate the intra-entity balances and to recognize the loss resulting from the effective retirement.
The difference between liability and investments balances & interest expense and interest income stem from the purchase price of the investment and the carrying amount of the liability. Recognition of this loss, in effect, bridges the gap between the divergent figures.
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Consolidation procedures transform individual accounting data into a unified economic entity view. Imagine merging multiple puzzle pieces into one coherent picture.

Assignment of Retirement Gain or Loss
An issue in accounting for intra-entity debt repurchases is deciding who is assigned the retirement gain/losses. Should the Alpha or the Omega report it? In the absence of the FASB guidance on the assignment of retirement gain or loss, all income effects in this textbook (relating to intra entity debt transactions are assigned solely to the parent company. This is to align with the perspective that the parent company ultimately controls the repurchase decision.
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Assigning the loss in intra-entity debt repurchases is like deciding which team member gets credit for a project's failure. Since the parent company (Alpha) controls the repurchase decision, it’s fair to attribute the loss to Alpha. This approach simplifies consolidated financial statements, reflecting the parent company's ultimate control over financial outcomes. Same goes for gains; the parent company would be responsible for receiving that gain.
3 Notes related to consolidation Entry B:
The individual account balances change during the present fiscal period due to the amortization process which then affects the current consolidation entry from Entry B.
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Think of Alpha as the main chef in a kitchen. When intra-entity debt transactions occur, all the income effects (like spices) are added to Alpha's dish. Entry *B adjusts Alpha's beginning Retained Earnings and increases current income by $10,967. Noncontrolling interests, like other chefs, aren't affected by this specific adjustment.
Noted previously — all income effects that come from intra-entity debt transactions are assigned to the parent company. The adjustment to beginning Retained Earnings in Entry B is attributed to Primary firm as well as increase in current income. Consequently, the noncontrolling interest balances are not altered by Entry *B.
TLDR: (AI assisted understanding)
Just like a sculptor reshapes clay over time, individual account balances evolve during the fiscal period due to amortization. This process modifies the consolidation entry, making it different from Entry B.
SMARTBOOK NOTES
In response to the evolving nature of control relationships among firms, the FASB expanded its definition of control beyond the long-standing criterion of a majority voting interest to include which of the following?
control exercised through variable interests
What does SPE stand for in terms of the names for the separate business structures that firms establish to help finance their operations at favorable rates?
Special-purpose entities
Variable interests entities are often established to provide
low-cost financing for asset purchases.
Research and development arrangement
leasing arrangements
Consolidation is required when one company possesses a controlling financial interest over another company. When is a majority voting interest not effective in identifying a controlling financial interest in an affiliated entity?
When variable interests allow a primary beneficiary to exercise financial control over a variable interest entity.
In evaluating an entity's status as a VIE, if equity at risk is less than _______ % of total assets, the risk is deemed insufficient and the entity is considered a VIE
10% (ten percent)
_______ interest entities emerged over recent decades as a new type of business structure that provided effective control of one firm by another without overt ownership.
Variable
Which of the following is not one of the names for the separate business structures that firms establish to help finance their operations at favorable rates?
special-purpose business units (is NOT one of the names)
What business types typically describe variable interest entities?
Corporations.
trusts.
joint ventures across two or more other business entities
A business enterprise is required to consolidate the assets, liabilities, and results of operations of a VIE in which it holds no equity interest if
it can exercise financial control over the VIE in its role as primary beneficiary.
In an acquisition-date consolidation, a primary beneficiary will include valuations of its VIE's assets, liabilities, at _______ value.
fair
Under what general conditions does an entity qualify as a variable interest entity?
The equity investors lack the ability to exercise financial control over the entity.
Equity investors' returns are capped by contractual arrangements with variable interest holders.
There is insufficient equity at risk to enable the entity to finance its activities without additional support.
For the January 1, 2024, consolidation of Payton and Vicente, Consolidation Entry P eliminates Vicente's long-term debt against Payton's _______ _______ from Vicente.
Loan Receivable
For the January 1, 2024, consolidation of Payton and Vicente, Consolidation S allocates the entire amount of Vicente’s owners’ equity balances to the _______ interest.
Noncontrolling
In response to the evolving nature of control relationships among firms, the FASB expanded its definition of control beyond the long-standing criterion of a majority voting interest to include which of the following?
control exercised through variable interests
Which of the following arrangements are considered encompassed within the IASB's control definition?
Majority voting rights over the decision-making of an entity held by an investor.
The obtaining of decision-making rights over an investee that dominate voting rights.
Less than 50% voting interest where the remaining shares are diffusely held across many owners.
True or false: Consolidated financial statements represent a business combination as a single economic entity.
TRUE
In consolidating a business entity VIE, any excess of the VIE’s total business fair value over the collective fair values of its net assets is recognized as _______
Goodwill
When one affiliate within a consolidated group acquires the debt of another affiliate from a third party, from a consolidated view this liability is effectively _______ as of the debt reacquisition date.
Retired
Which of the following consolidation procedures are needed when one affiliate within a consolidated group acquires the debt of another affiliate from a third party?
The ongoing amortization of intra-entity discounts and premiums must be taken into account in the consolidation process.
The intra-entity interest payable and receivable must be eliminated.
US GAAP specifies separate models (voting vs. variable interests) in assessing financial control. IFRS employs a ________ consolidation model for assessing financial control across voting and variable interests.
single
Why are consolidation procedures needed to adjust for the effect of intra-entity activities across the members of the consolidated group?
Consolidated statements must reflect the financial position and results of operations from the viewpoint of the combined business entity.
Consolidation Entry B adjusts which of the following accounts generated by the affiliates preparing consolidated financial statements in the year of an intra-entity bond reacquisition?
Gain/Loss on Retirement of Bonds
Investment in Bonds
Bonds Payable
EXAMPLE (if there was a loss):
dr. bonds payable
dr. interest income
dr. loss on retirement of bonds
cr. discount on bond payable
cr. investment in ““ company bonds
cr. interest expense
When one affiliate within a consolidated group acquires the debt of another affiliate from a third party, then from a consolidated reporting viewpoint
The reacquired debt is effectively retired
Because a parent company likely controls intra-entity debt reacquisition activity, the textbook attributes the gain or loss from retirement on such intra-entity debt
Solely to the parent company.
Which of the following consolidation procedures are needed when one affiliate within a consolidated group acquires the debt of another affiliate from a third party?
Intra-entity liabilities must be eliminated
Intra-entity interest revenue and expense must be eliminated
Intra-entity investment in debt securities must be eliminated
Which of the following consolidation procedures are needed when one affiliate within a consolidated group acquires the debt of another affiliate from a third party?
The ongoing amortization of intra-entity discounts and premiums must be taken into account on the consolidation process
The intra-entity interest payable and receivable must be eliminated
In years subsequent to the acquisition of bonds payable of one affiliate by another affiliate, when the parent uses either the initial value or partial equity method
the parent's retained earnings are adjusted for previous years' income effects from the effective retirement.
True or false: The existence of subsidiary preferred stock has no impact on the valuation principles for an acquired subsidiary's assets and liabilities.
TRUE
A gain or loss from reacquisition of the debt of one company by an affiliated firm
is typically recognized via a consolidated worksheet entry rather than an entry on the individual books of an affiliate.
In allocating the income effect of a gain or loss from retirement of the debt of one affiliate that has been purchased by another affiliate, the entire income effect is allocated to the _______ interest.
controlling
Identify the major categories in a statement of cash flows. (Select all that apply.)
cash flows from operating
cash flows from investing
cash flows from financing
Clark Company acquires Transport Company in exchange for a cash payment to the former owners of Transport. Included in the assets received by Clark is Transport Company's cash balance. The current year consolidated statement of cash flows would report
The net cash paid for the acquisition (cash paid less cash received) as an investing activity.
How does the statement of cash flows report the net cash outflow that occurs when a parent company acquires a business for cash?
As an investing activity.
Subsidiary preferred stock not owned by the parent is a component of the _______ interest.
noncontrolling
In a period when a mid-term business combination occurs, only post-acquisition excess fair-value amortizations are added back to _______ _______ in computing cash flows from operating activities using the indirect method.
Net Income
Subsidiary dividends paid to its parent company
do not appear on the consolidated statement of cash flows.
Note: It would appear if the parent paid dividends to its subsidiary though.
Subsidiary dividends paid appear as a financing outflow on the consolidated statement of cash outflows
only when paid to the noncontrolling interest.
True or false: Assuming no carryover balances from operating accounts acquired in a previous year business combination, no special adjustments are required to prepare a consolidated statement of cash flows in periods subsequent to a business combination.
TRUE
To prepare a consolidated statement of cash flows in the year of a business acquisition, the subsidiary's acquisition-date accounts receivable balance
must be removed in computing cash flows from operating activities.
If the consolidated entity has dilutive securities in its capital structure, then in addition to basic EPS the consolidated financial statements must also disclose _______ EPS.
diluted
The potential dilutive effect of a less-than-100% owned subsidiary's stock options
can affect the parent's share of the consolidated net income.
will not affect the parent's computation of basic EPS.
If a less-than-100% owned subsidiary has dilutive securities in its capital structure, the parent's share of subsidiary earnings used in deriving diluted EPS
May change when assuming the conversion of the dilutive securities.
The starting figure for preparing the operating section (indirect method) of a consolidated statement of cash flows is consolidated
Net Income
In computing consolidated EPS, the numerator contains earnings
attributable only to the controlling interest
When a subsidiary company issues additional shares of common stock that are not purchased by the parent,
the parent's percentage ownership in the subsidiary will change.
The parent’s investment in Subsidiary account may need to be adjusted
Assuming neither the parent nor its 90% owned subsidiary have dilutive securities or preferred shares, what EPS calculations are required for consolidated financial statements?
Basic EPS = Parent's share of consolidated net income divided by the parent's weighted average shares outstanding.
When the parent acquires none of a post-acquisition subsidiary stock issue but maintains a controlling interest, the change in the carrying amount of the parent's investment account is recorded as
additional paid-in capital.
In computing consolidated EPS, net income shall exclude the income attributable to the _______ interest in the subsidiary
Noncontrolling
When a subsidiary company issues additional shares of its own common stock to outside third parties, the parent will need to decrease its investment account if the per share price received for the additional shares issued is ________ than the time-adjusted per share acquisition-date subsidiary fair value
LESS
A subsidiary issues new ownership shares to outside parties at a price other than its book value per share. Although the parent acquires none of the newly issued shares, it continues to maintain control over the subsidiary. What is the effect on the parent's financial records?
The investment account should be adjusted.
Additional paid-in capital is adjusted
Why did Antioch decrease its Investment in Westminster Company balance as a result of Westminster's post-acquisition stock issue?
Because Antioch's 72% share of Westminster's post-stock issue value is smaller than its 90% pre-stock issue value.
Because the $14.40 price per share is less than the $16.40 ($1,640,000/100,000 shares) time-adjusted acquisition-date per share value of Winchester.
HOMEWORK/QUIZ NOTES
An enterprise that holds a variable interest in a variable interest entity (VIE) is required to consolidate the assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and noncontrolling interest of that entity if:
The enterprise has a controlling financial interest in the VIE.
Dane, Incorporated, owns Carlton Corporation. For the current year, Dane reports net income (without consideration of its investment in Carlton) of $232,000 and the subsidiary reports $94,000. The parent had a bond payable outstanding on January 1, with a carrying amount of $256,000. The subsidiary acquired the bond on that date for $247,000. During the current year, Dane reported interest expense of $23,200 while Carlton reported interest income of $20,500, both related to the intra-entity bond payable. What is consolidated net income?
$337,700
Mattoon, Incorporated, owns 80 percent of Effingham Company. For the current year, this combined entity reported consolidated net income of $965,900. Of this amount, $920,400 was attributable to Mattoon’s controlling interest while the remaining $45,500 was attributable to the noncontrolling interest. Mattoon has 177,000 shares of common stock outstanding, and Effingham has 34,000 shares outstanding. Neither company has issued preferred shares or has any convertible securities outstanding. On the face of the consolidated income statement, how much should be reported as Mattoon’s earnings per share?
$5.20
Pesto Company possesses 80 percent of Salerno Company's outstanding voting stock. Pesto uses the initial value method to account for this investment. On January 1, 2020, Pesto sold 8 percent bonds payable with a $6.0 million face value (maturing in 20 years) on the open market at a premium of $1,040,000. On January 1, 2023, Salerno acquired 40 percent of these same bonds from an outside party at 96.6 percent of face value. Both companies use the straight-line method of amortization. For a 2024 consolidation, what adjustment should be made to Pesto's beginning Retained Earnings as a result of this bond acquisition?
$409,600 increase
On January 1, Tesco Company spent a total of $4,557,000 to acquire control over Blondel Company. This price was based on paying $462,000 for 20 percent of Blondel’s preferred stock and $4,095,000 for 90 percent of its outstanding common stock. At the acquisition date, the fair value of the 10 percent noncontrolling interest in Blondel’s common stock was $455,000. The fair value of the 80 percent of Blondel’s preferred shares not owned by Tesco was $1,848,000. Blondel’s stockholders’ equity accounts at January 1 were as follows:
Preferred stock—9%, $100 par value, cumulative and participating; 10,000 shares outstanding $ 1,000,000
Common stock—$50 par value; 40,000 shares outstanding 2,000,000
Retained earnings 3,650,000
Total stockholders’ equity $ 6,650,000
Tesco believes that all of Blondel’s accounts approximate their fair values within the company’s financial statements. What amount of consolidated goodwill should be recognized?
ANS: $210,000.
Which of the following variable interests entitles a holder to residual profits, losses, and dividends?
Common stock
A variable interest entity can take all of the following forms except a(n)
estate
 Knowt
Knowt